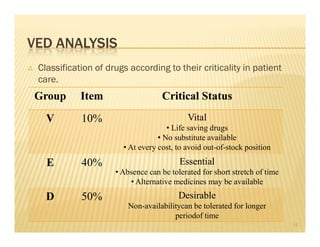
The document discusses the importance of inventory management in organizations and the methods used for inventory control, including ABC, HML, VED, and FSN analyses. It emphasizes the need for maintaining optimum stock levels and offers insights into demand forecasting and procurement strategies. Additionally, it highlights the significance of record-keeping for effective inventory management.