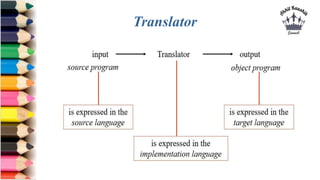
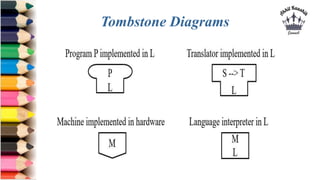
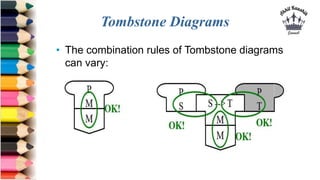
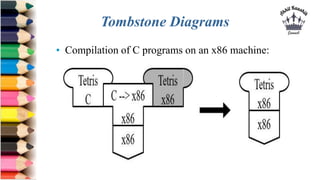
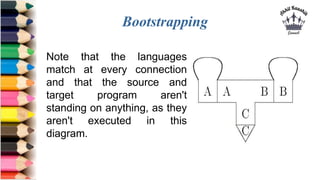
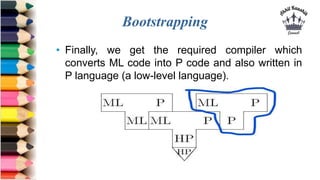
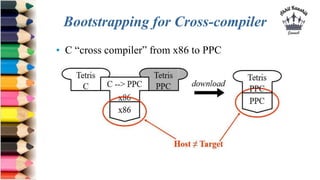
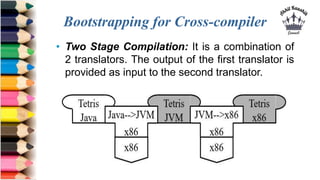
The document discusses tombstone diagrams, which use puzzle pieces to represent language processors and programs. It then explains bootstrapping, which refers to using a compiler to compile itself. This allows obtaining a compiler for a new target machine by first writing a compiler in a high-level language, compiling it on the original machine, and then using the output compiler to compile itself on the new target machine. The document provides examples of using bootstrapping to generate cross-compilers that run on one machine but produce code for another.