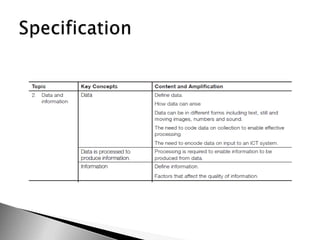
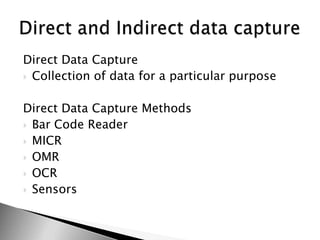
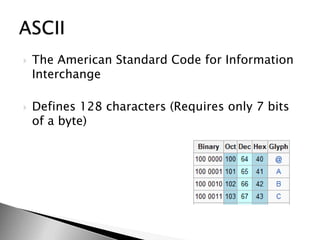
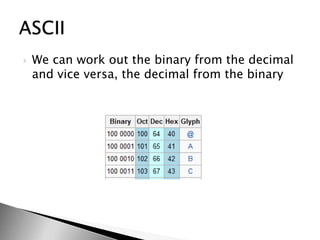
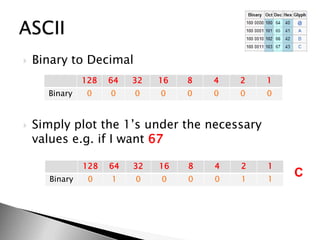
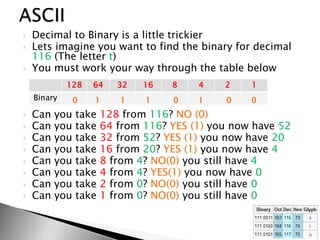
This document discusses data and information. It begins by defining data as raw facts and figures without meaning. There are different types of data such as text, numbers, audio, images and video. Data is converted to binary for computer processing and is encoded using standards like ASCII. Information is defined as data that has been processed and given meaning and context. The quality of information depends on it being accurate, up-to-date, complete and from reliable sources. Coding is used to reduce data storage size.