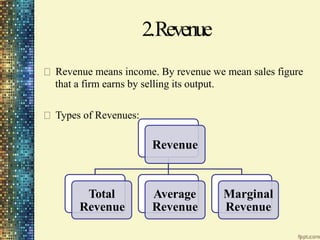
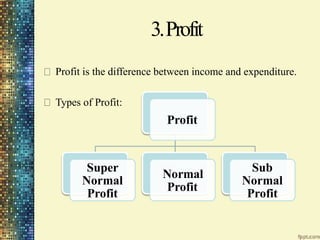
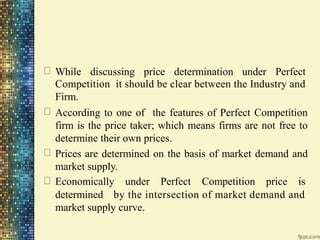
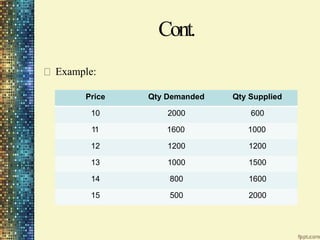
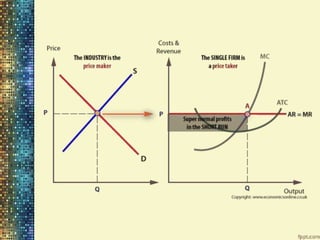
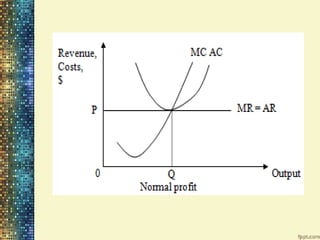
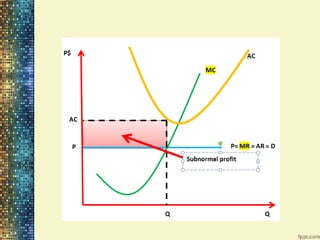
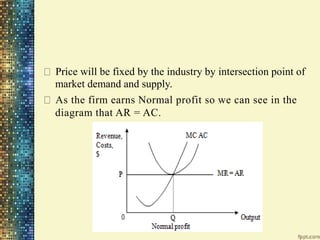
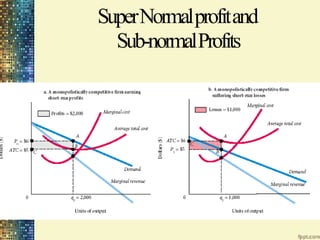
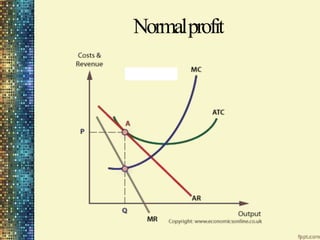
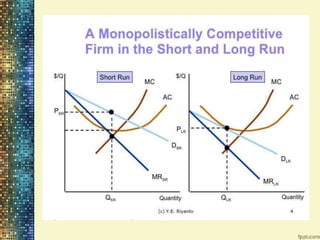
This document discusses different market structures and concepts related to price and output determination. It begins by defining key terms like market, revenue, profit, and price determination under perfect competition in both the short and long run. It then discusses monopoly markets in the short run and monopolistic competition. Monopolistic competition allows for some product differentiation and involves both price and non-price competition. The document notes firms under monopolistic competition will earn only normal profits in the long run as new firms enter if super normal profits exist or exit if sub normal profits exist. It concludes by defining oligopoly as a market with a few large firms making interdependent decisions.
















![Cont.
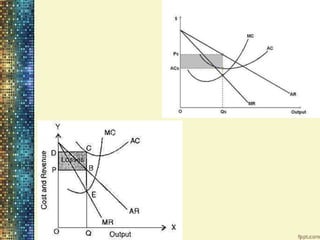
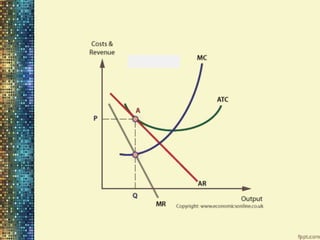
Features of Monopolistic Market:
Large no. of sellers
Large no. of buyers
Production differentiation
Free entry and exit
Price and Non-price competition [variation, advts.,
promotion]
The group
Two dimensional competition [price and non-price]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/priceandoutputdetermination-220911143157-4cf48db8/85/Price-and-Output-Determination-pptx-27-320.jpg)




![Features:
Small no. of large sellers
Interdependence
Price Rigidity [reducing or increasing price]
Presence of monopoly element
Advertising](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/priceandoutputdetermination-220911143157-4cf48db8/85/Price-and-Output-Determination-pptx-35-320.jpg)