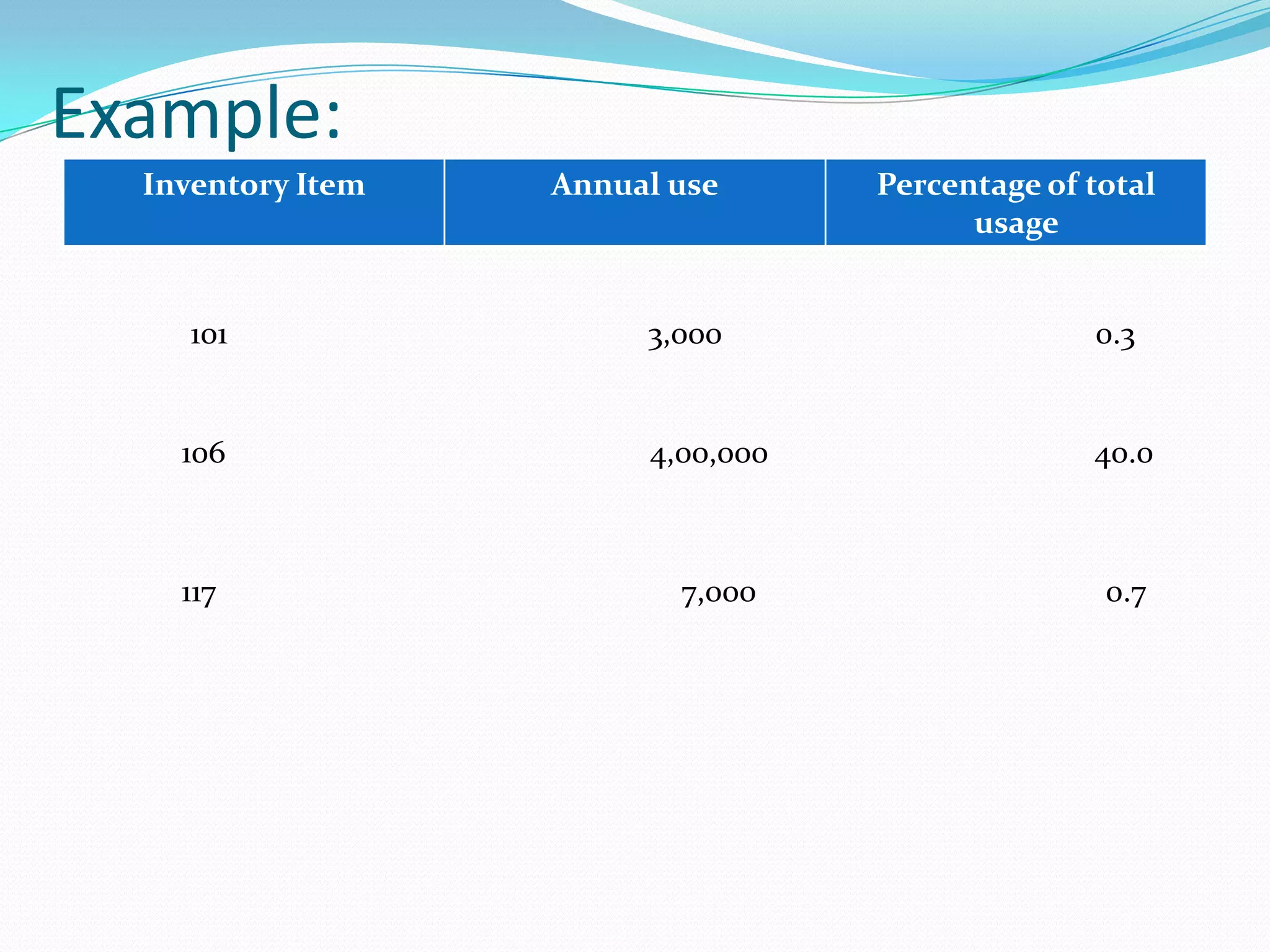
This document discusses several inventory classification techniques: ABC analysis classifies inventory based on usage value; HML classification is similar but uses unit value; VED classification determines criticality of spare parts; SDE classification considers ease of acquisition; FSN analysis identifies fast, slow, and non-moving items; XYZ analysis focuses on high-value items; and GOLF analysis considers supply sources. The techniques help prioritize inventory items to aid management and control of stock.