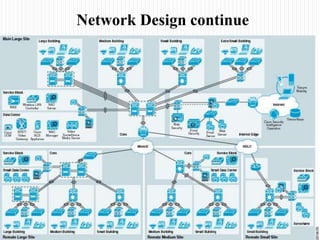
This document provides information on IP addressing including:
- IP versions 4 and 6, their address formats, and the differences between them. IP version 4 uses 32-bit addresses divided into 4 octets while version 6 uses 128-bit addresses divided into 8 portions of 16 bits each.
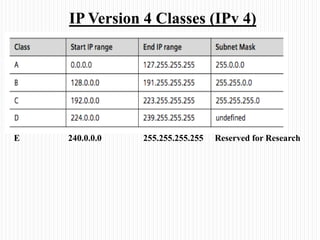
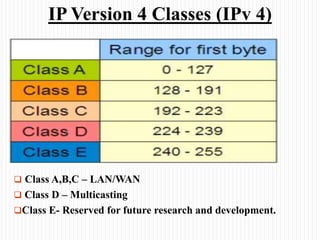
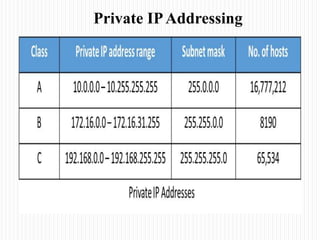
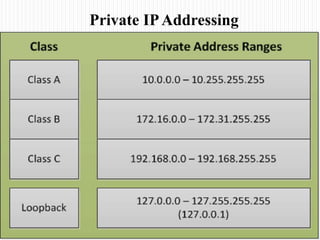
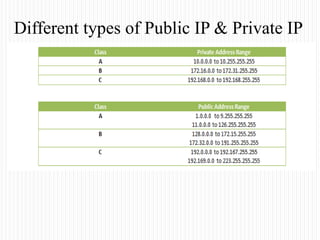
- The classes of IP addresses (A, B, C) and how they relate to network size. Class A is for large networks, B for medium, and C for small networks.
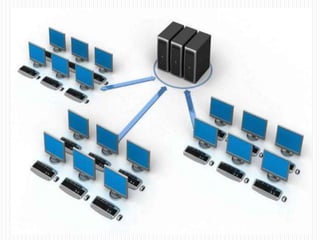
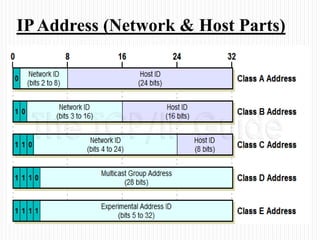
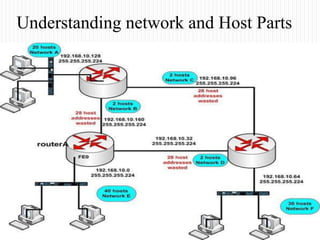
- How the network and host parts of an IP address are used, with the network part identifying the network and the host part identifying a specific device on that network.
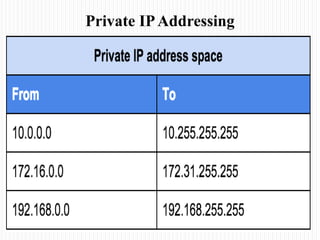
- An overview of private IP address ranges that are not