This document discusses three concepts related to international trade:
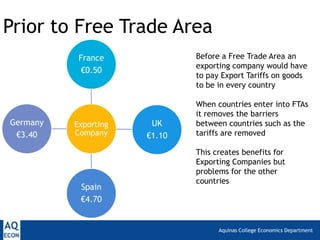
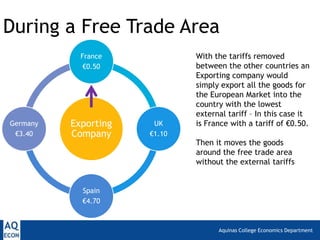
1. Trade deflection, which occurs when exporters divert goods through the country with the lowest external tariffs in a free trade area. This can harm other countries. Rules of origin help address this issue.
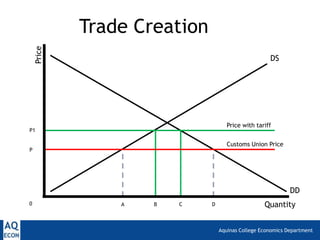
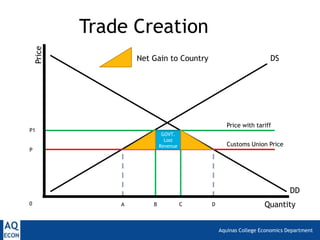
2. Trade creation, which happens when tariff removal in a customs union expands the domestic tariff-free market, benefiting consumers.
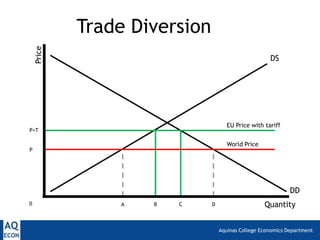
3. Trade diversion, which is a potential problem if countries must pay more due to a common external tariff, subsidizing inefficient industries and preventing imports from lower-cost partners outside the trade bloc.