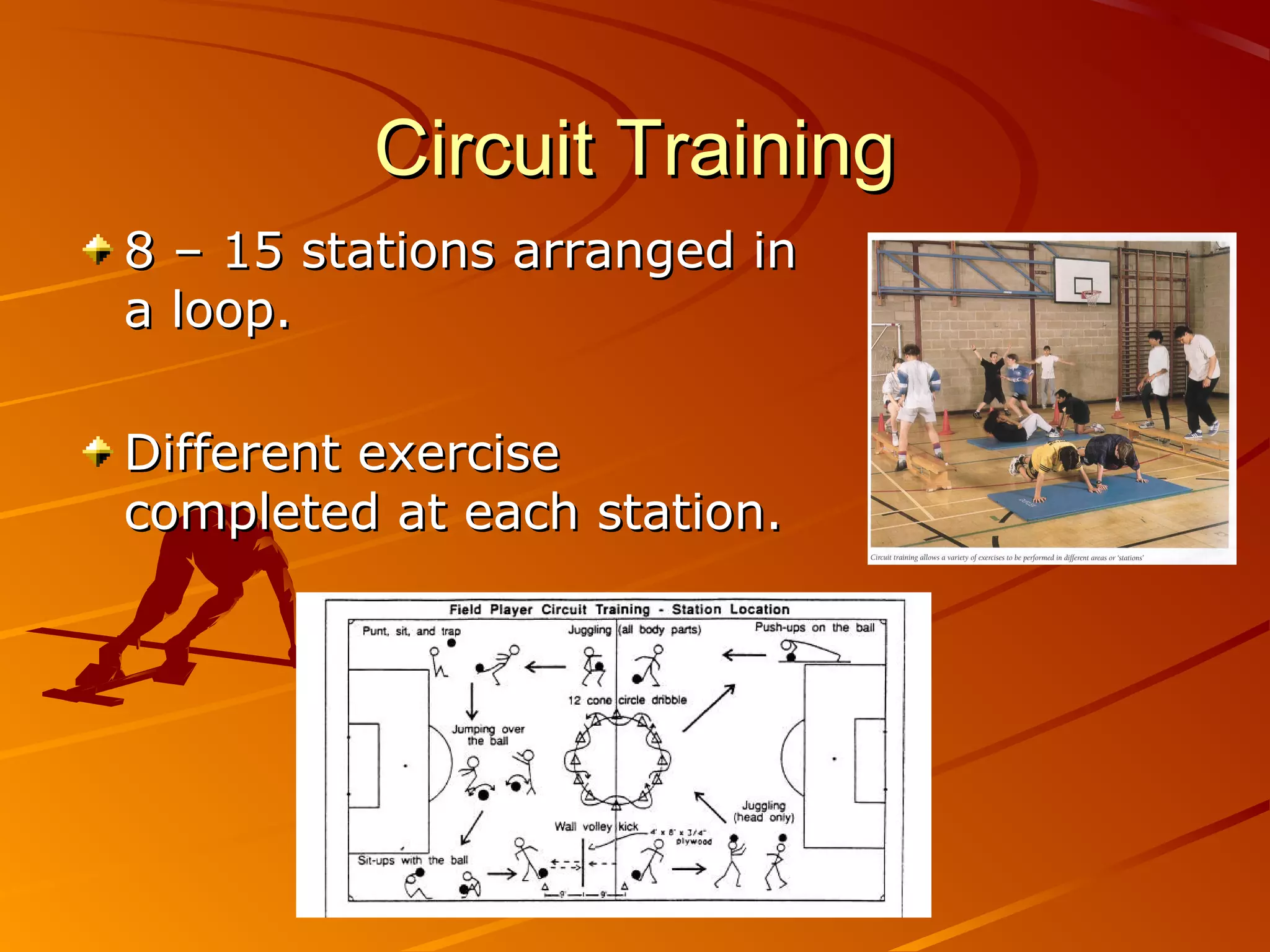
1. The document discusses different types of training methods including continuous training, fartlek training, interval training, weight training, and circuit training.
2. It explains the principles of training such as specificity, progression, overload, reversibility, and tedium.
3. Key factors for an effective exercise program are outlined including having a goal, training method, applying training principles, and planning sessions.