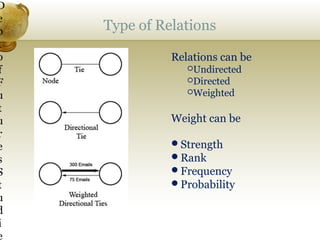
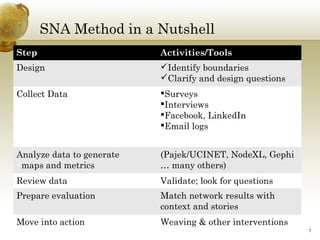
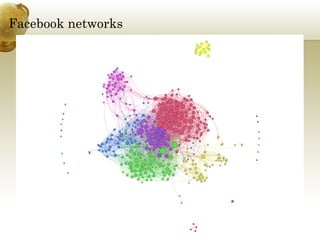
The document discusses social network analysis (SNA) as a multidisciplinary approach to mapping and measuring relationships among various entities such as individuals, organizations, and countries. It outlines SNA methods, applications, and various properties of networks, emphasizing its practicality in fields like sports and organizational dynamics. Additionally, it provides insight into using SNA to enhance collaboration and organizational productivity through understanding interactions and connections among network participants.