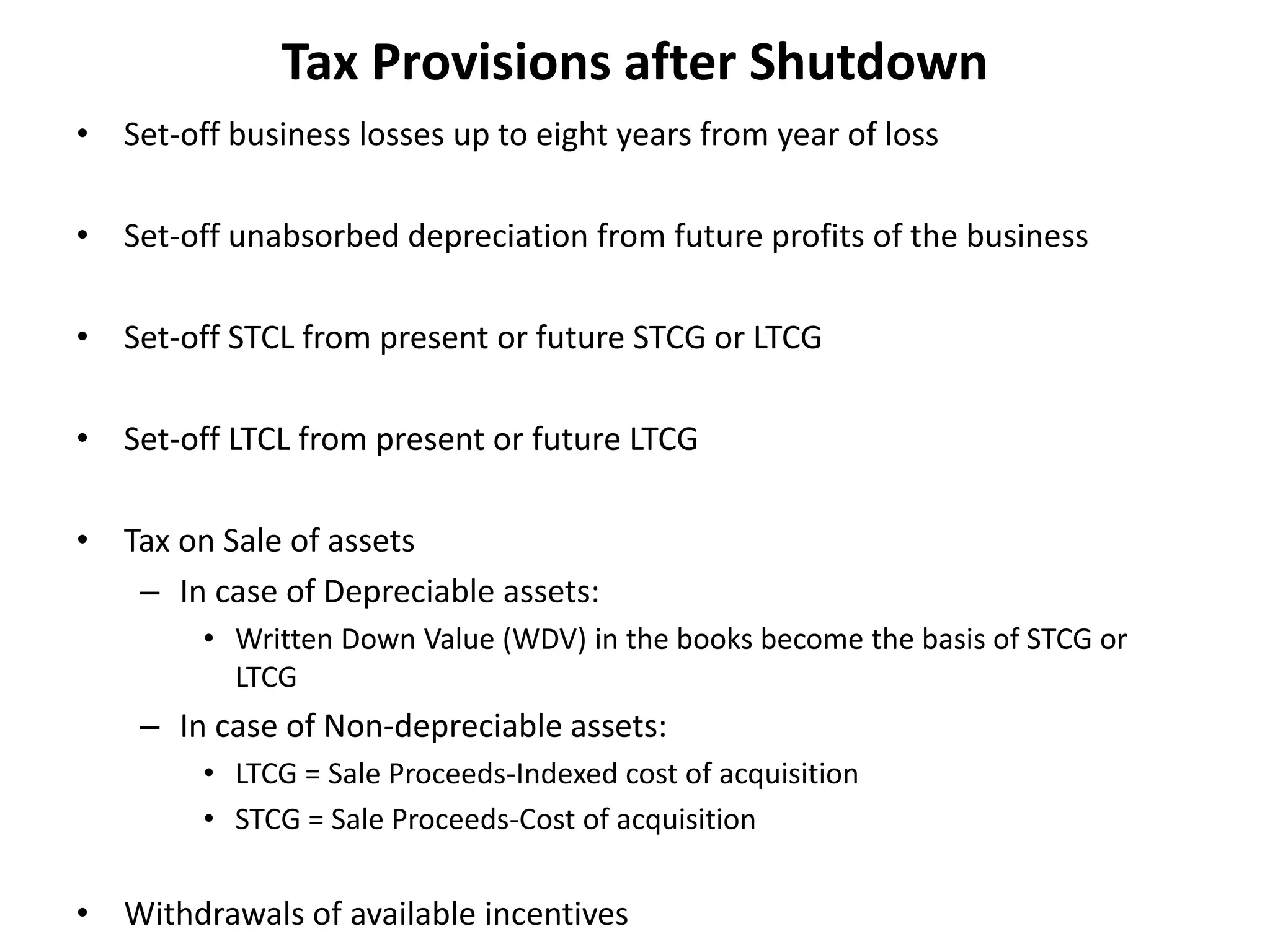
The document discusses tax planning considerations for owning or leasing assets, repairing vs replacing assets, decisions to make or buy products, and tax provisions related to shutting down a business. It provides guidance on comparing the present value of cash outflows for owning vs leasing, when it is preferable to lease vs own, and how to treat the sale of former research assets. It also outlines tax treatments and deductions allowed for repairs, and considerations for shut down like set-off of losses and depreciation.