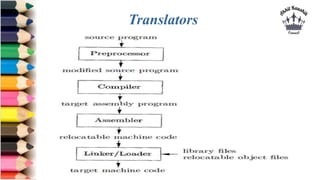
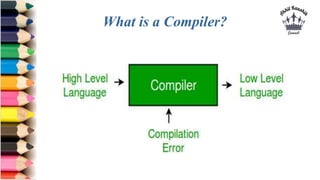
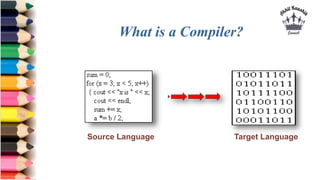
This document provides an introduction to Python programming. It discusses that Python is an interpreted, object-oriented, high-level programming language with simple syntax. It then covers the need for programming languages, different types of languages, and translators like compilers, interpreters, assemblers, linkers, and loaders. The document concludes by discussing why Python is popular for web development, software development, data science, and more.































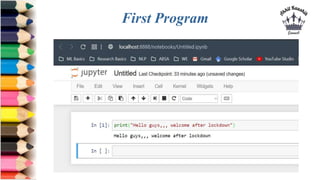
![Keyboard shortcuts - Jupyter Notebook
• Shift + Enter run the current cell, select
below
• Ctrl + Enter run selected cells
• Alt + Enter run the current cell, insert below
• Ctrl + S save and checkpoint
• Ctrl + ] indent
• Ctrl + [ dedent
• H show all shortcuts
• Z undo cell deletion
• S Save and Checkpoint
• A insert cell above
• B insert cell below
• X cut selected cells
• C copy selected cells
• V paste cells below
• Shift + V paste cells above
• Y change the cell type to
Code
• M change the cell type to
Markdown](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pp1-intro-200817043613/85/Introduction-to-Python-Programming-46-320.jpg)