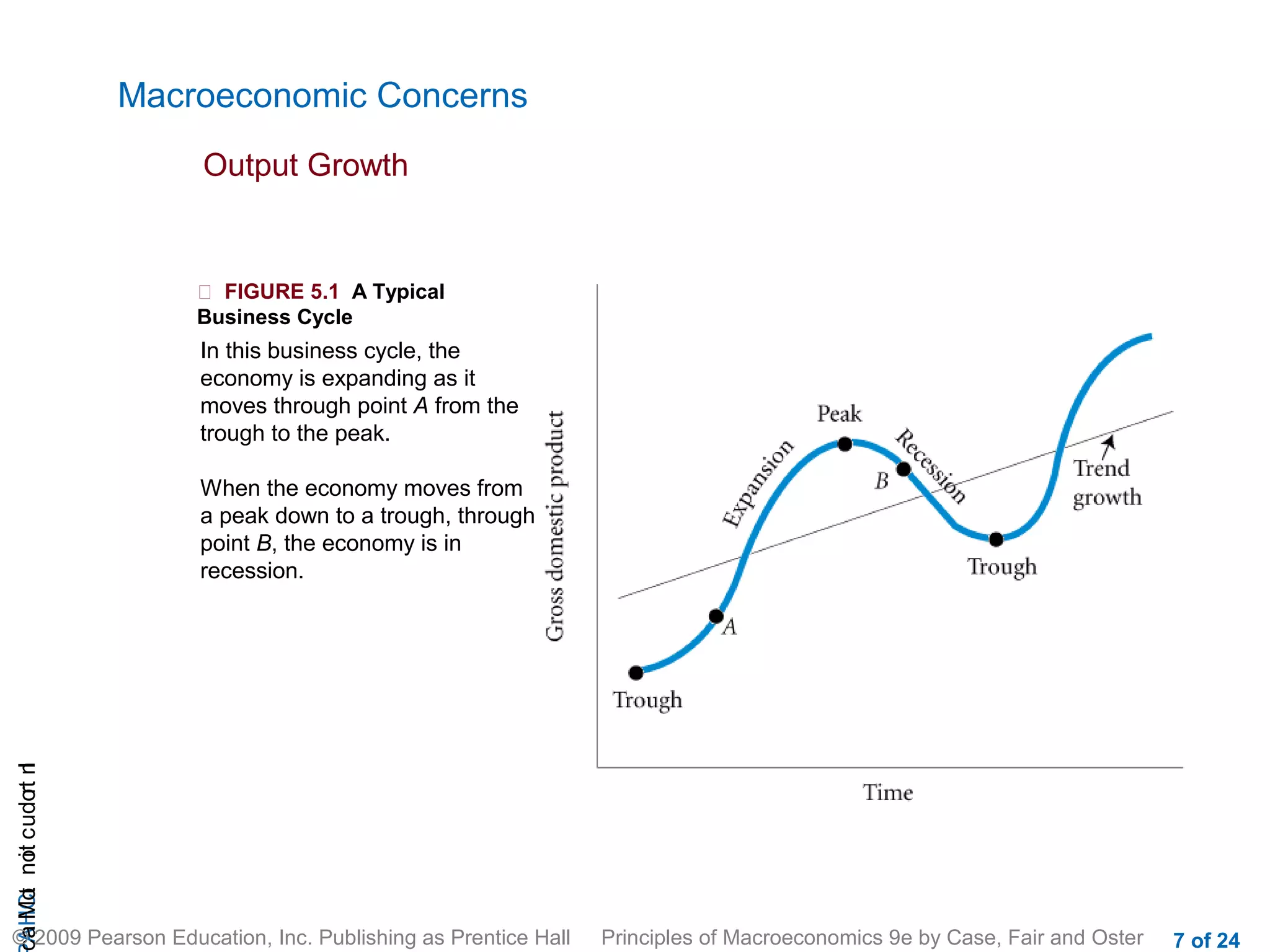
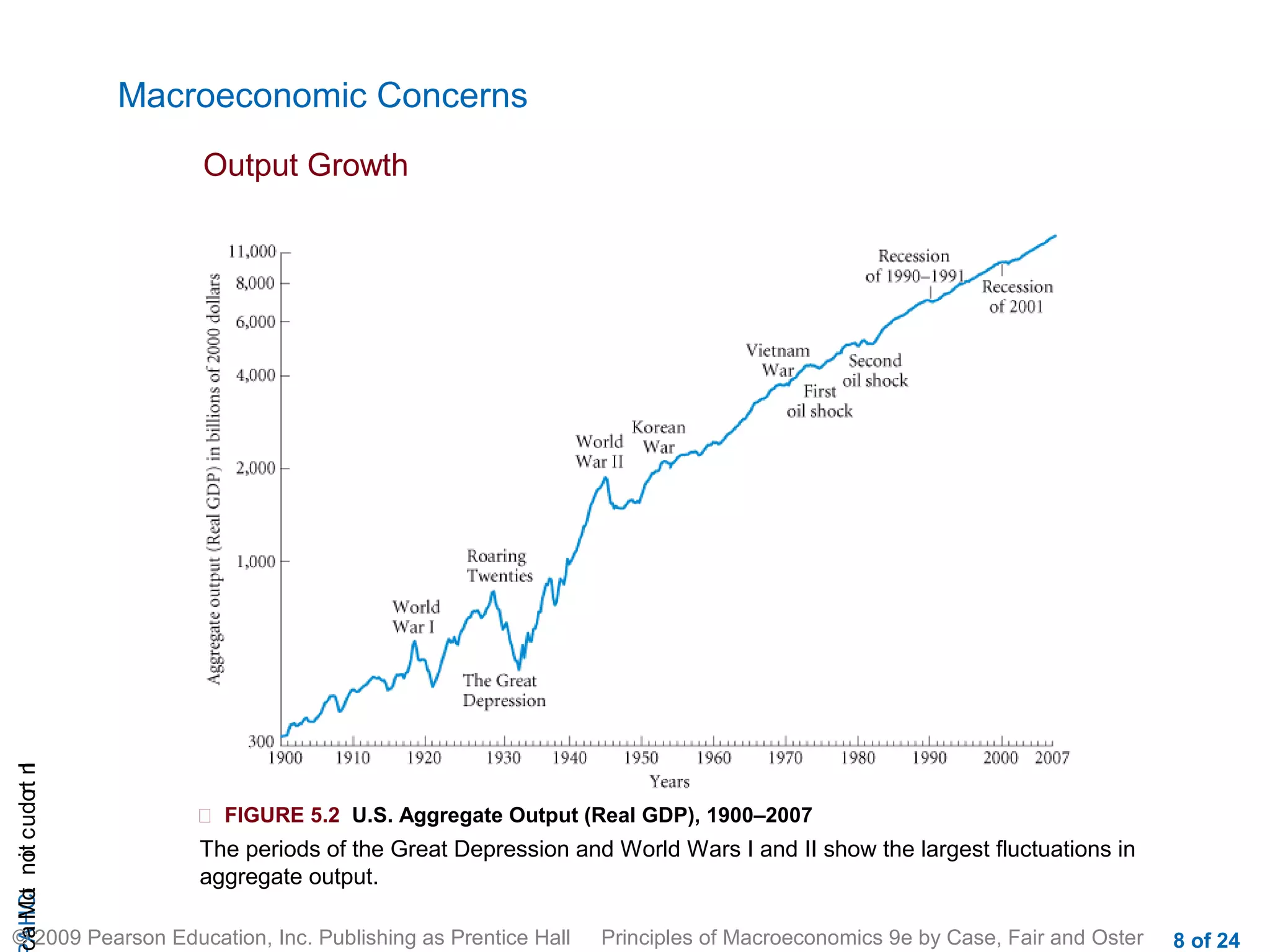
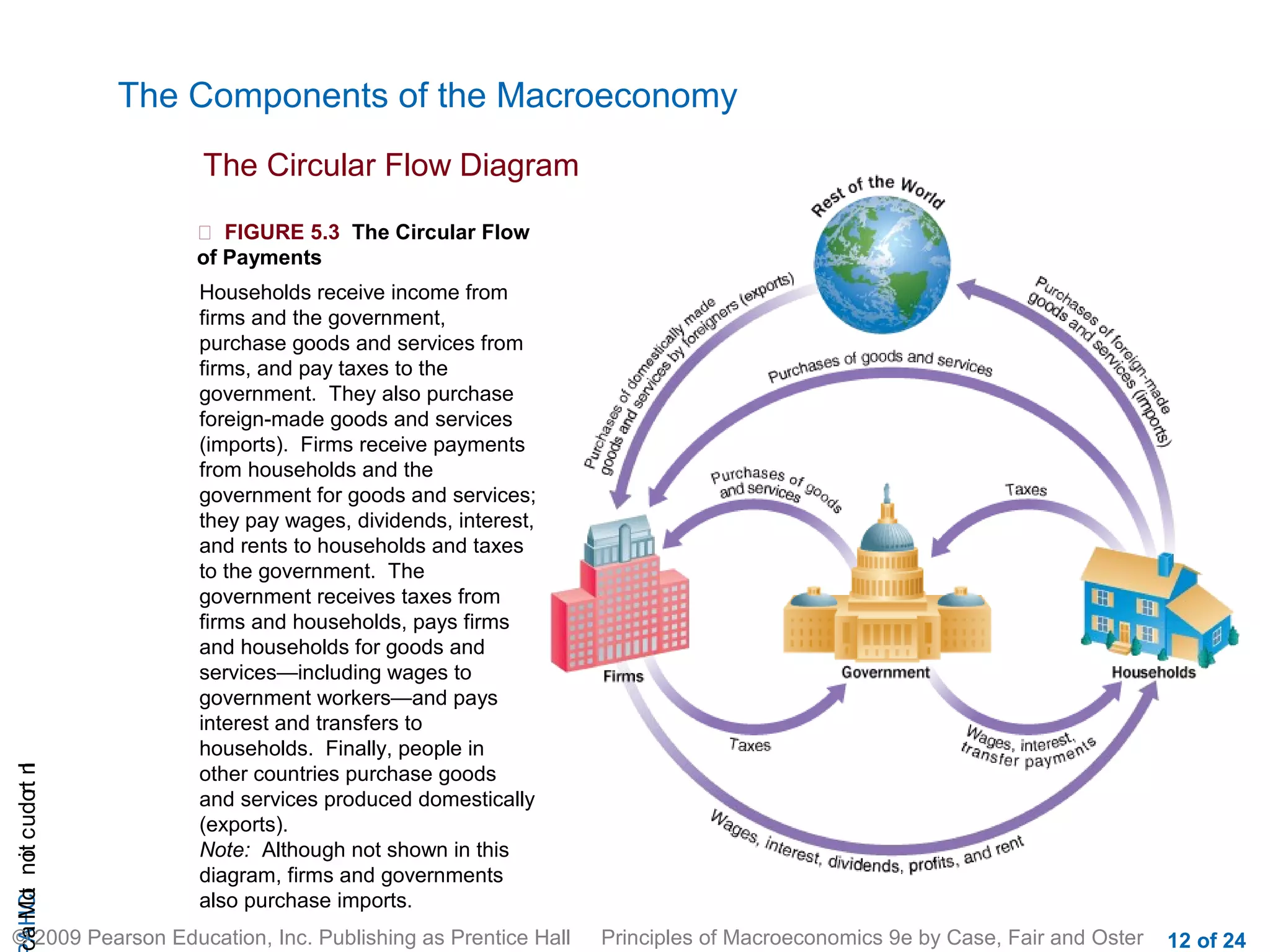
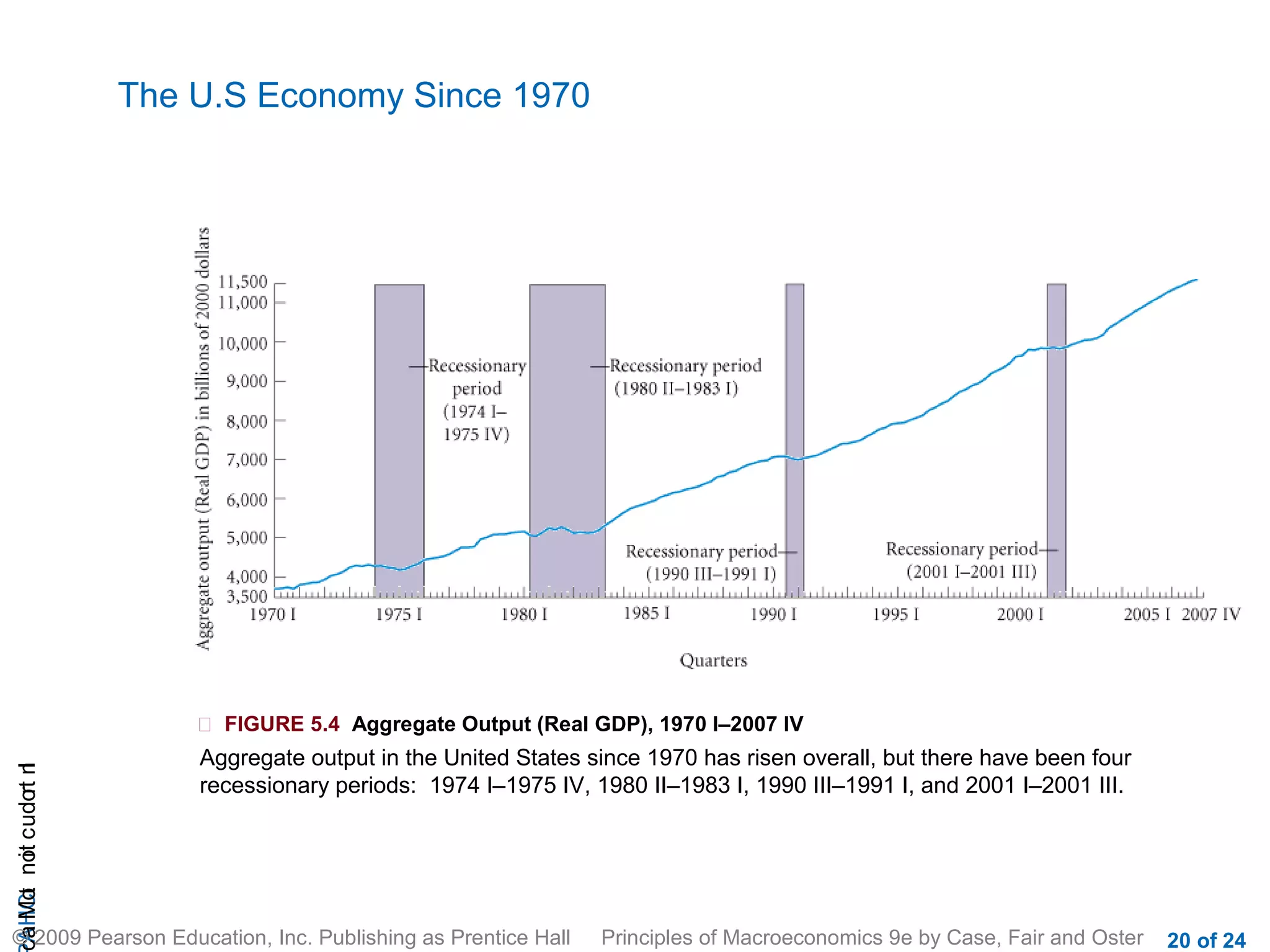
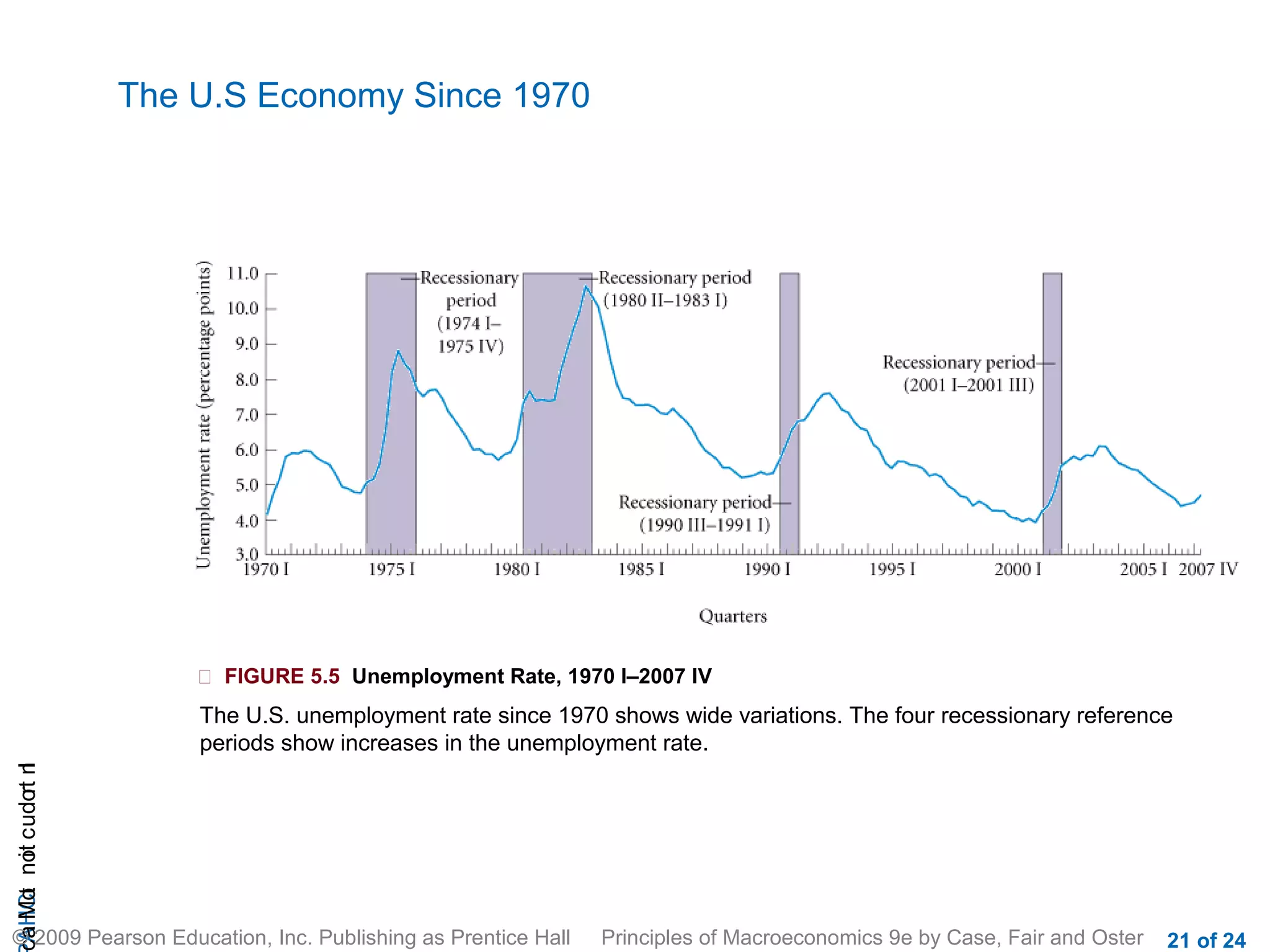
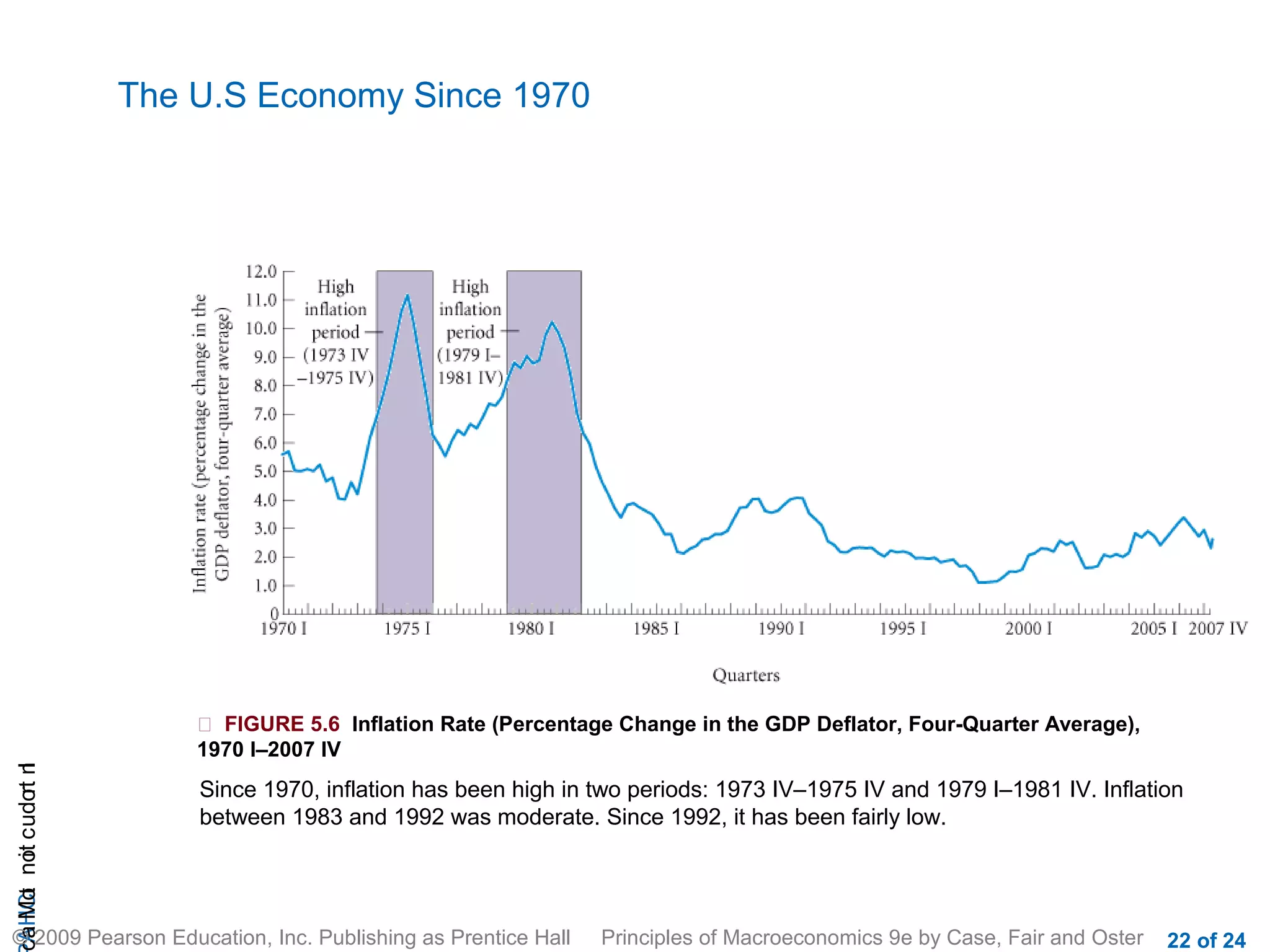
This document provides an introduction to macroeconomics, outlining some of its key concepts and components. It discusses how macroeconomics examines the economy as a whole by focusing on aggregates like total output and the overall price level, rather than individual markets. It identifies three main macroeconomic concerns: output growth, unemployment, and inflation/deflation. It also outlines the four main groups that make up the macroeconomy - households, firms, government, and the rest of the world - and illustrates their interactions through a circular flow diagram.