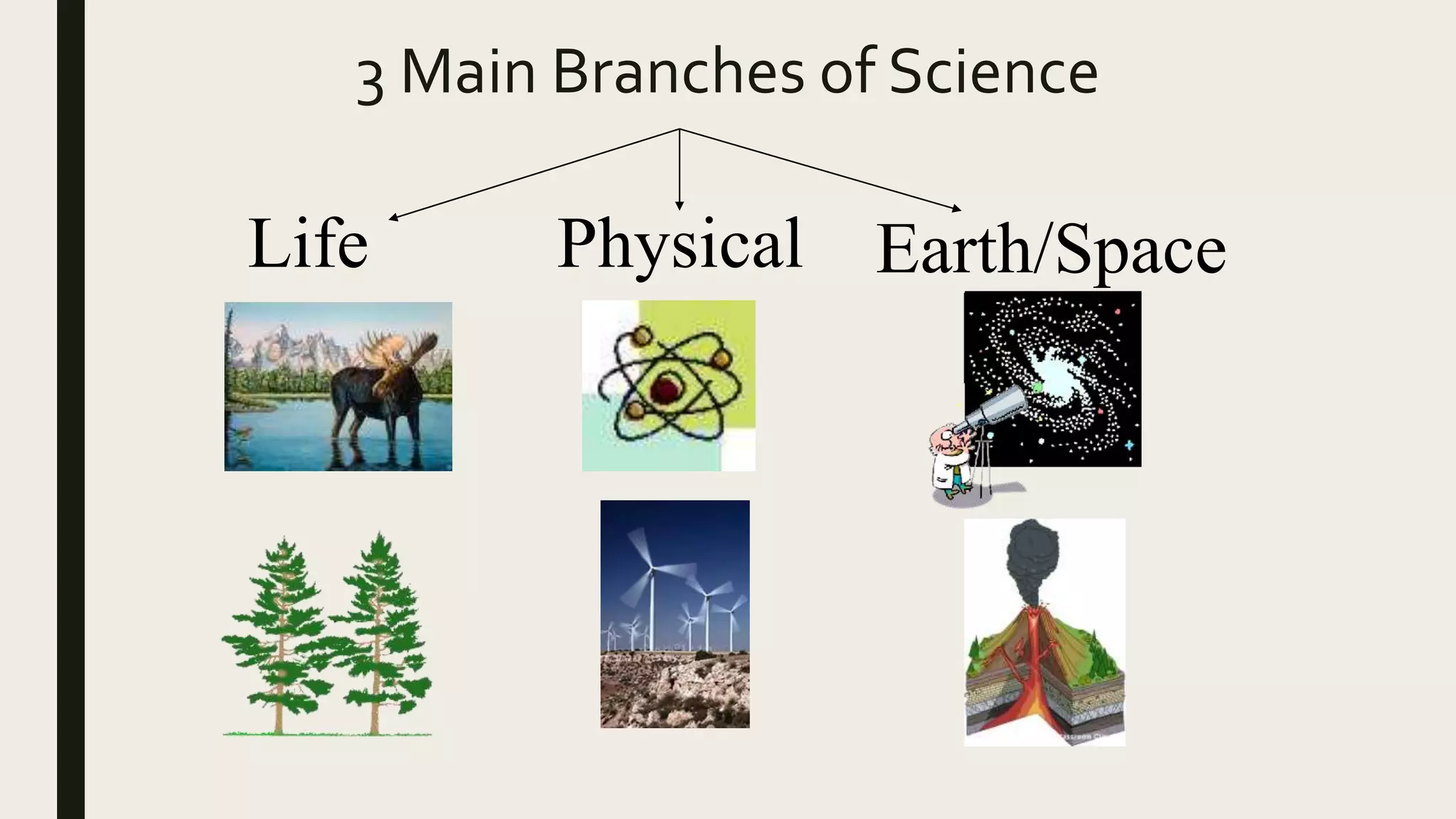
Science is defined as a systematic attempt to establish knowledge through objective means. It employs skills like measuring, analyzing, observing, and experimenting. Science can be classified into pure science, applied science, and technology. Pure science involves experimentation for the pursuit of knowledge, while applied science searches for practical uses of scientific knowledge. Technology applies science to improve life. The three main branches of science are life science, physical science, and earth/space science. Life science studies living things, physical science deals with matter and energy, and earth science examines our planet and surroundings.