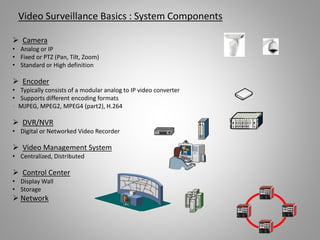
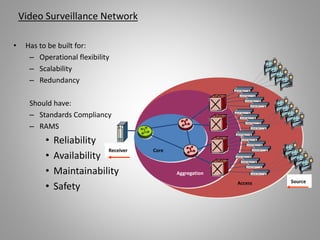
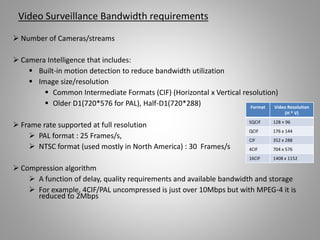
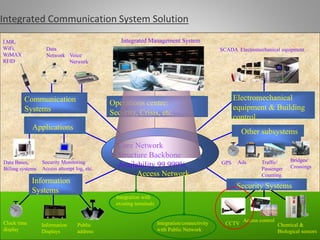
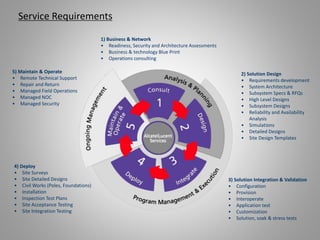
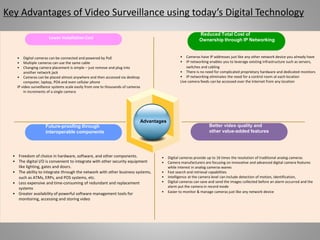
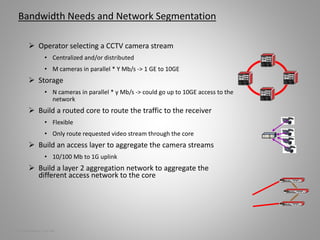
The document outlines key aspects of video surveillance, emphasizing its importance for public safety, crime prevention, and efficiency improvements. It discusses various applications across sectors such as transportation, education, and public security, and details the necessary system components including cameras, encoders, and network infrastructure. Additionally, it highlights the benefits of modern IP-based surveillance solutions, including reduced costs, scalability, and superior video quality.