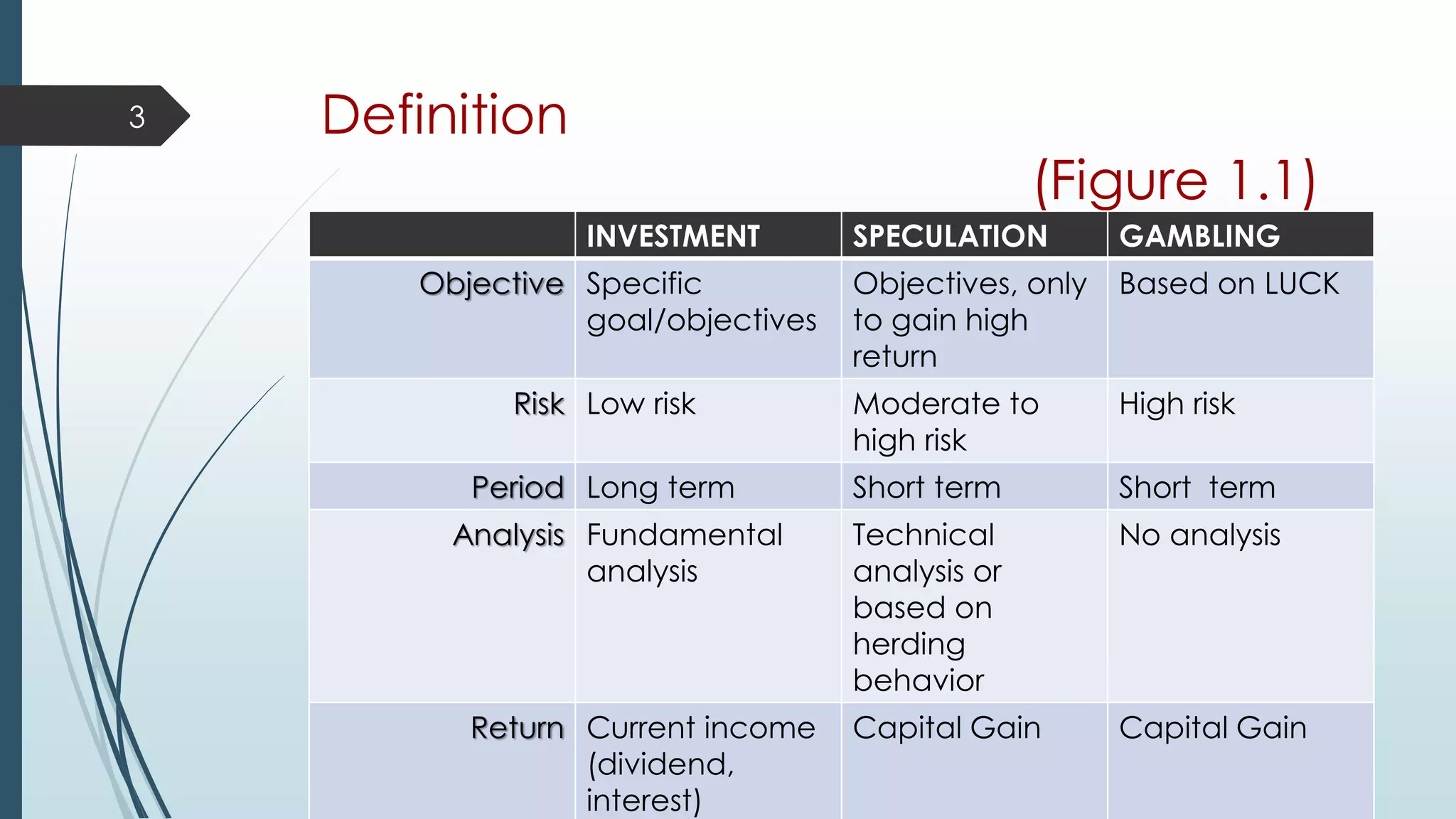
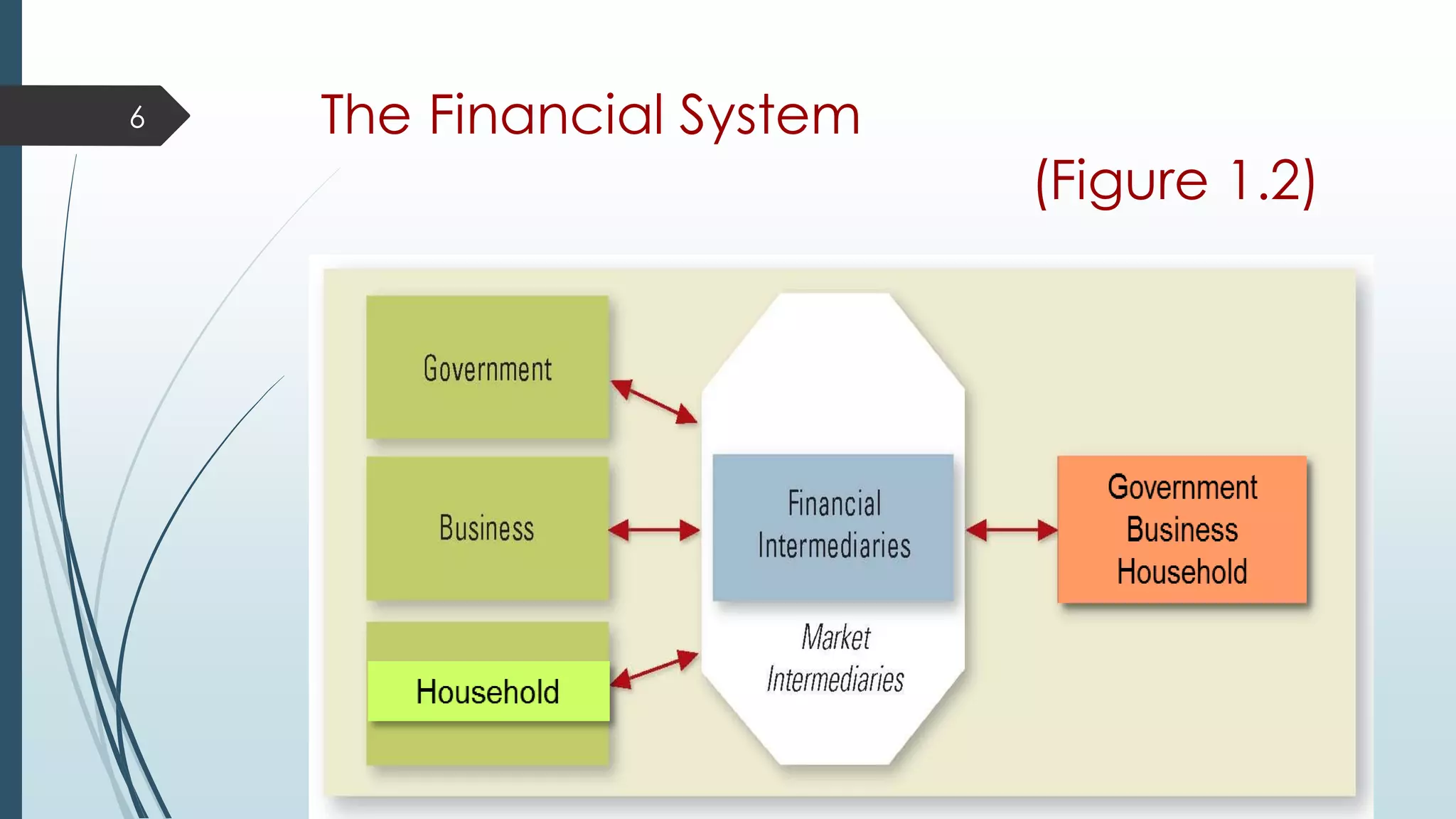
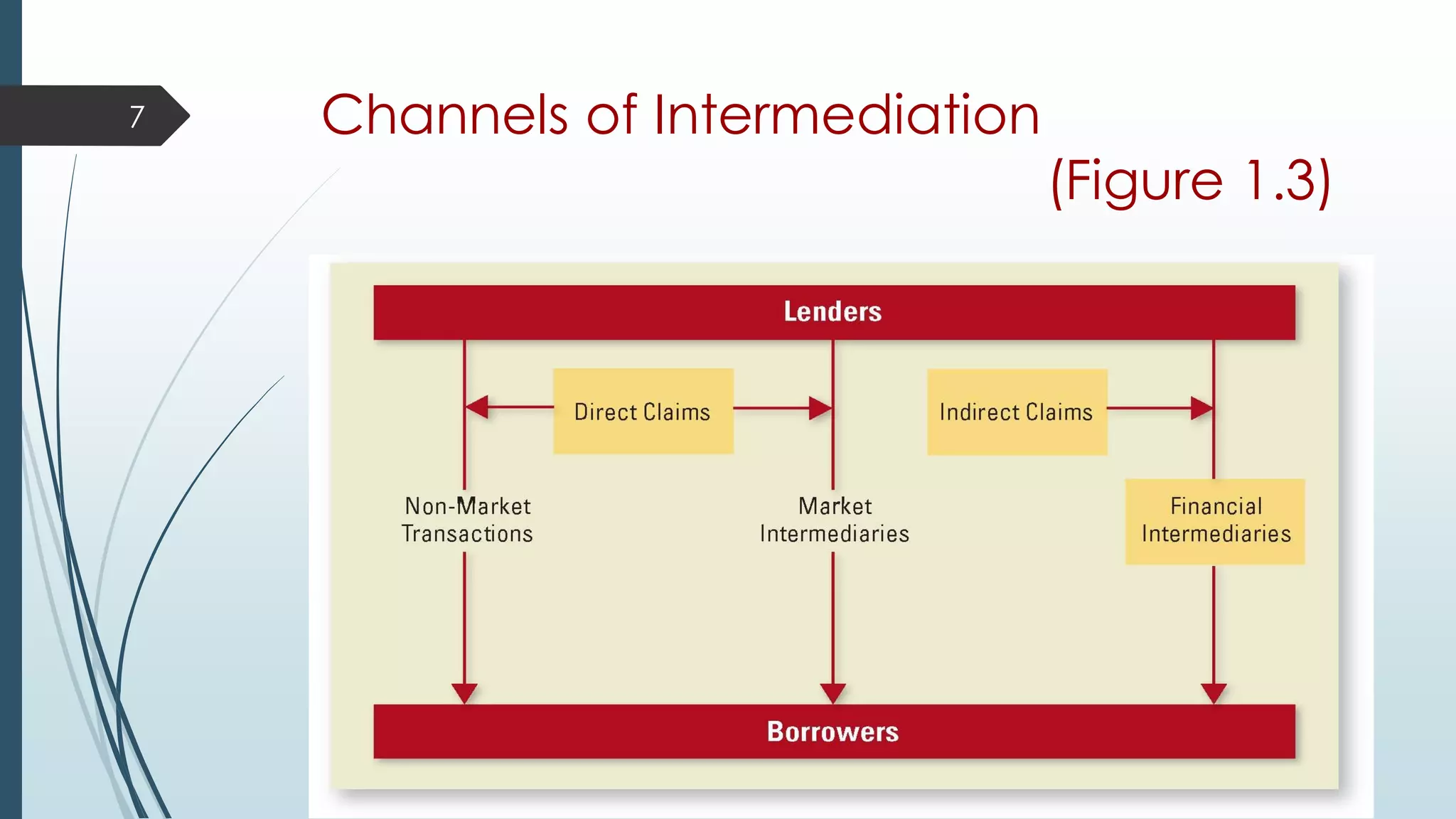
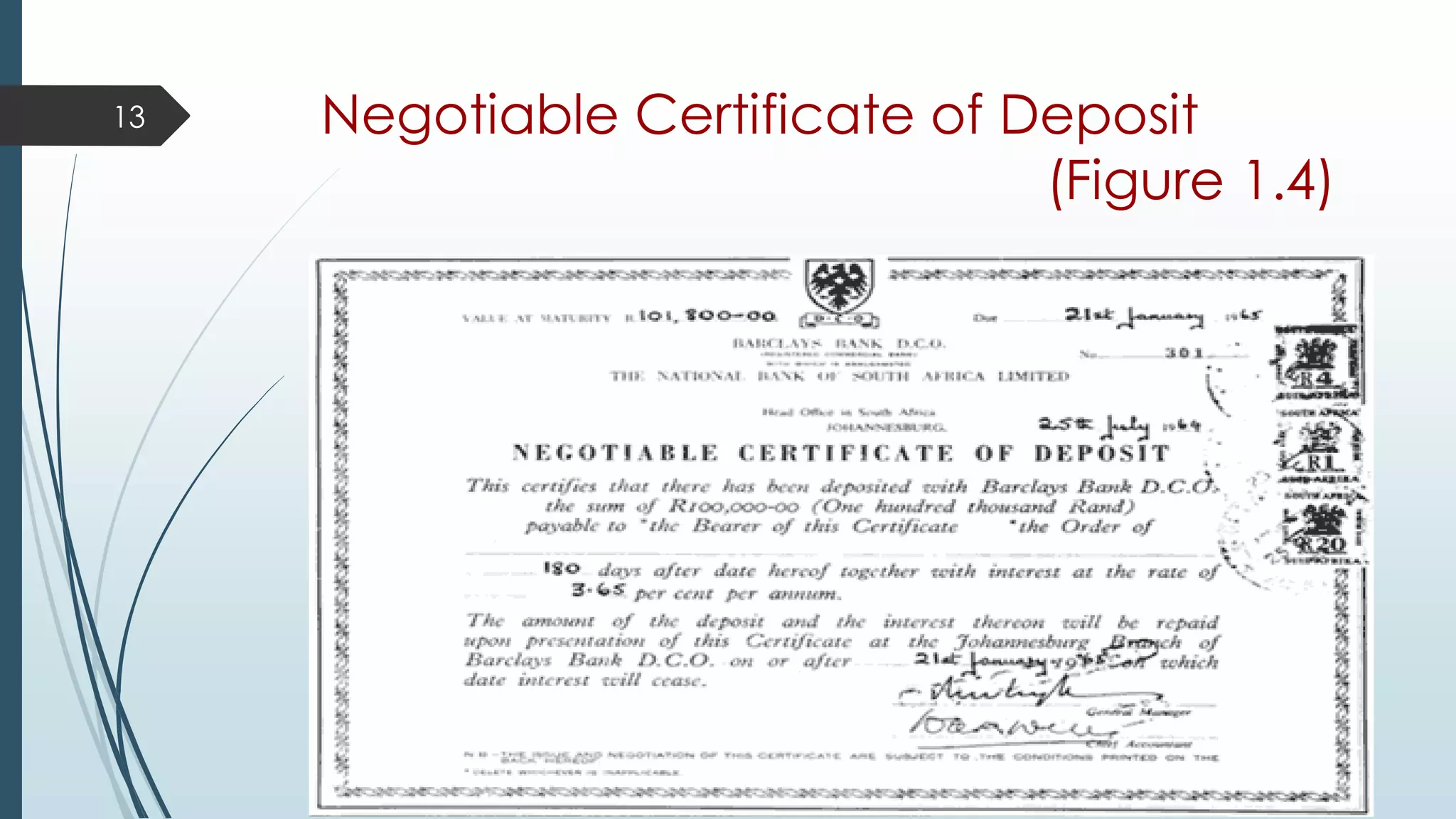
This document provides an introduction to investment terminology and concepts. It defines key terms like finance, investment, and different types of financial assets. It also summarizes the major participants in the financial system including households, financial intermediaries like banks and mutual funds, and the markets they interact in such as primary and secondary markets. Different types of financial securities are also outlined including debt instruments and equity instruments.