The document discusses various techniques for making investment decisions under risk and uncertainty. The main techniques discussed are:
1) Risk Adjusted Discount Rate (RADR) which adds a risk premium to the risk-free interest rate to calculate the discount rate.
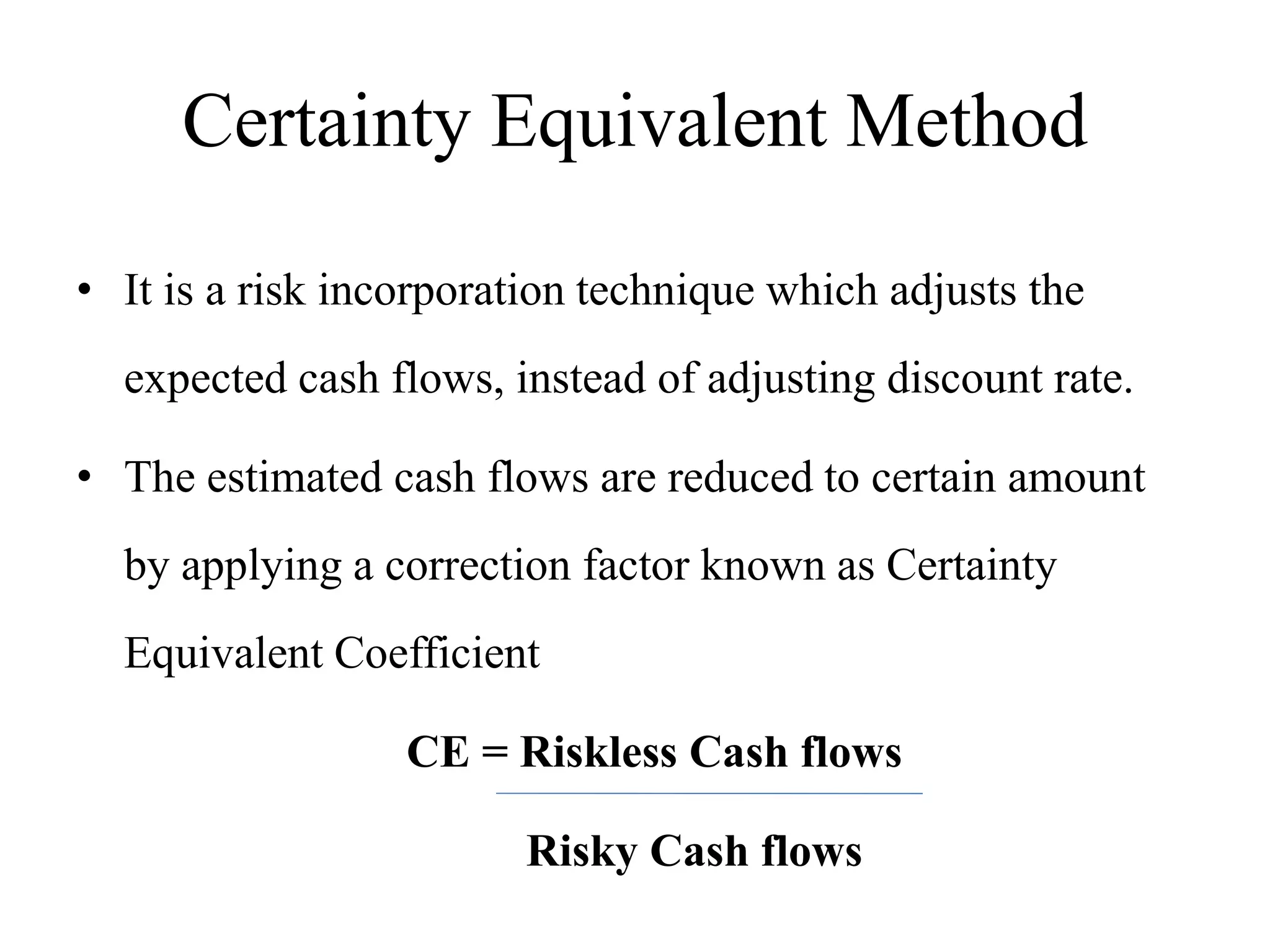
2) Certainty Equivalent Method which adjusts expected cash flows using a certainty equivalent coefficient to account for risk.
3) Statistical methods like standard deviation and coefficient of variation which measure the variability of cash flows.
4) Sensitivity analysis which evaluates cash flows under different assumptions.
5) Simulation and decision tree analysis which use random variables and graphical representations to evaluate investment decisions over multiple time periods and scenarios.