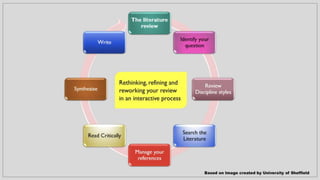
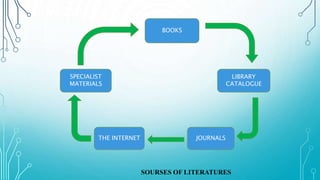
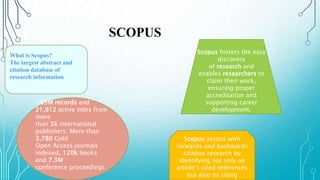
The document presents an introduction to research in science, covering fundamental concepts, the research process, and emphasizing the importance of literature reviews and ethics in research. Key operations in research include data collection, analysis, and report writing, while Scopus is highlighted as a vital database for accessing research information. Ethical principles related to research are also outlined, ensuring the protection of subjects' rights and maintaining integrity in the research process.