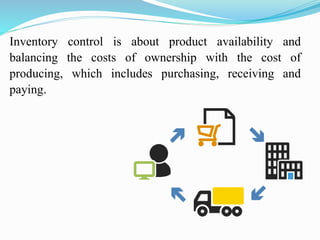
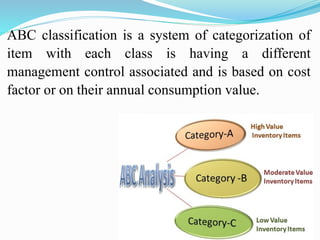
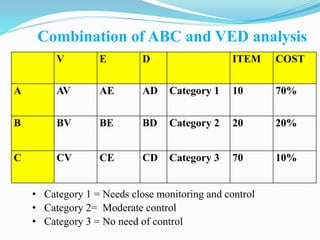
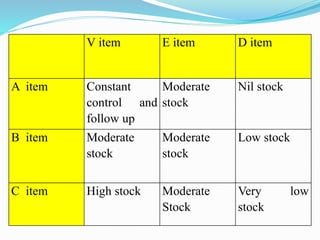
The document discusses inventory control in hospitals, highlighting its importance in managing supplies effectively to reduce costs and ensure timely delivery. It covers techniques like ABC and VED analysis for categorizing inventory based on usage and criticality, as well as the role of nurses in managing inventory, ensuring safety, and maintaining supplies. The overall objective is to optimize inventory levels, enhance service delivery, and minimize wastage.