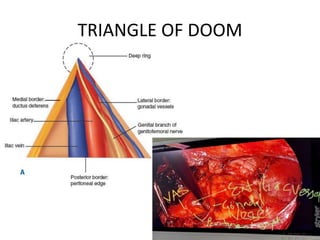
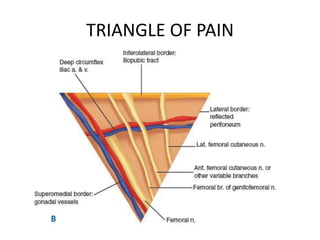
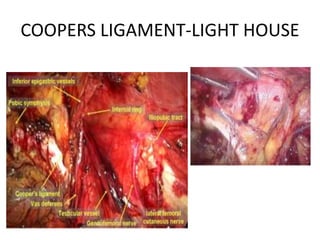
This document discusses the anatomy and clinical presentation of inguinal hernias. It describes the boundaries and contents of the inguinal canal, as well as structures like the superficial and deep inguinal rings. There are three main types of inguinal hernias - indirect, direct, and sliding. Indirect hernias are more common and involve a defect in the processus vaginalis. Direct hernias involve a weakness in the posterior inguinal wall. Hernia contents can include omentum, intestine, bladder, or other organs. Clinical presentation may include a groin bulge or heaviness, with pain or other symptoms if incarcerated or strangulated.