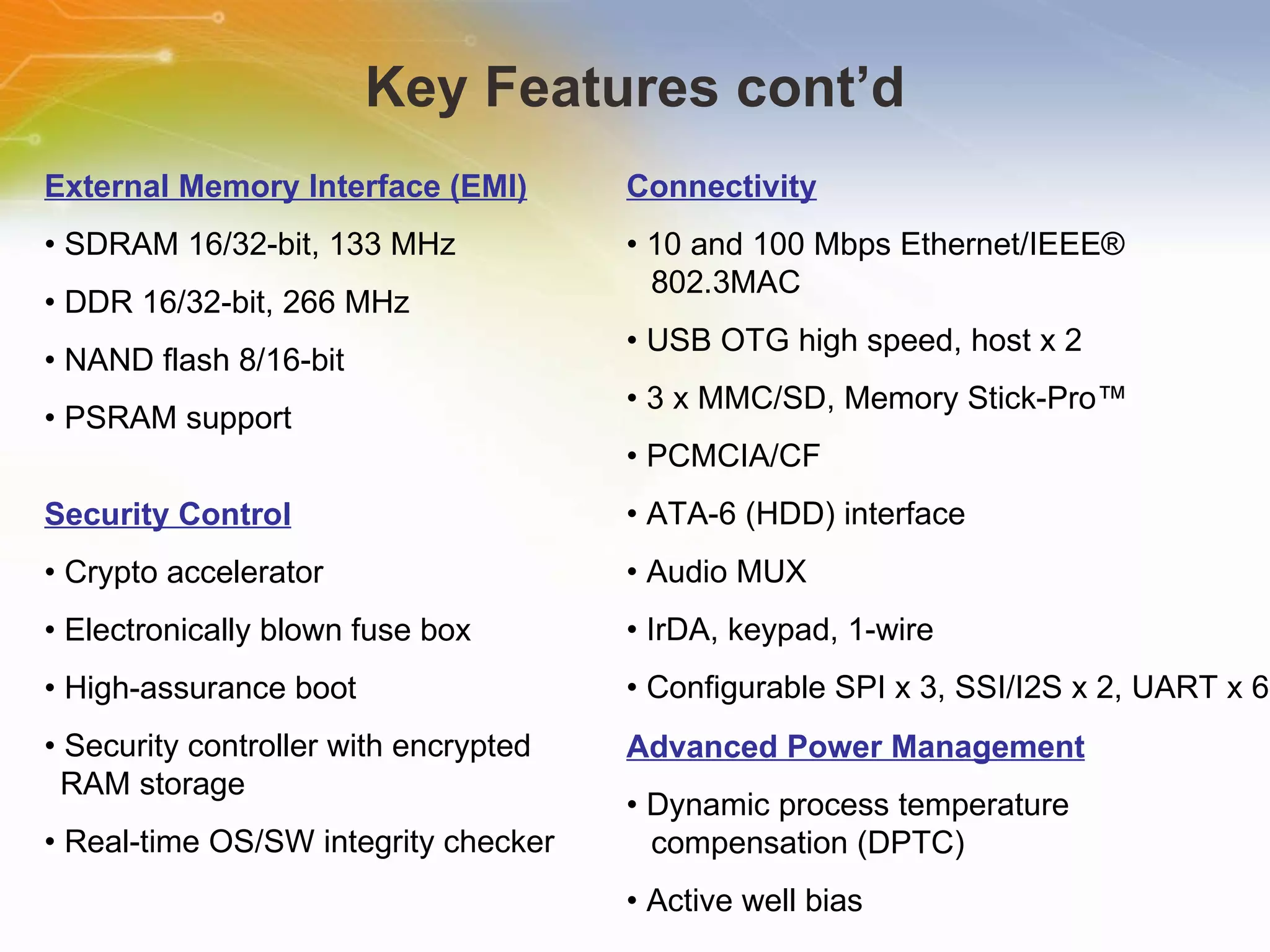
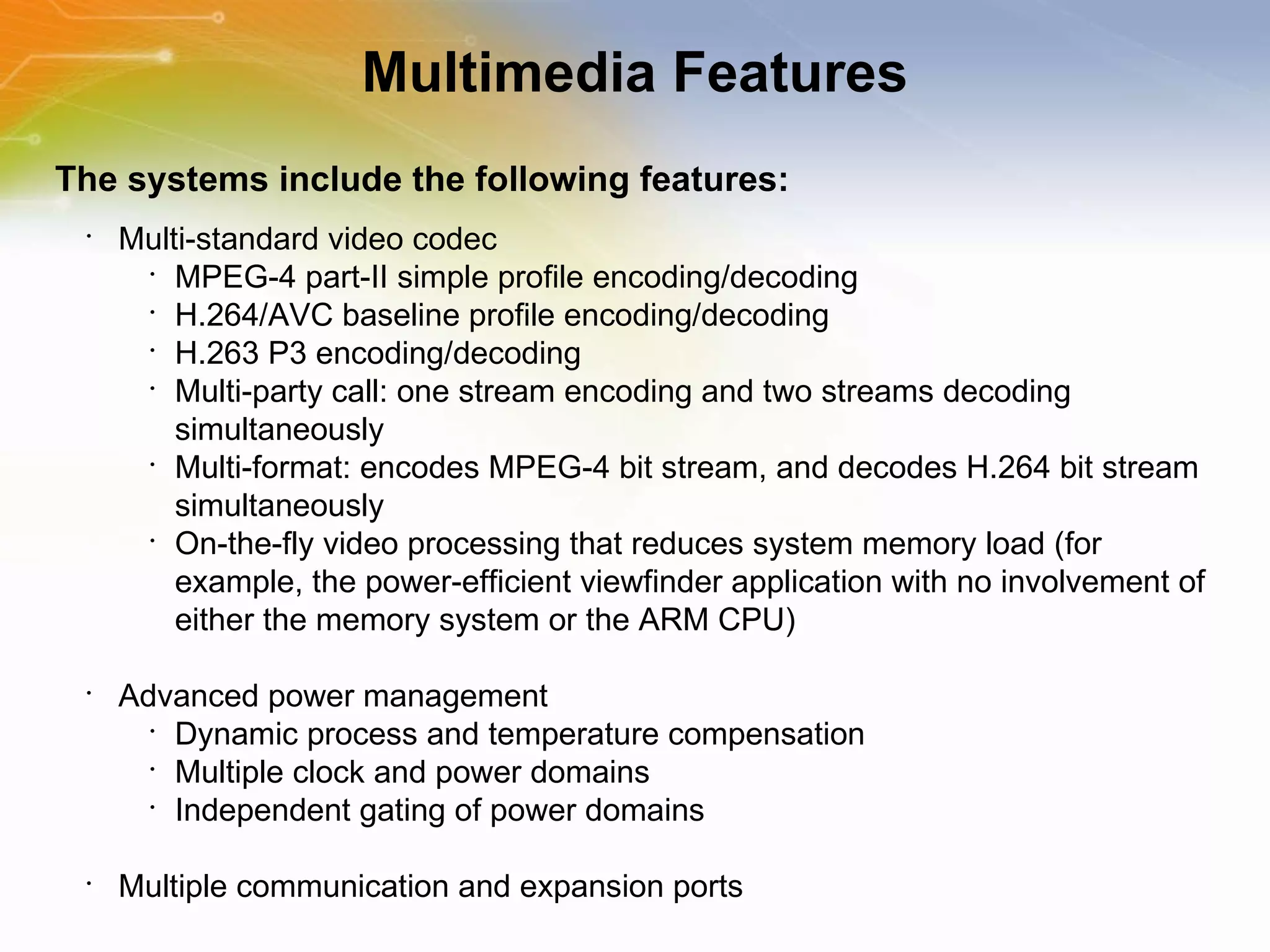
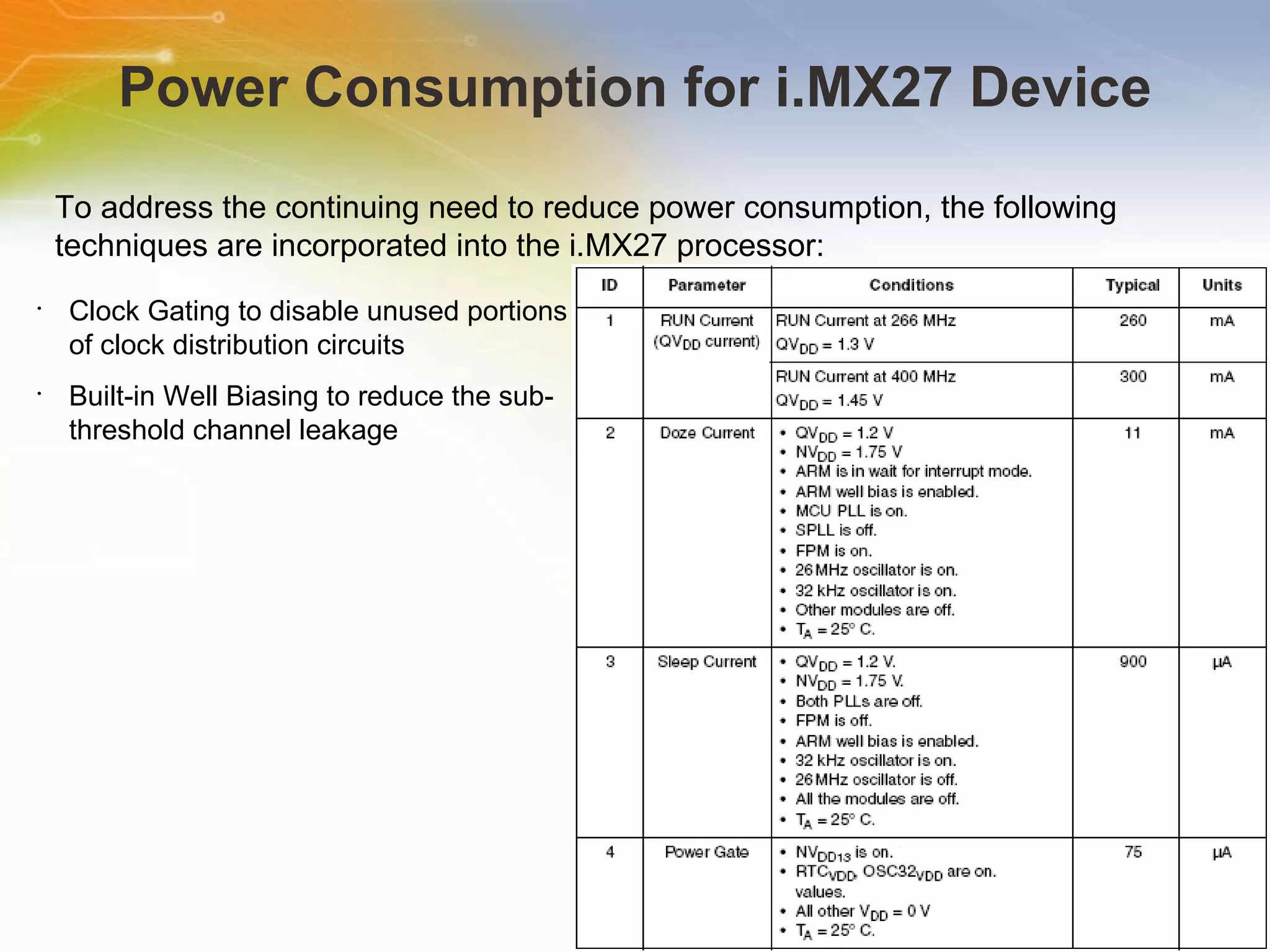
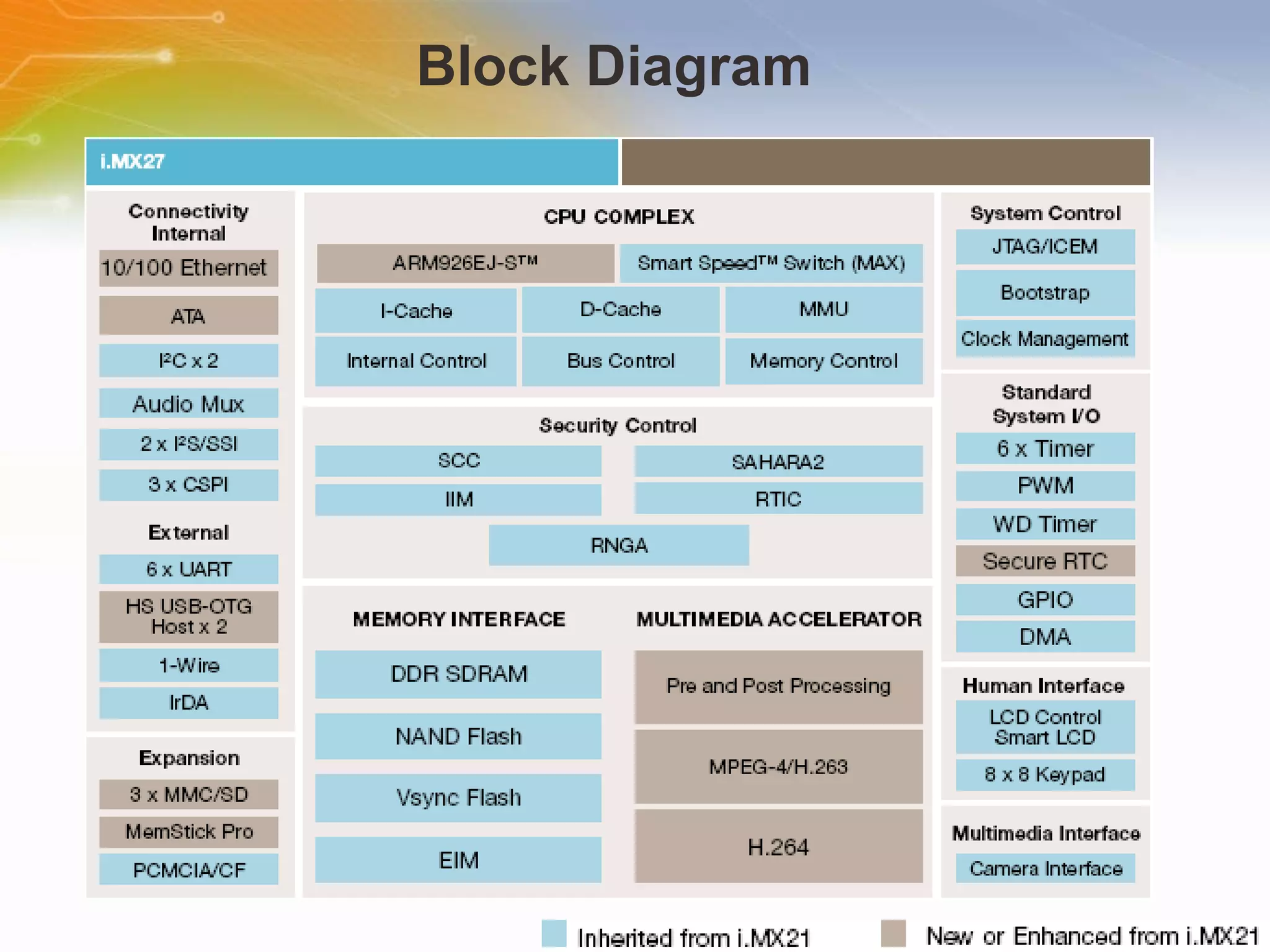
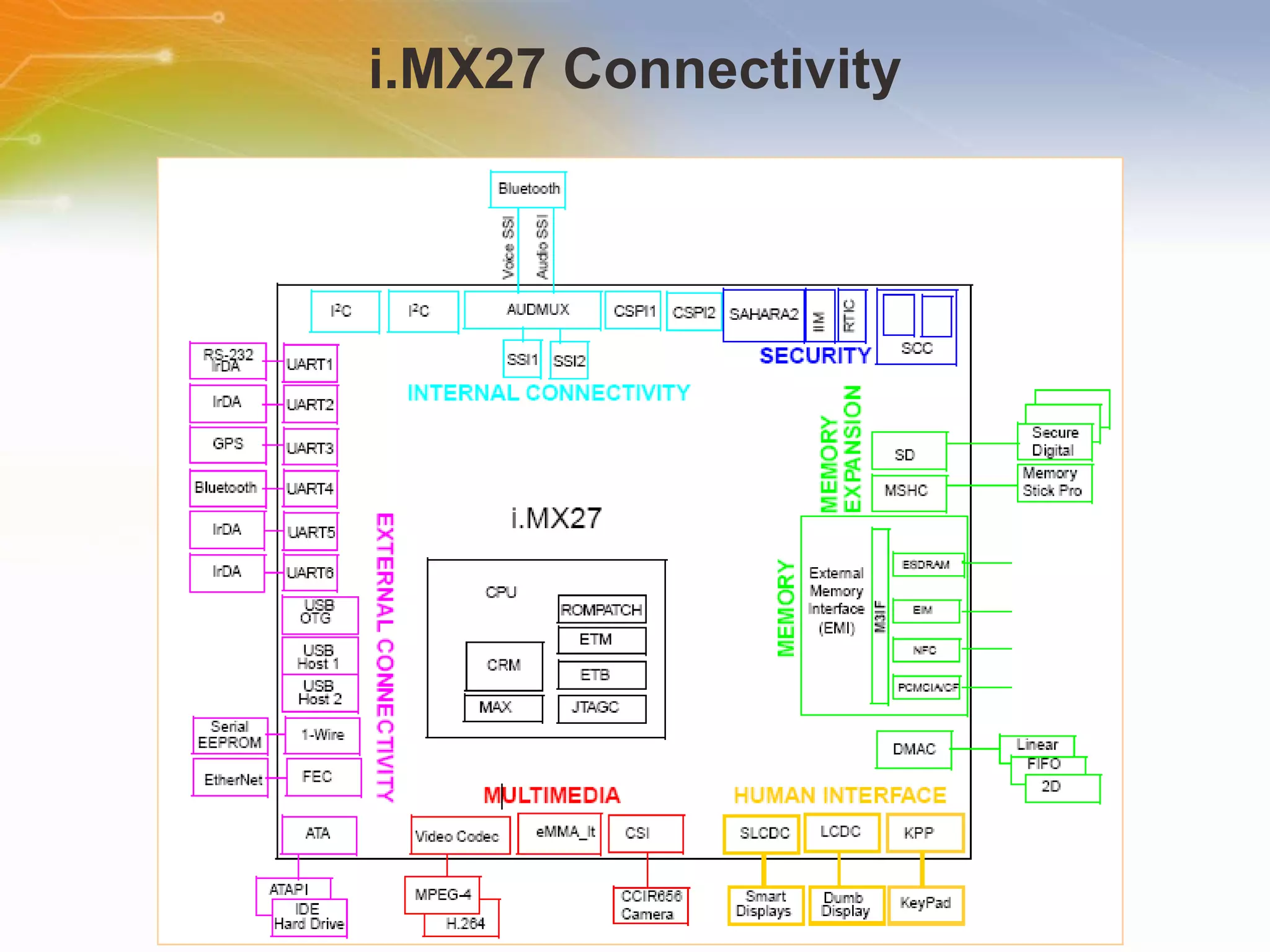
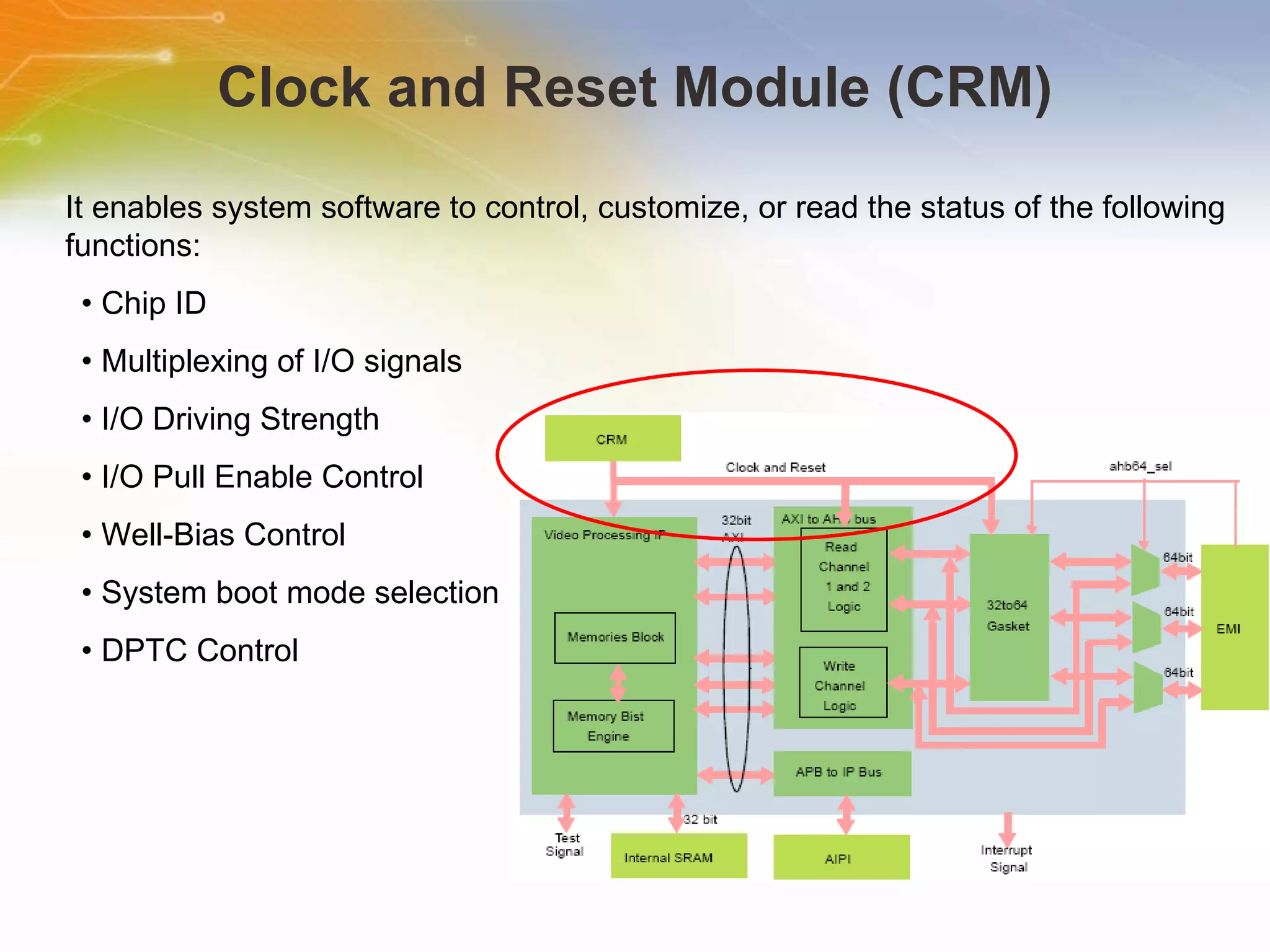
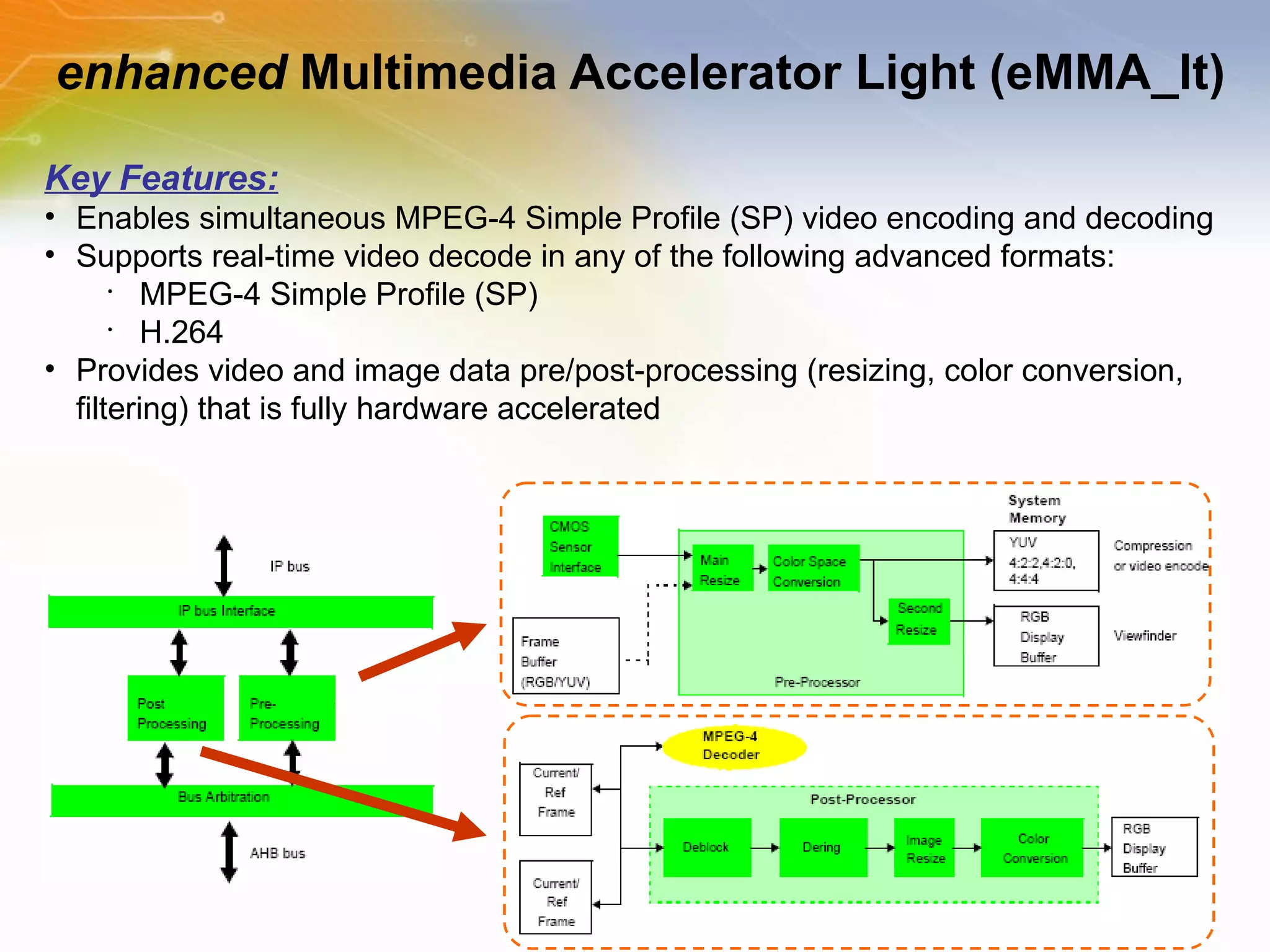
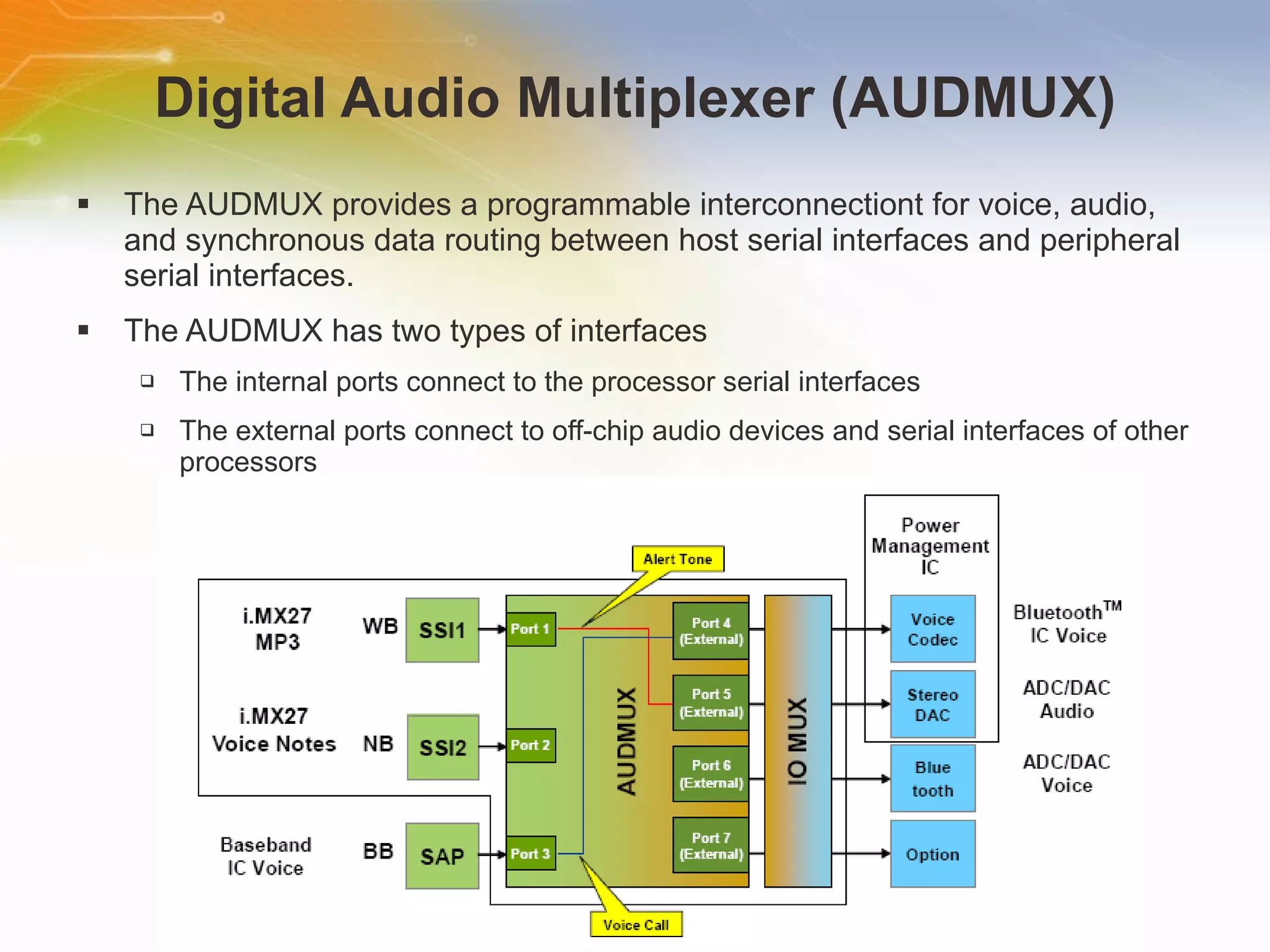
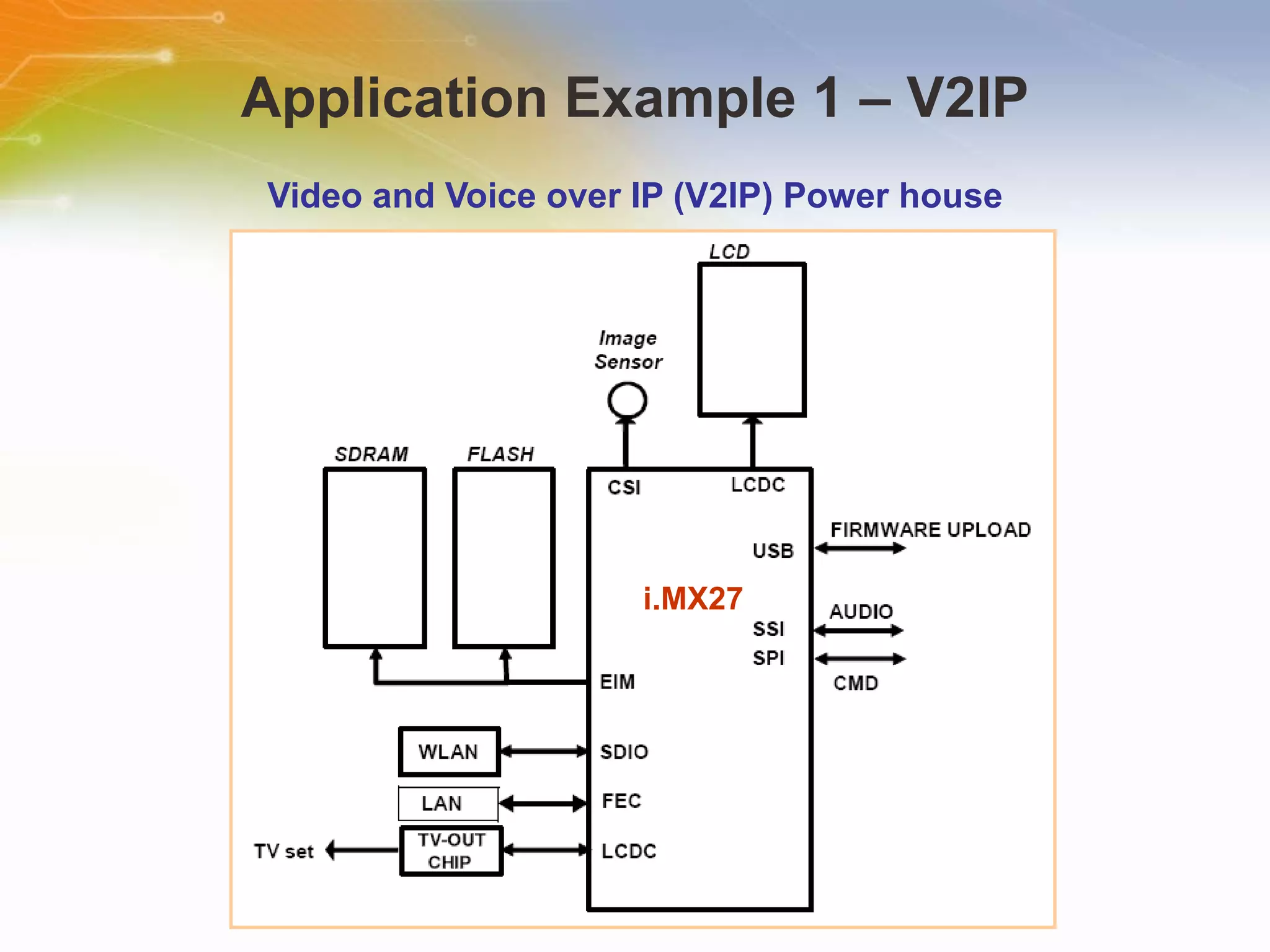
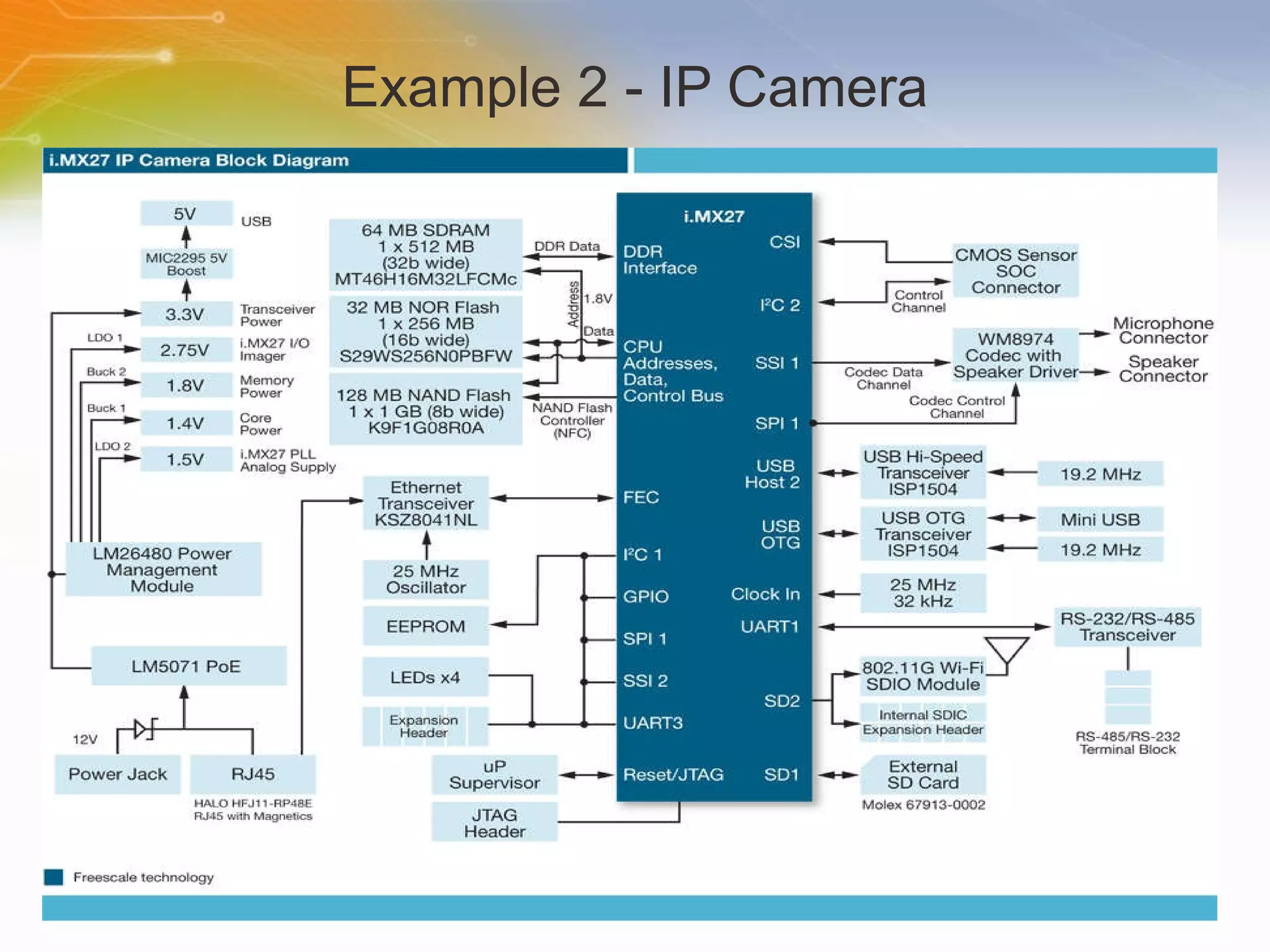
The document provides an overview of the i.MX27 Multimedia Applications Processor from Freescale. It describes the processor's key features such as its ARM926EJ-S 400MHz core, multimedia capabilities including video encoding/decoding, and connectivity options. Application examples using the processor for video and voice over IP and IP cameras are also mentioned.