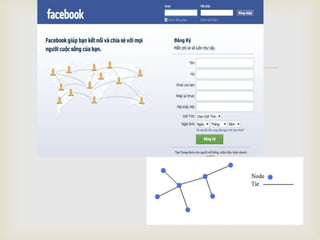
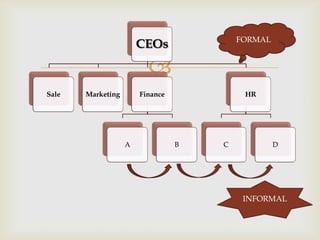
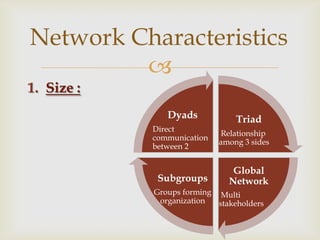
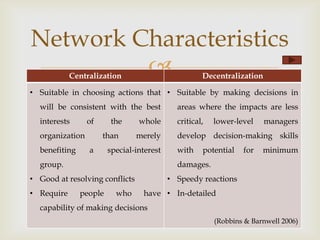
This document discusses social network theory and analysis. It defines a social network as including actors (nodes) and the relationships (ties) between them. Social network analysis examines the relationships and structure of relationships between social entities like individuals or organizations. The document outlines some key concepts in social network theory including centrality, which looks at the importance of individual actors, and multiplexity, which refers to relationships serving multiple functions. It also discusses how network characteristics like size, subgroups, and centralization vs decentralization impact information sharing and decision making in organizations.