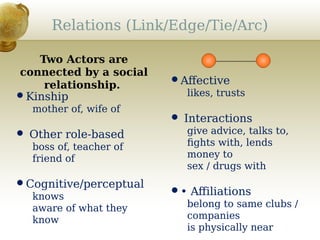
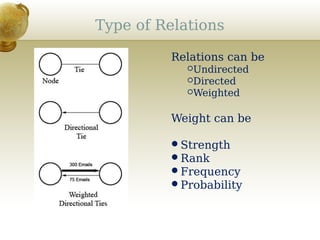
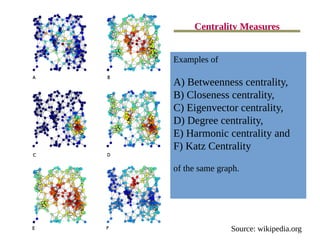
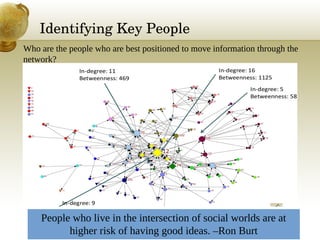
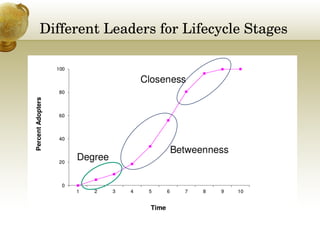
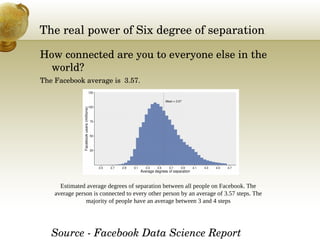
This document provides an overview of social network analysis (SNA). It defines SNA as mapping and analyzing connections between individuals, groups, and institutions. The document outlines key concepts in SNA including actors (nodes), relations (links between actors), types of relations, centrality measures to identify influential individuals, and different software tools to conduct SNA. It also discusses real-world examples like Facebook data that demonstrate concepts like degrees of separation and diffusion of information through social networks.