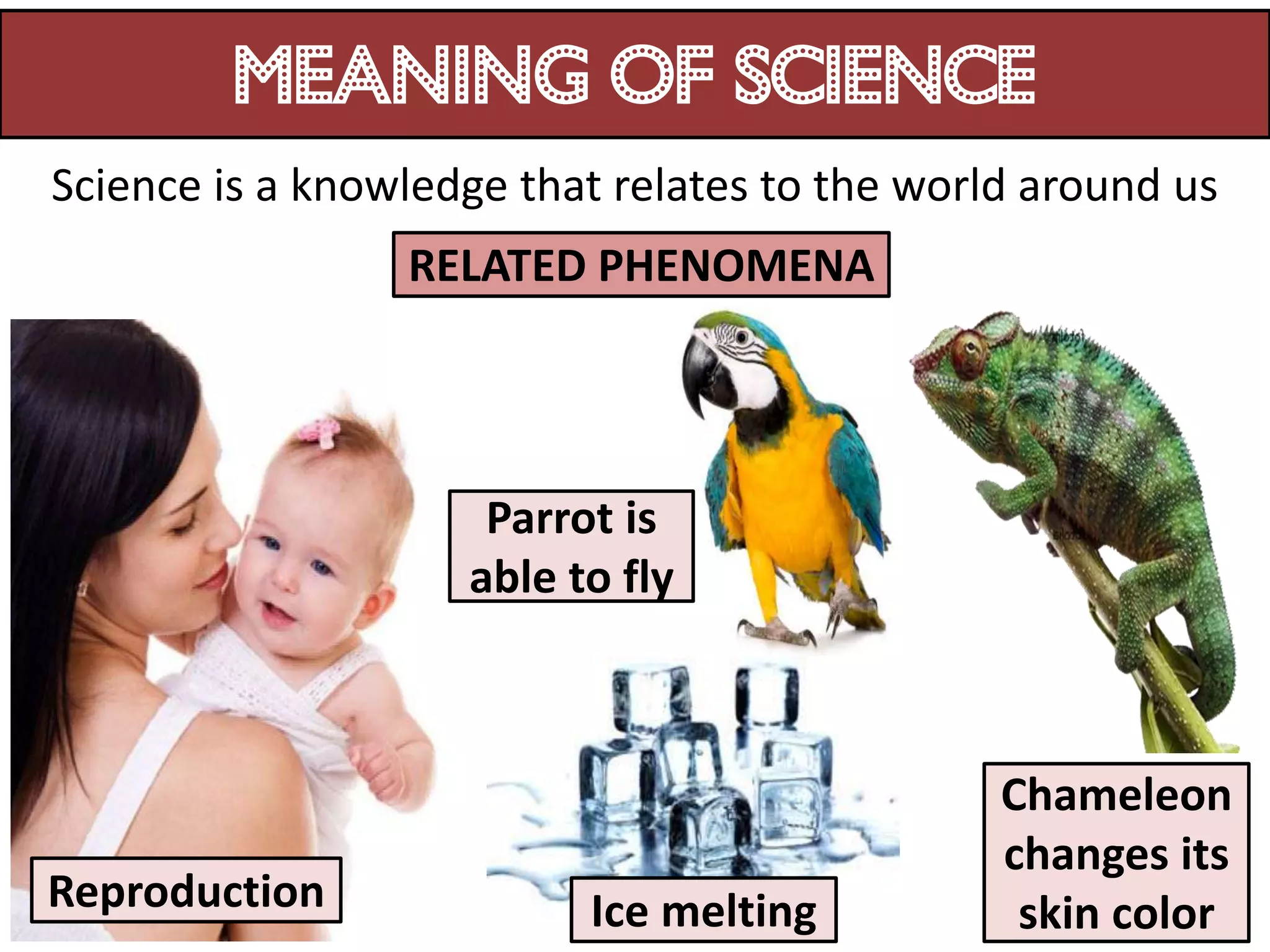
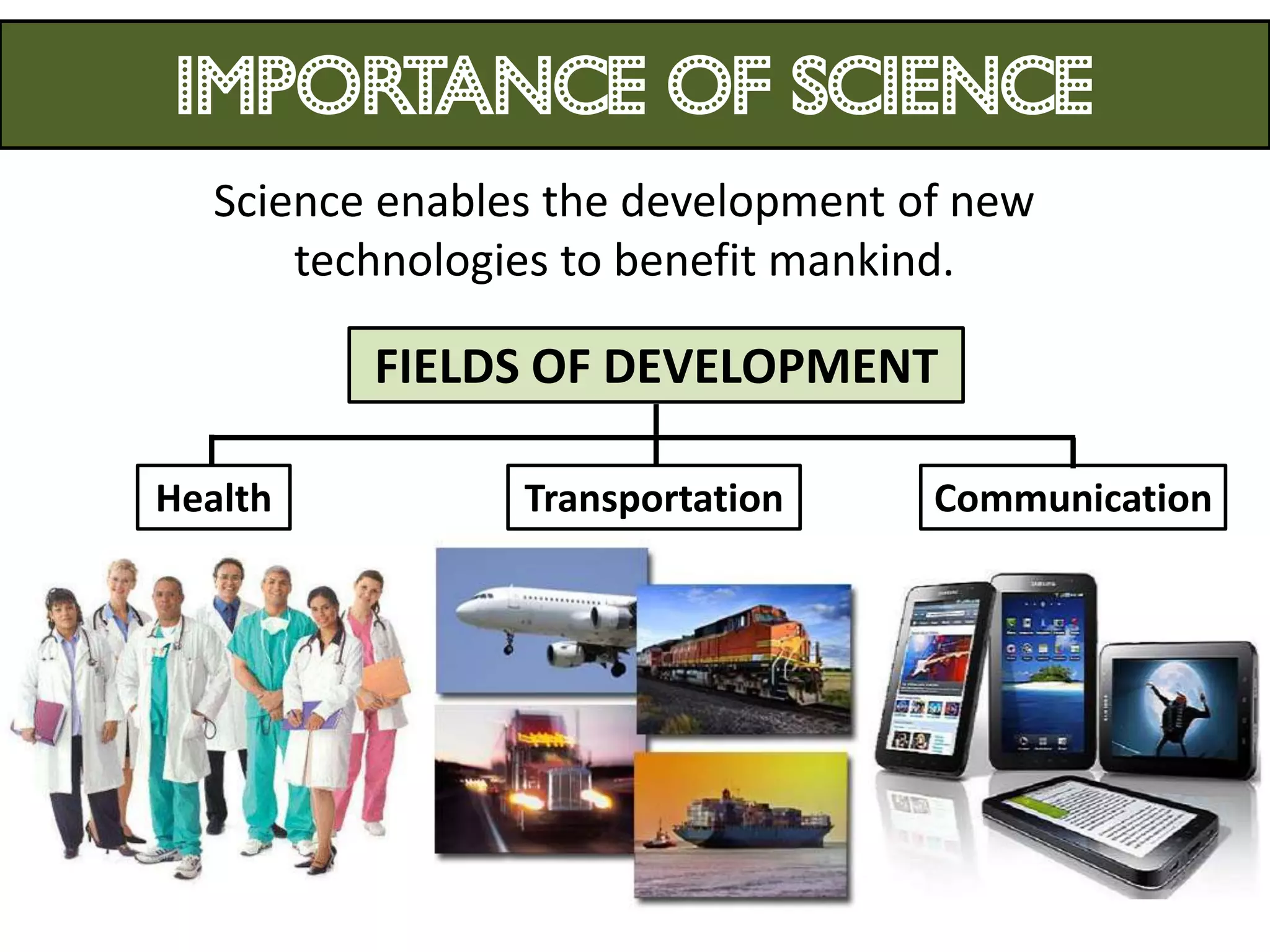
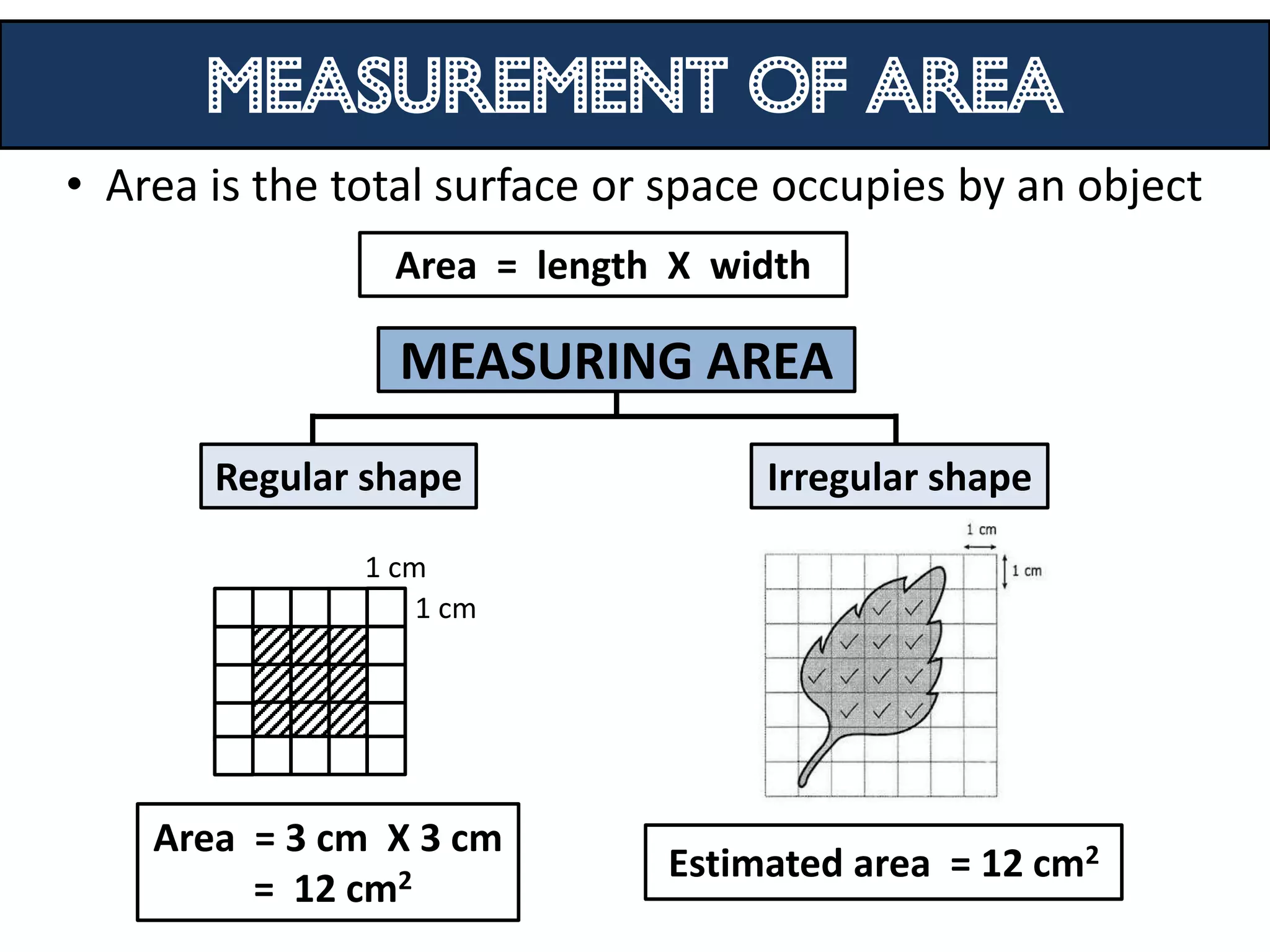
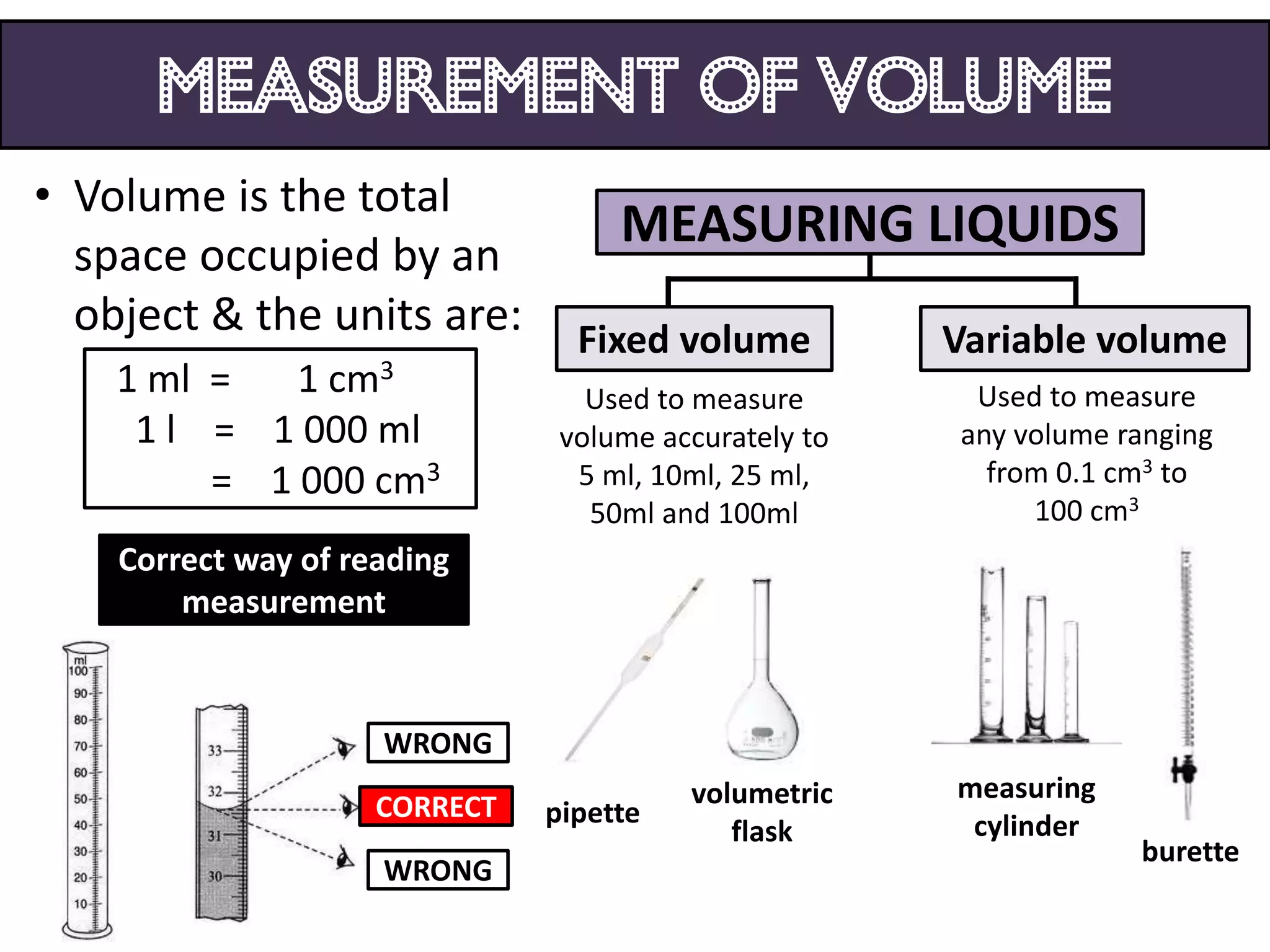
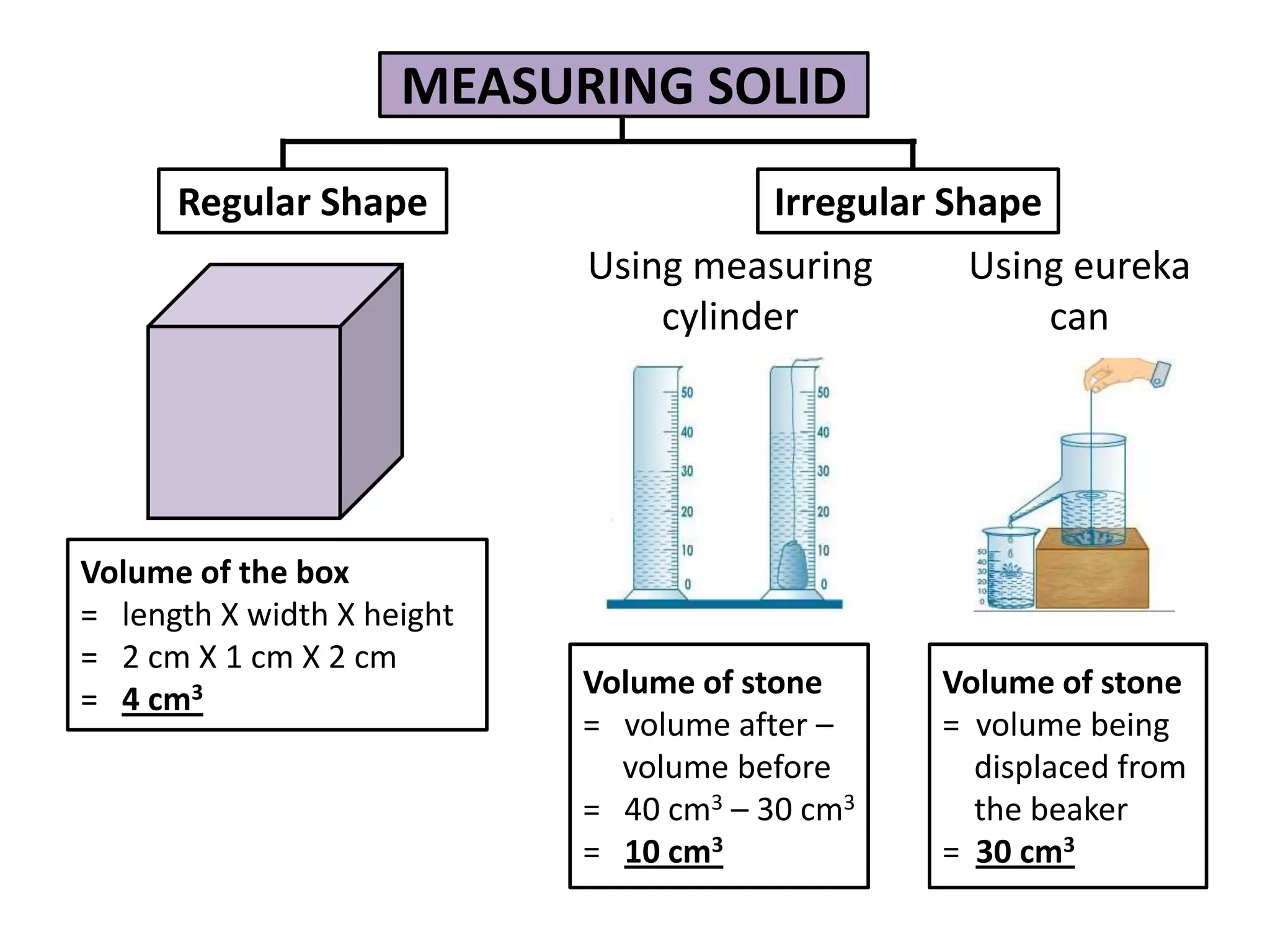
1. Science relates to phenomena in the natural world and enables technological development that benefits humanity.
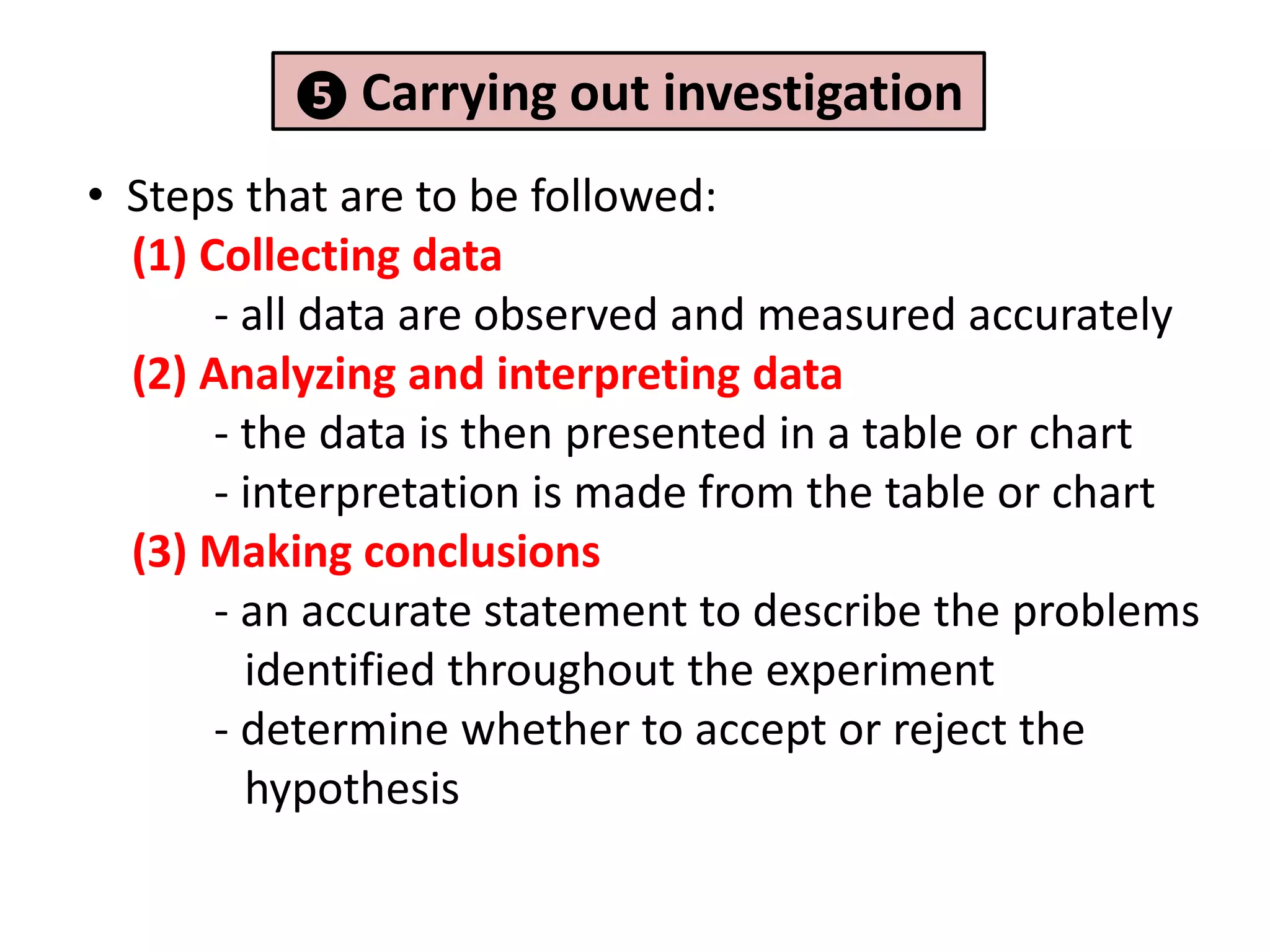
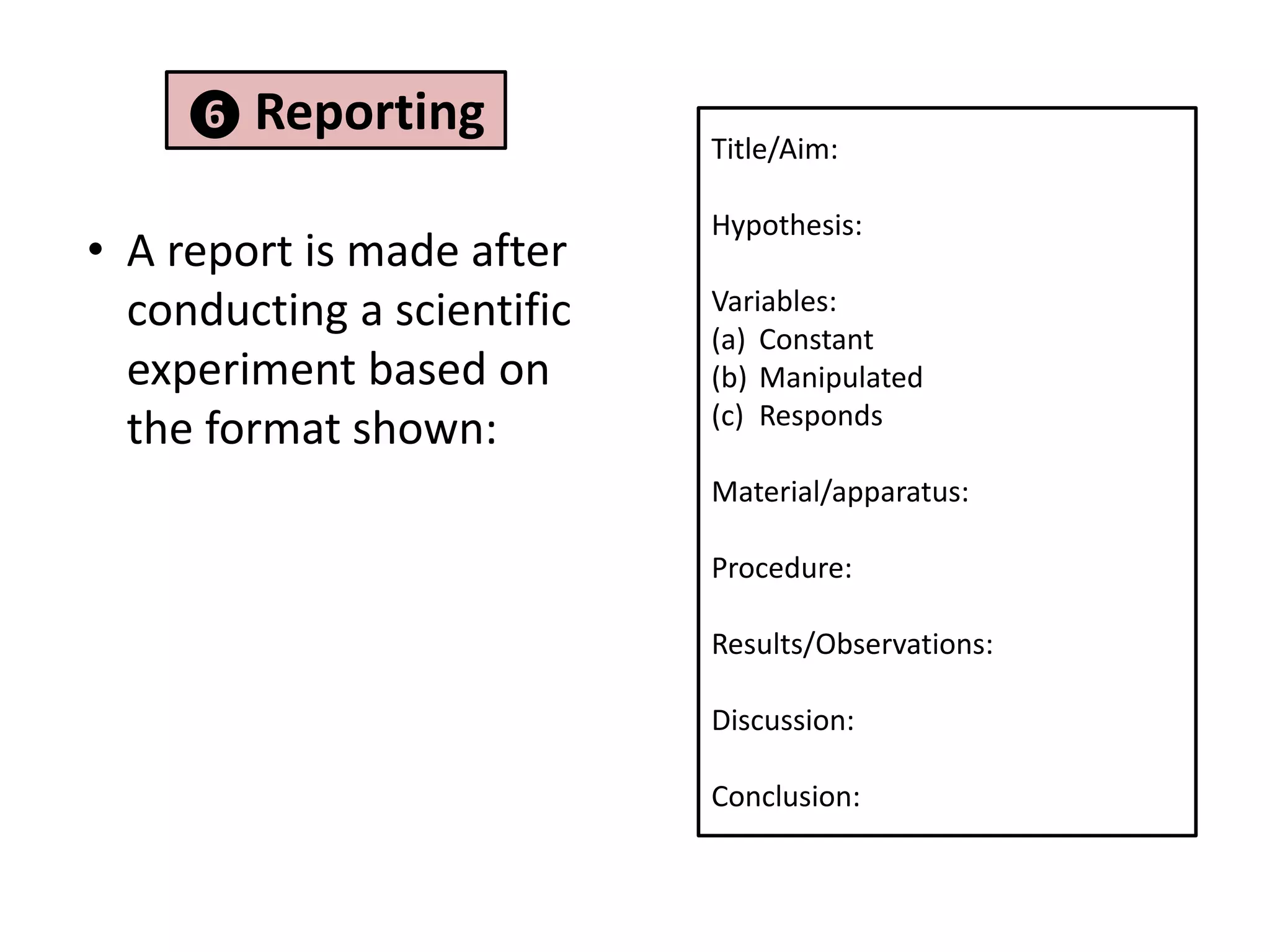
2. It involves identifying problems, forming hypotheses, planning experiments, collecting and analyzing data, and reporting conclusions.
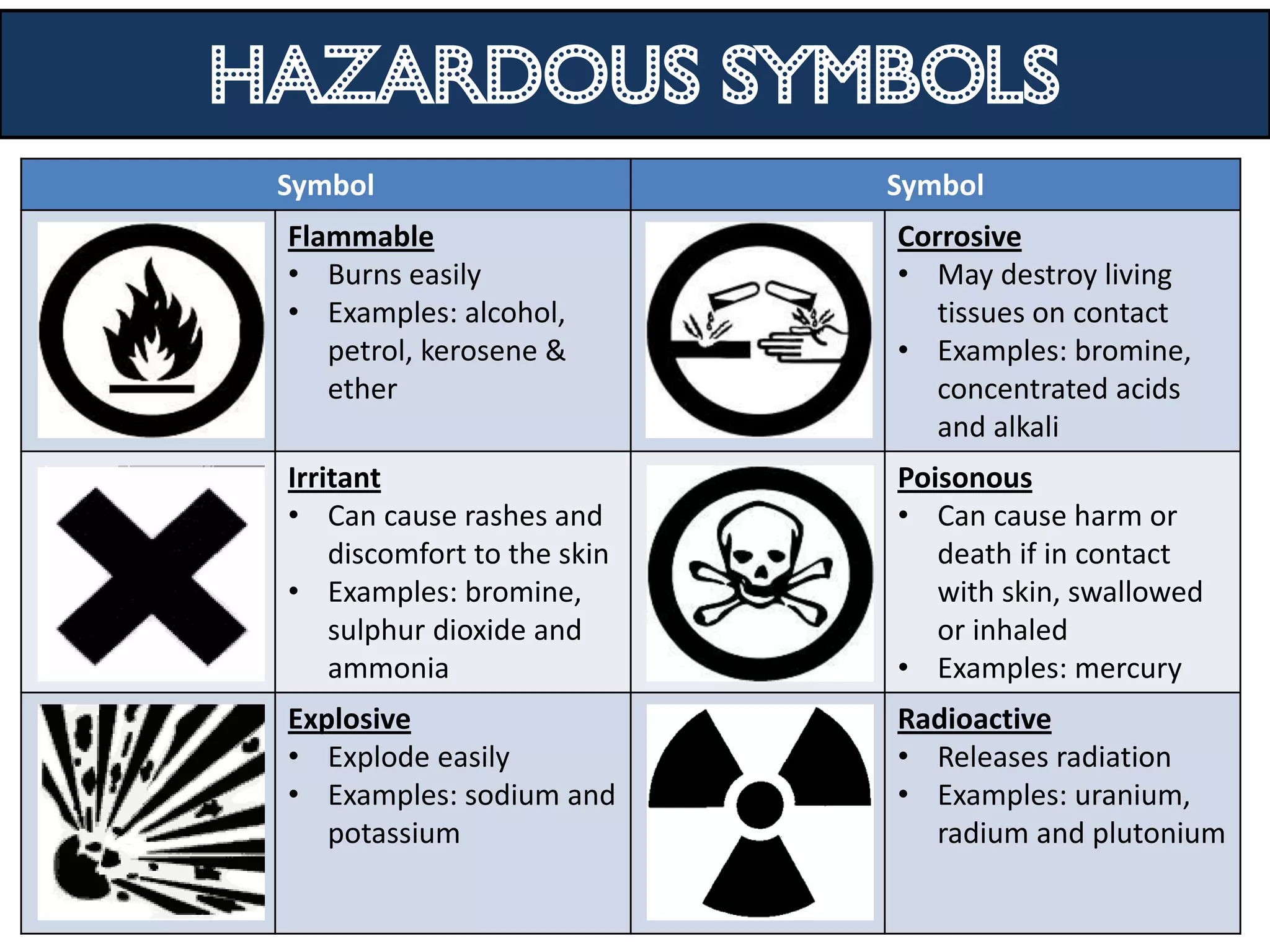
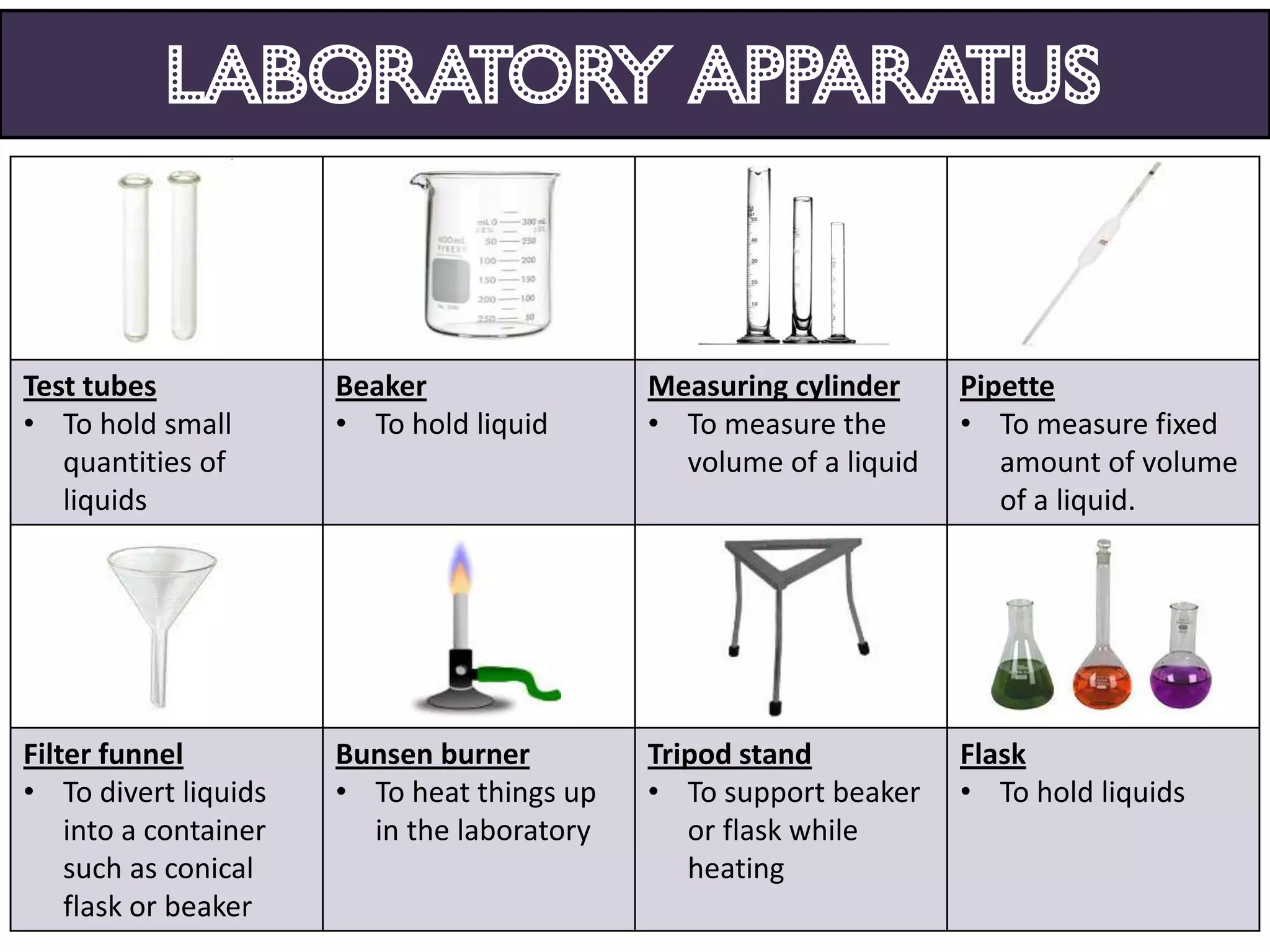
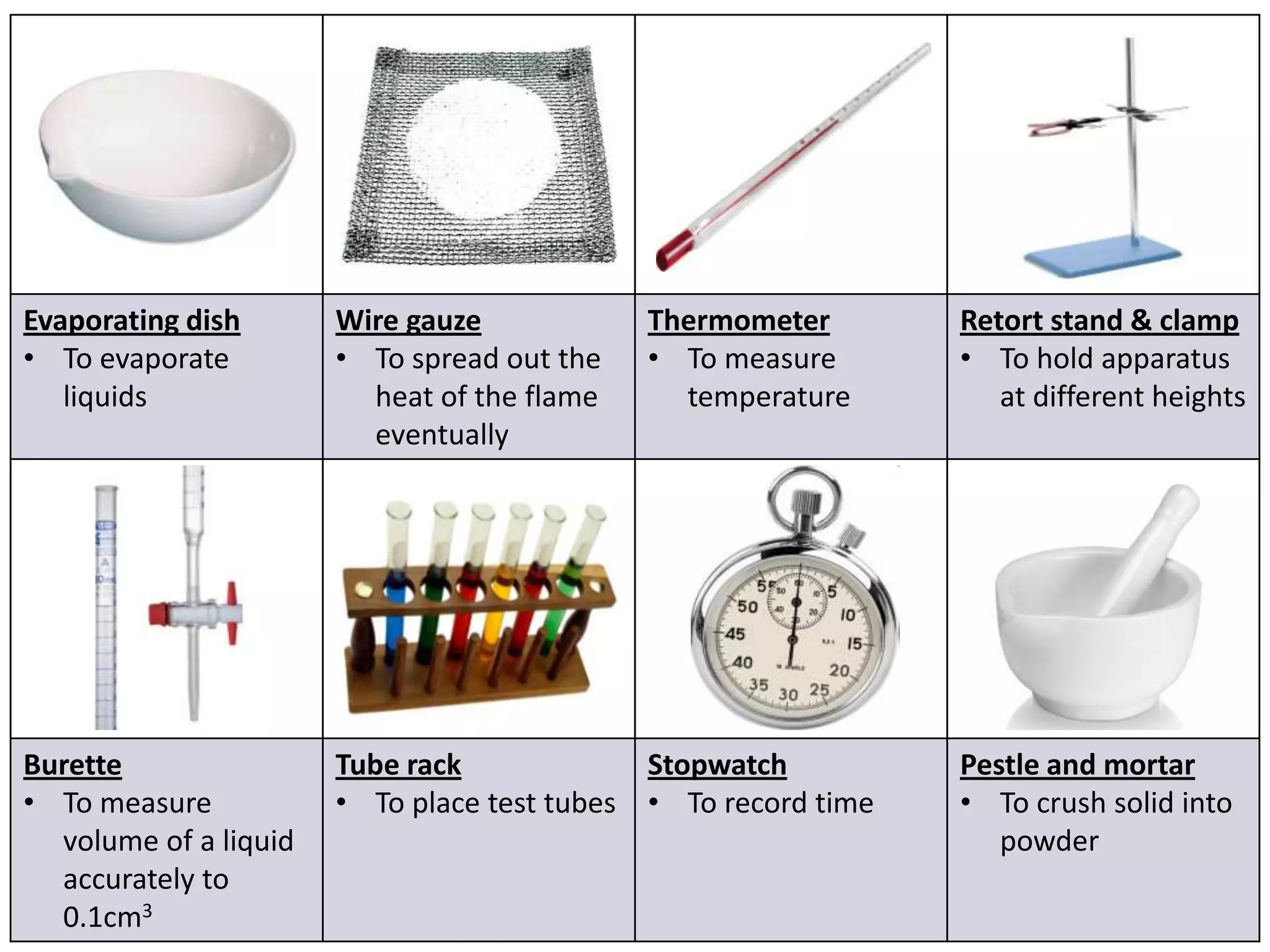
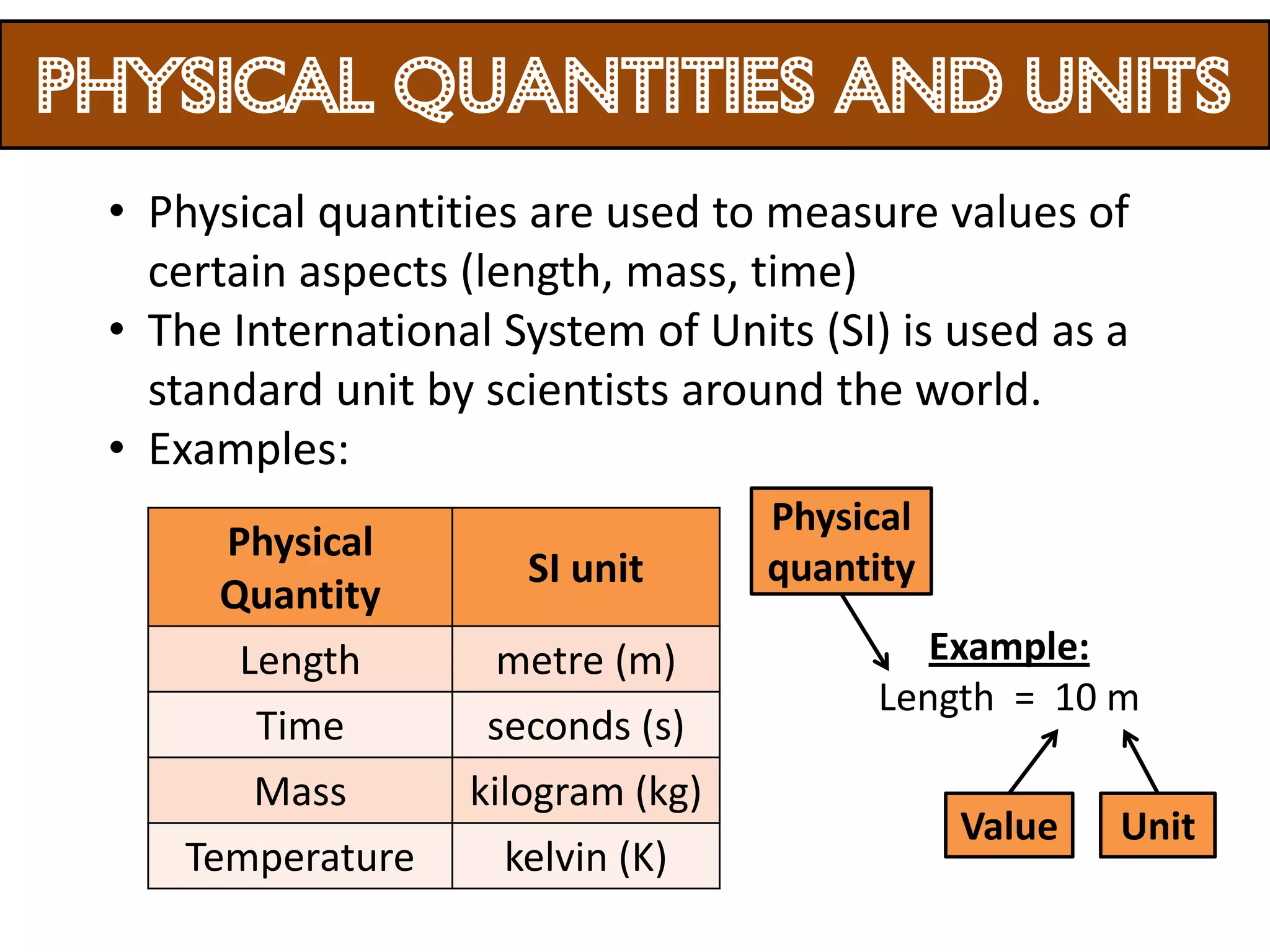
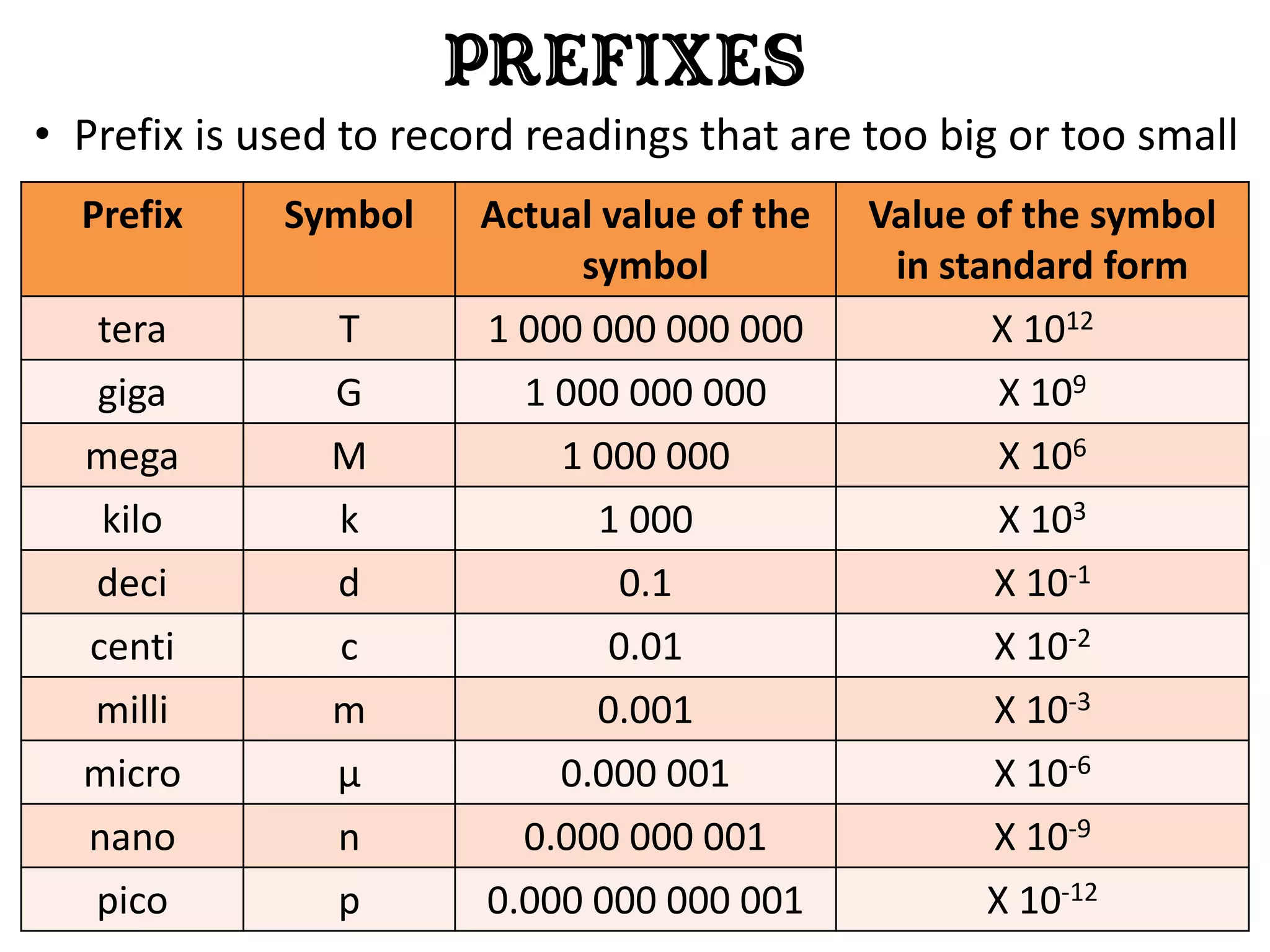
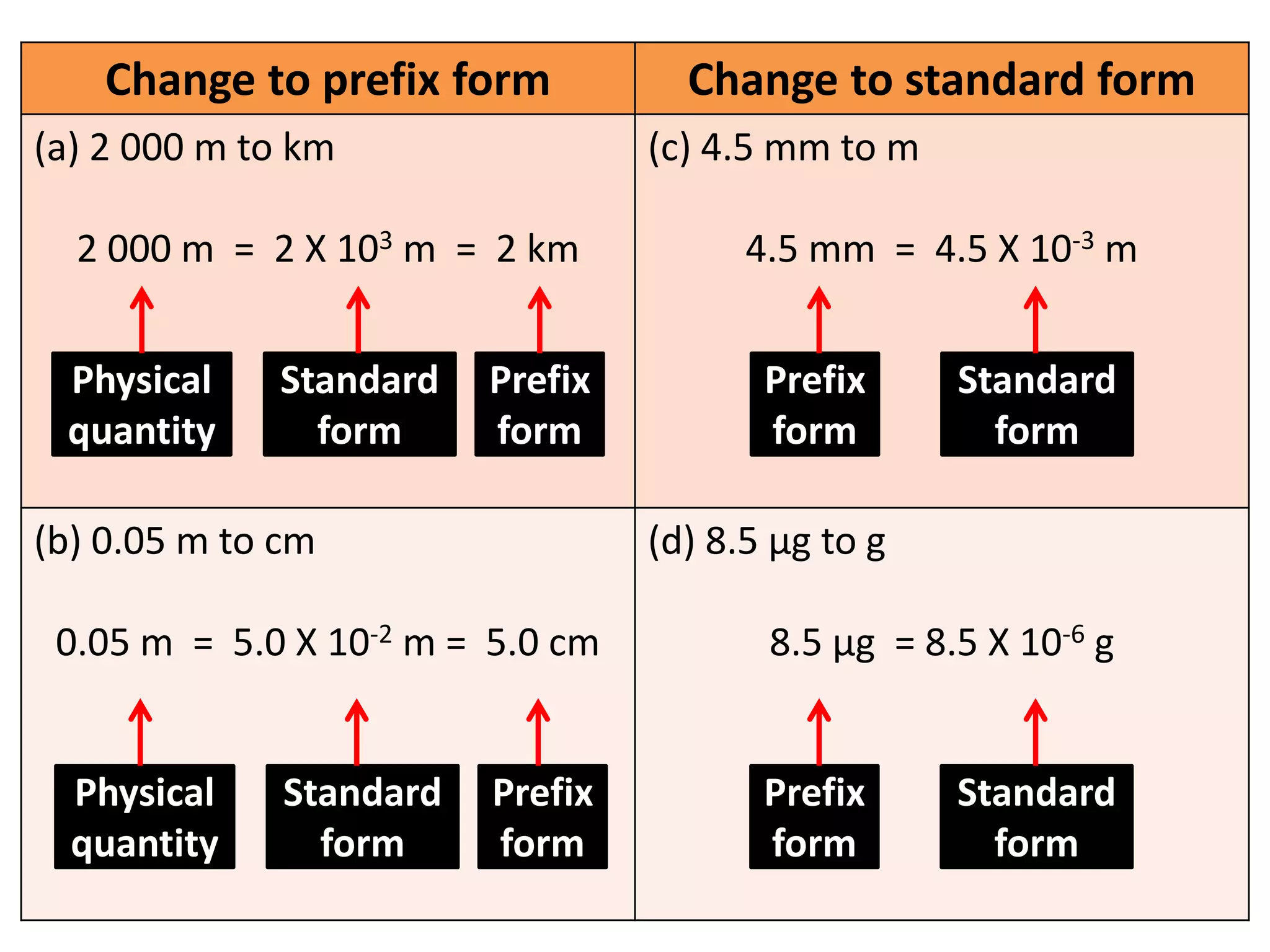
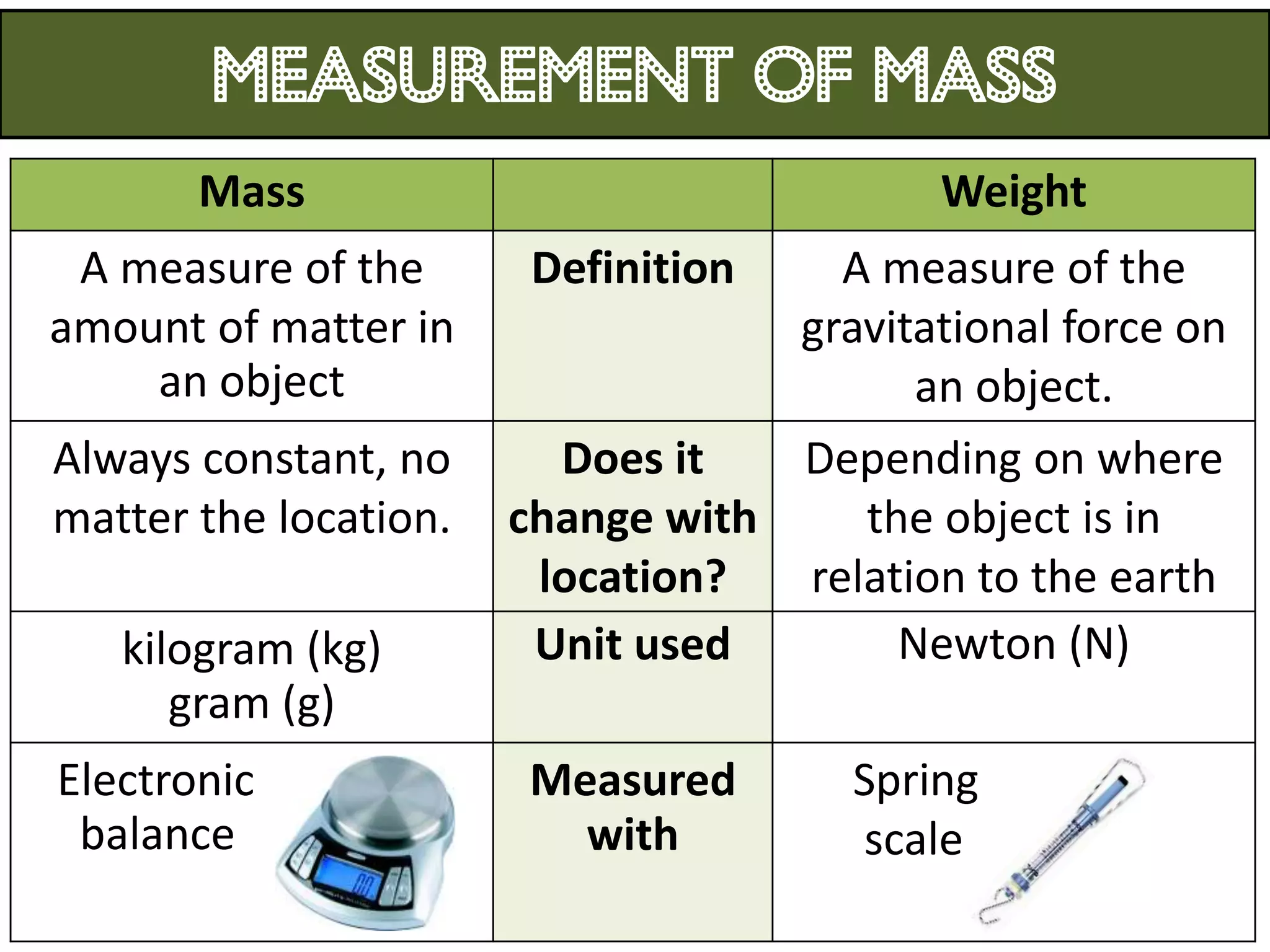
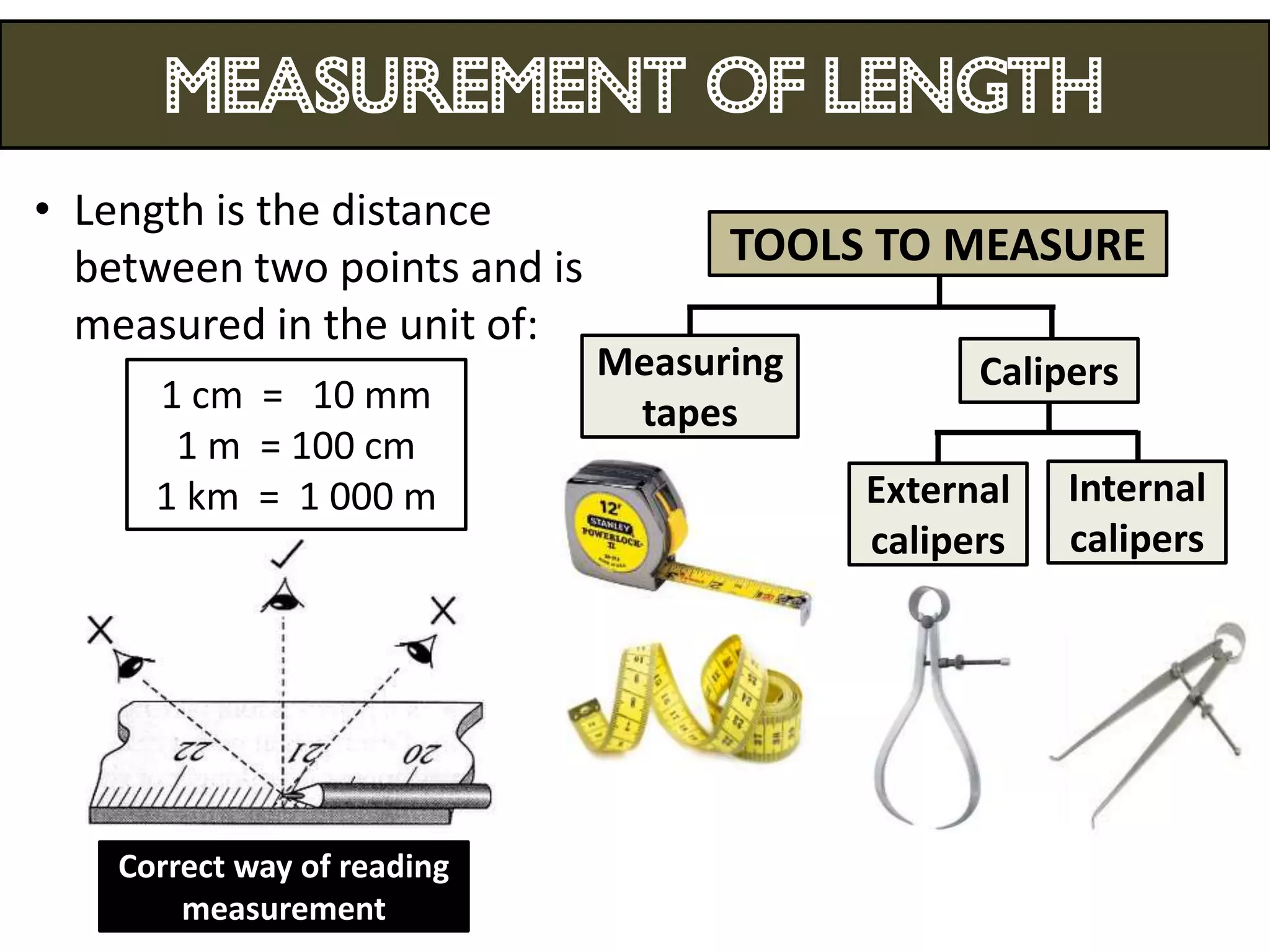
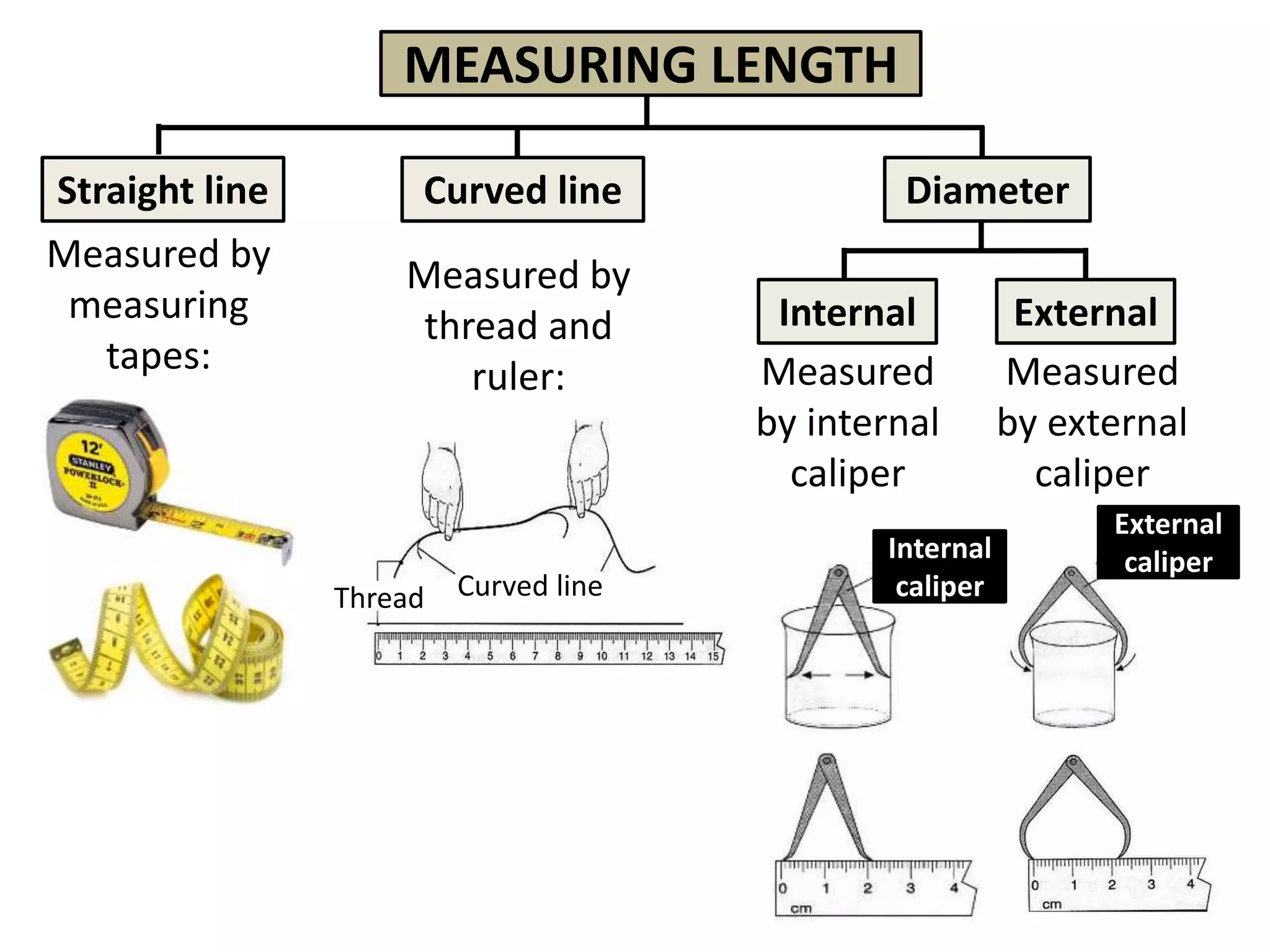
3. Scientists use various instruments and follow standardized measurement systems to study topics like health, transportation, and communication.