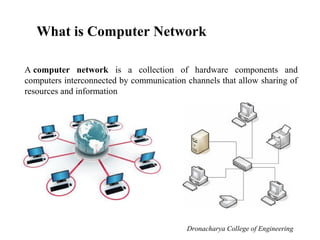
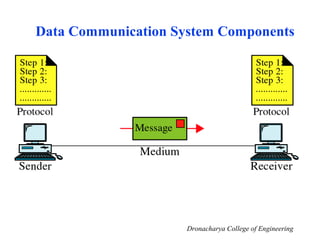
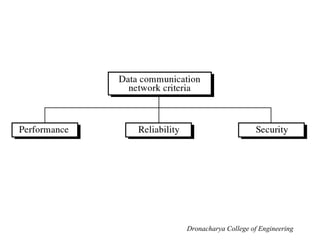
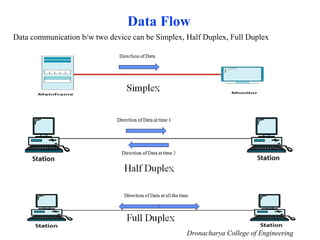
This document outlines the syllabus for a computer networks course. Section A covers the OSI reference model and network architecture, including different network topologies and the functions of each OSI layer. Section B discusses TCP/IP, including its history and key protocols like IP, TCP, UDP, and DNS. Section C covers local area networks, standards, and connecting devices. Section D examines wide area network technologies. The final section introduces network management topics and network operating systems. A brief history of computer networks starting with ARPANET in the 1960s is also provided.