This document provides an introduction and overview of key concepts in Microsoft Project 2010, including:
- What MS Project is and its main goals of creating and managing project schedules.
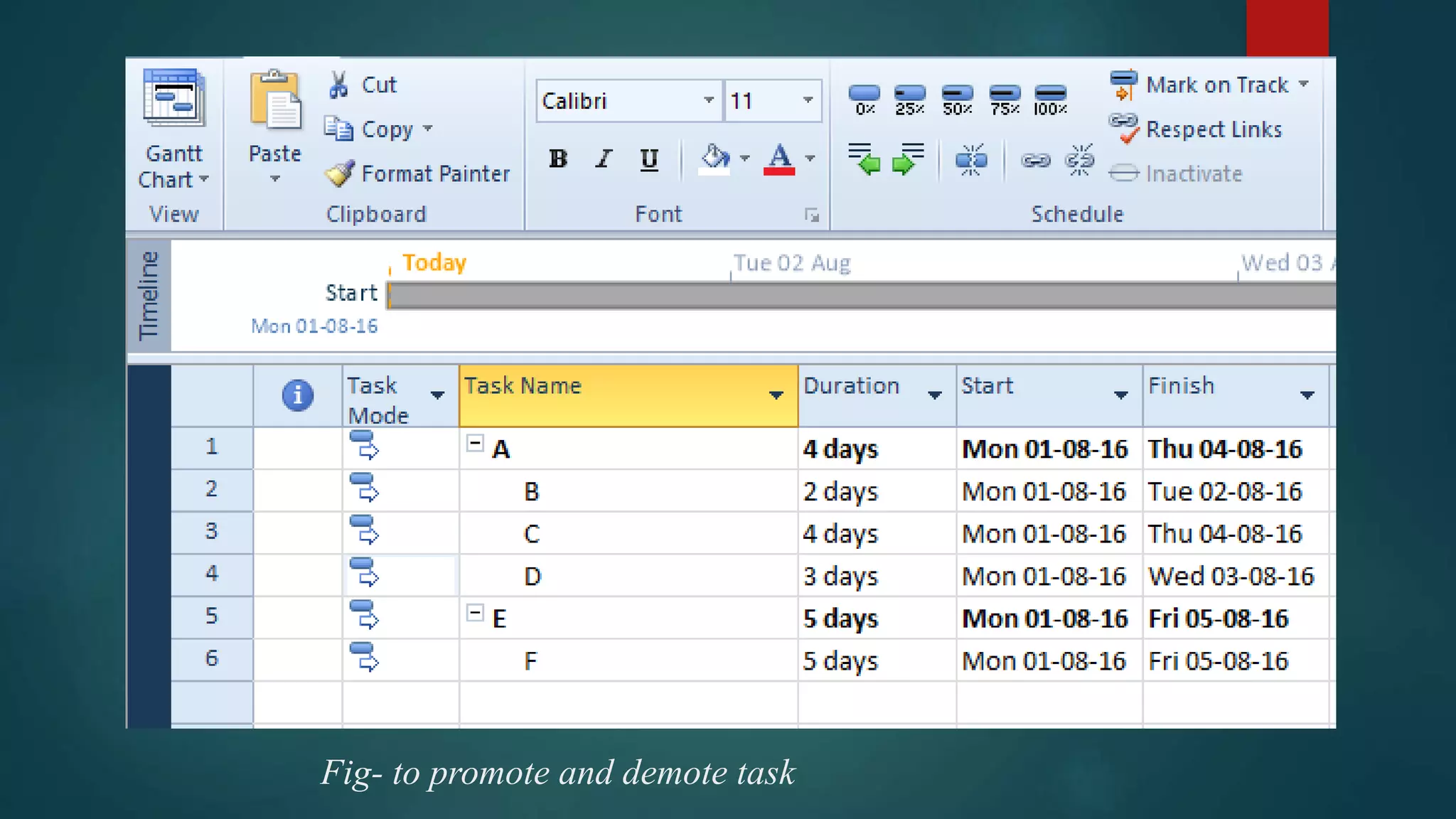
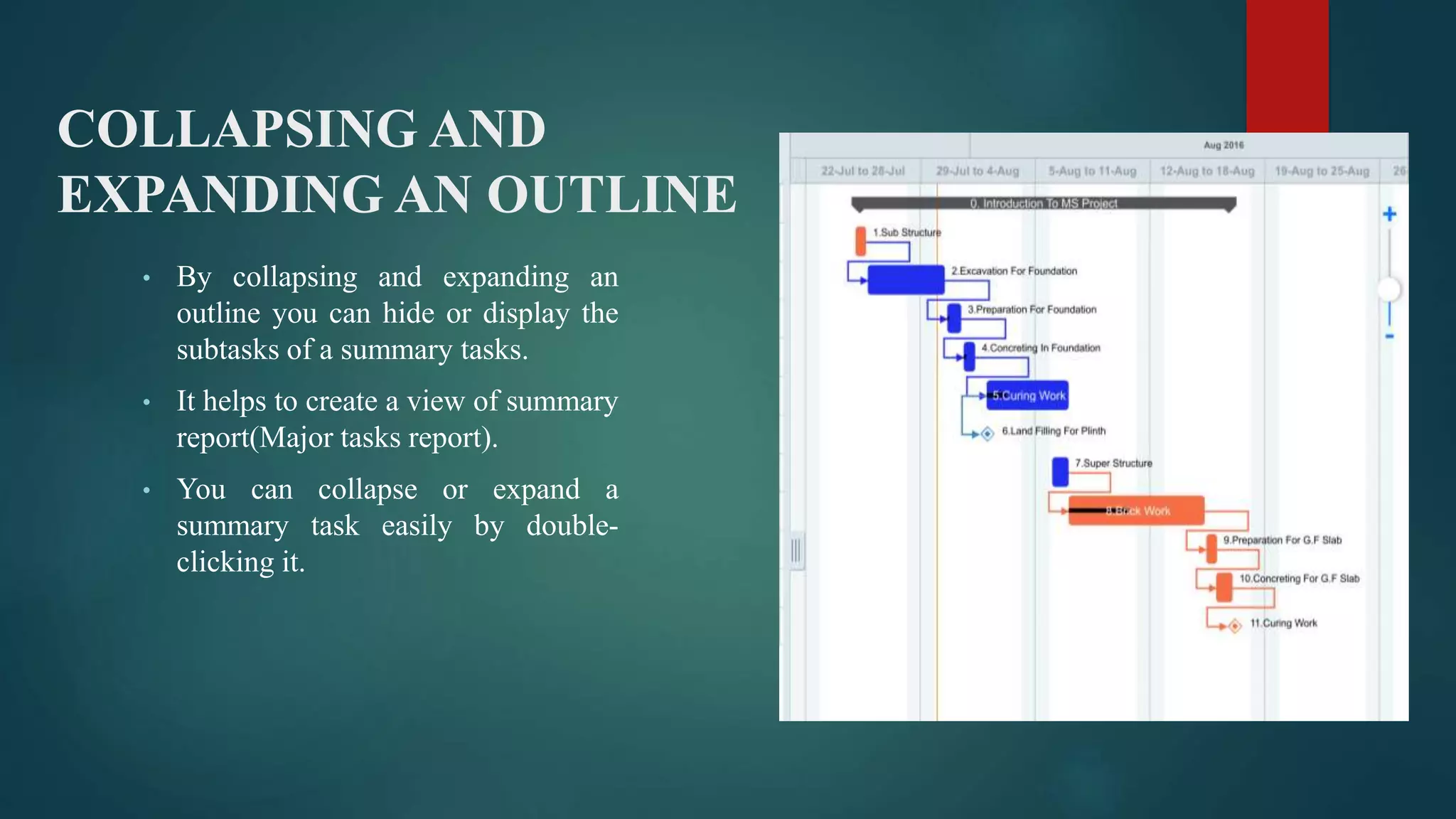
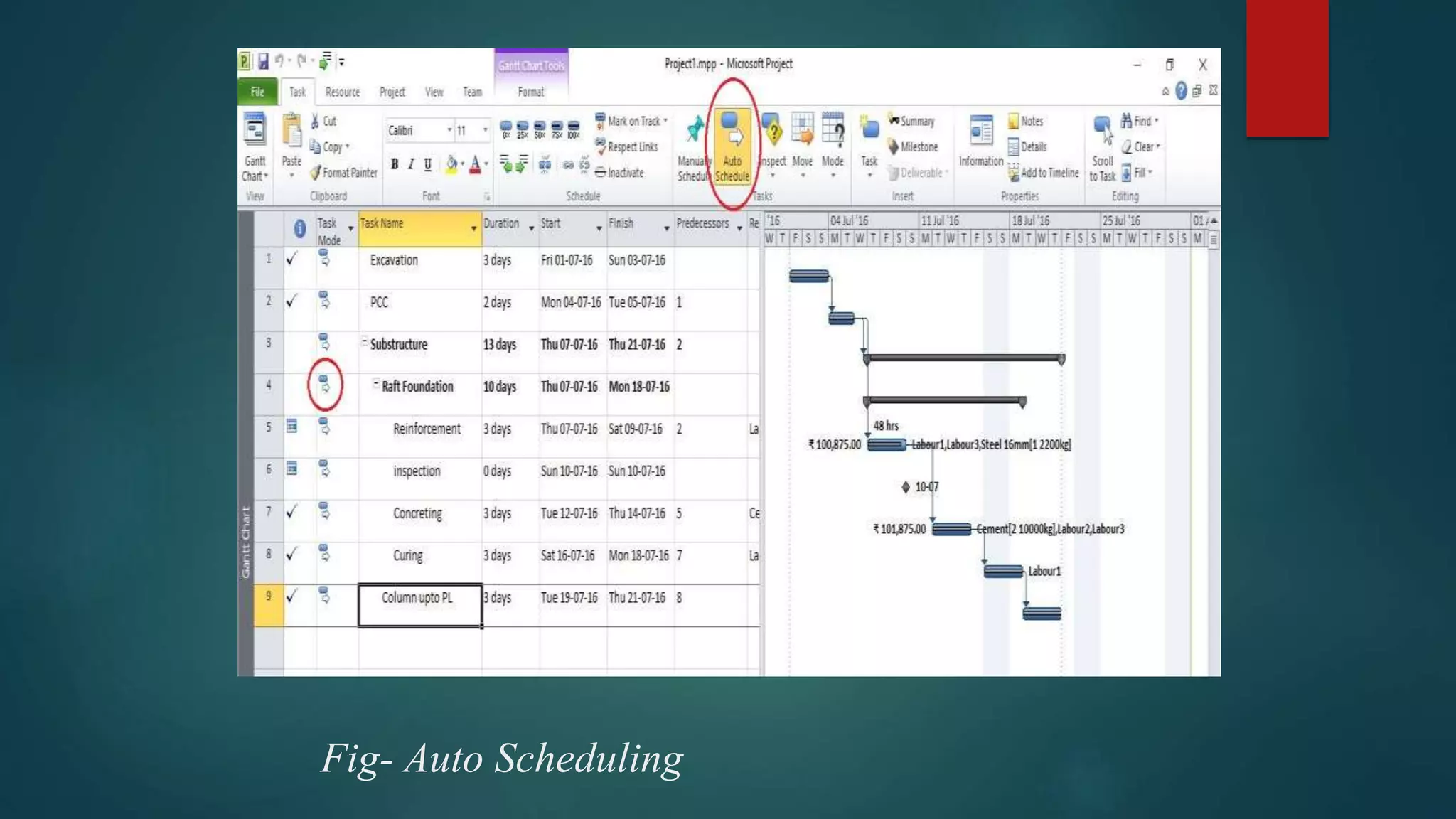
- How to create a new project schedule by entering tasks, durations, resources, and linking tasks.
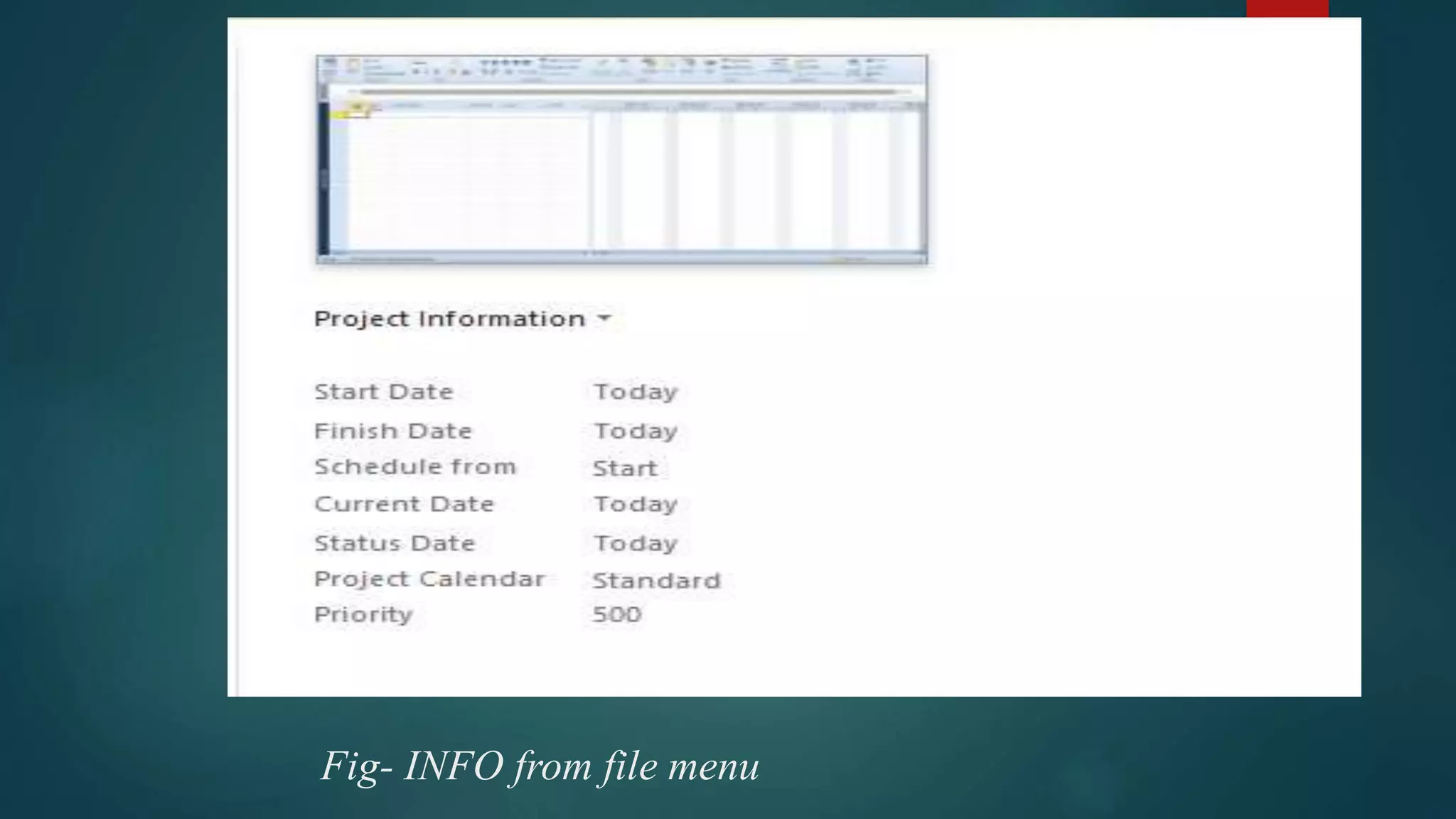
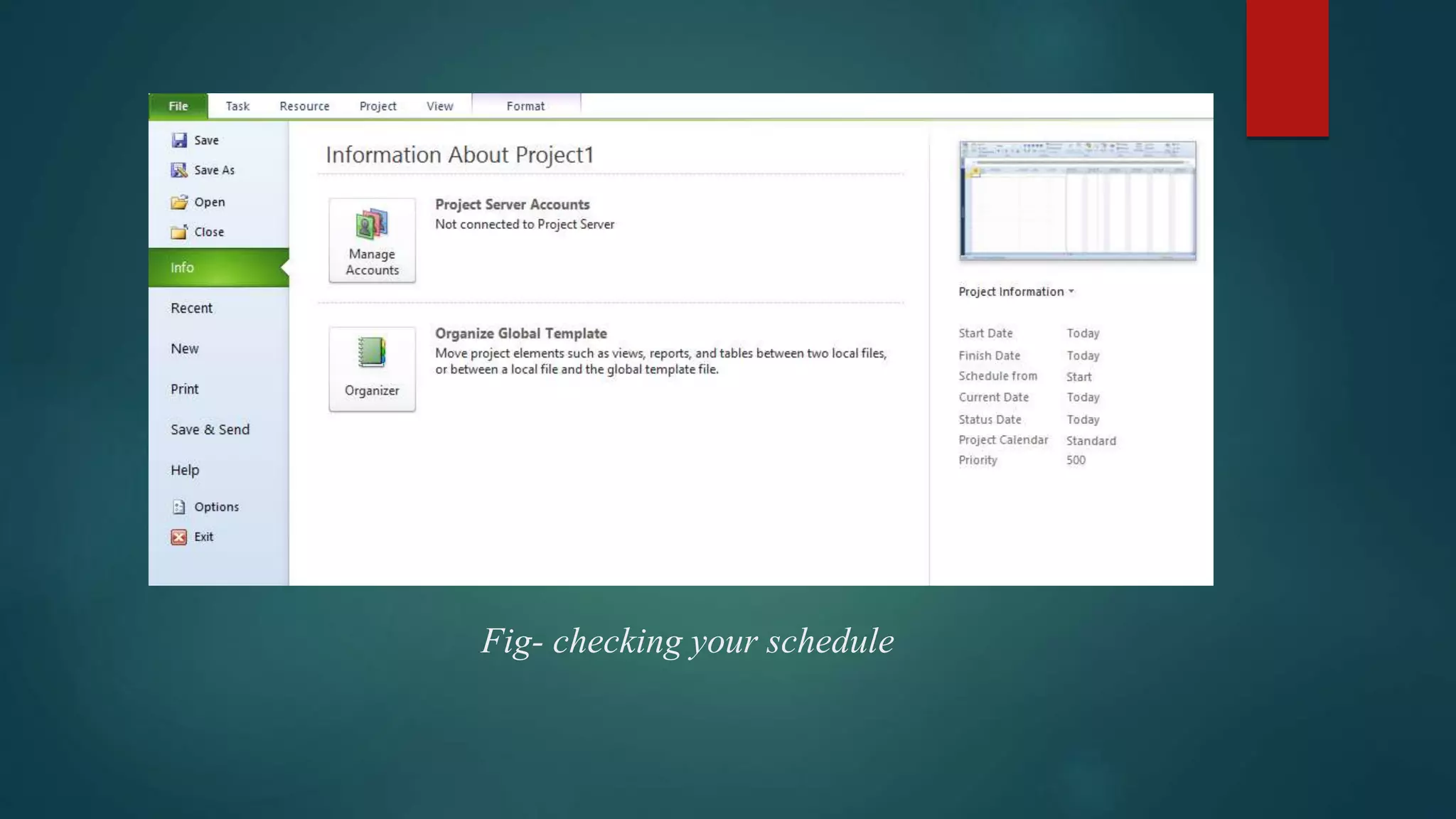
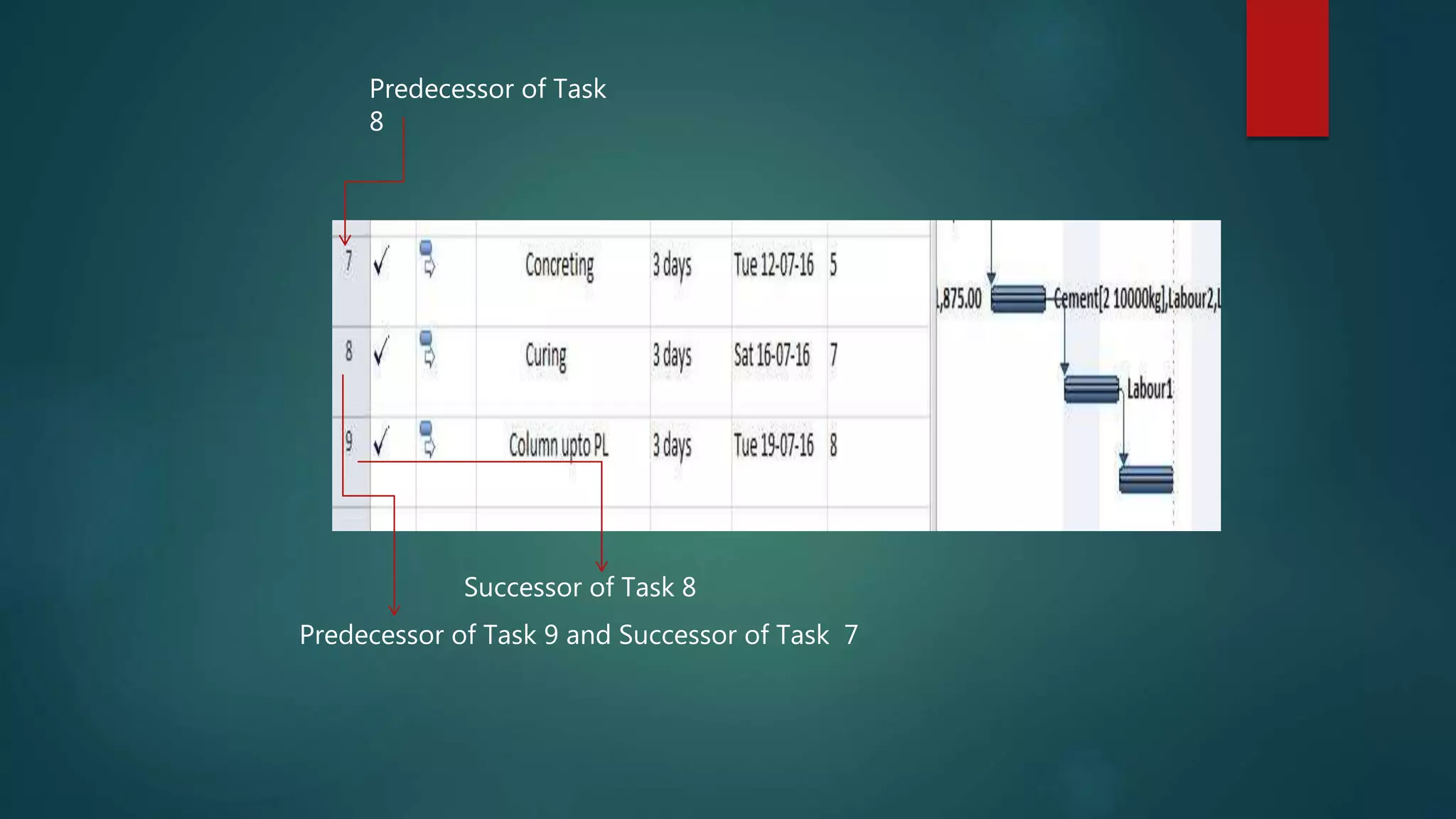
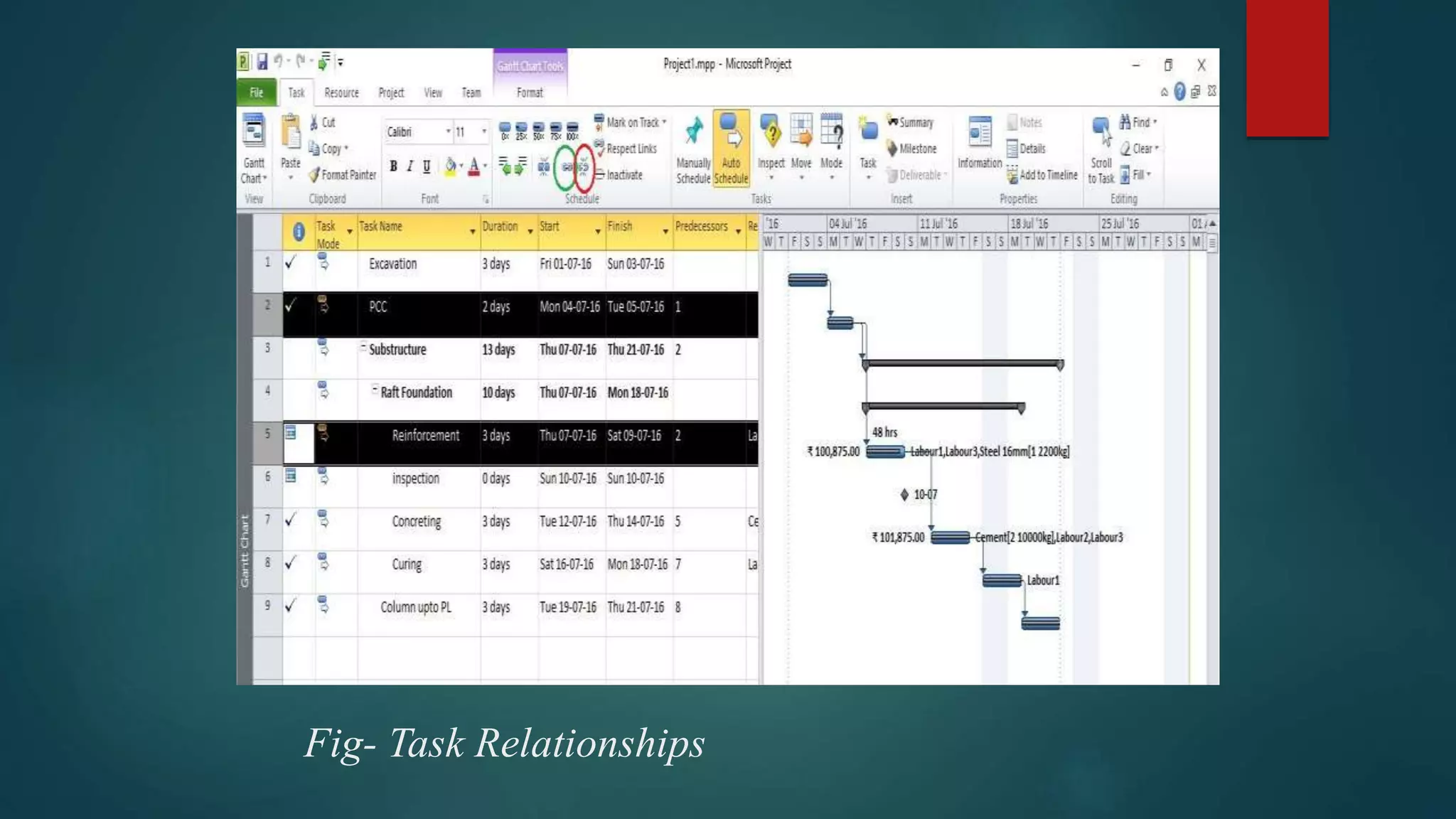
- How to evaluate a schedule by checking task relationships, identifying critical paths, examining slack times, and resolving issues like overallocated resources or high task costs.