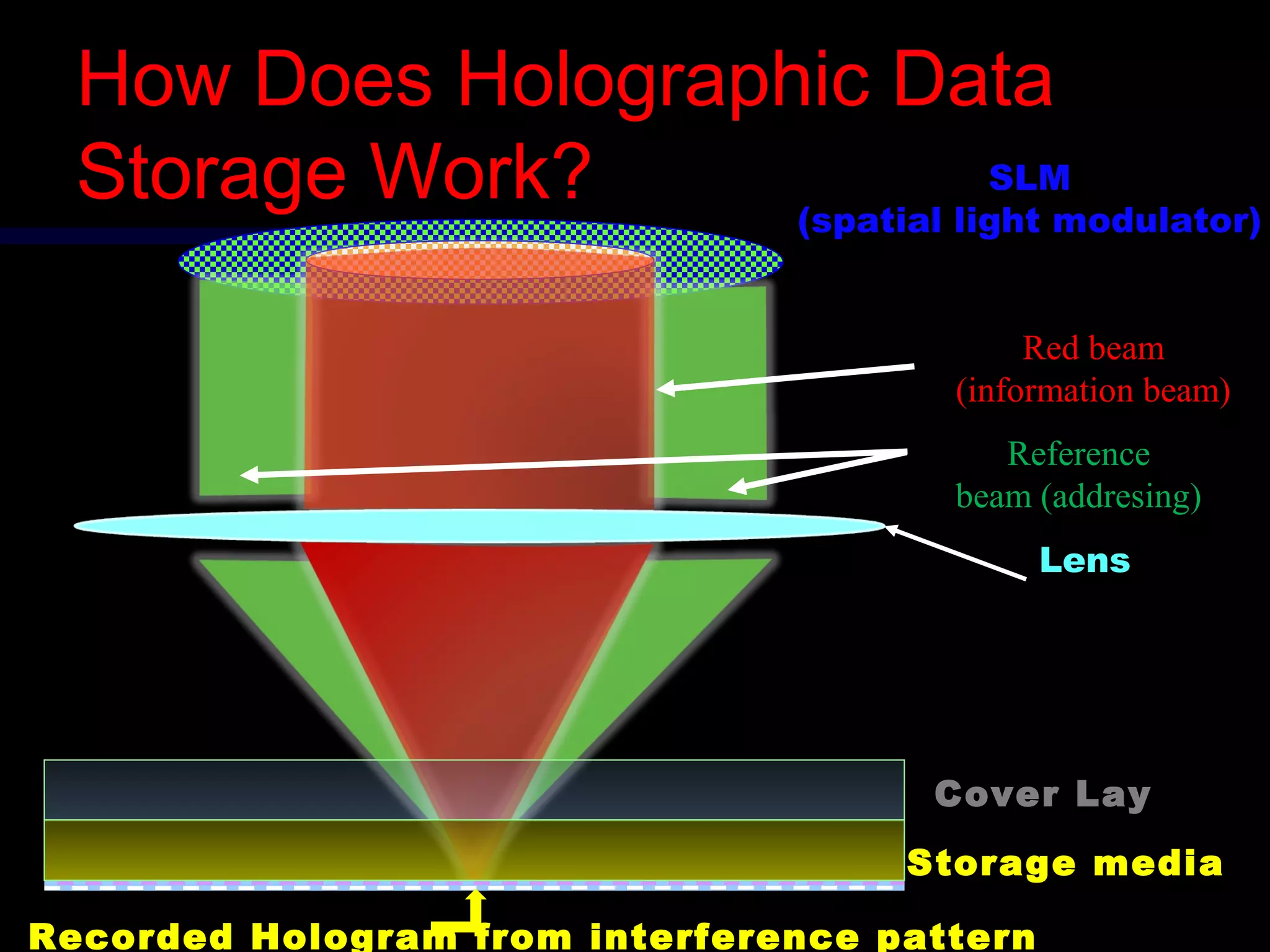
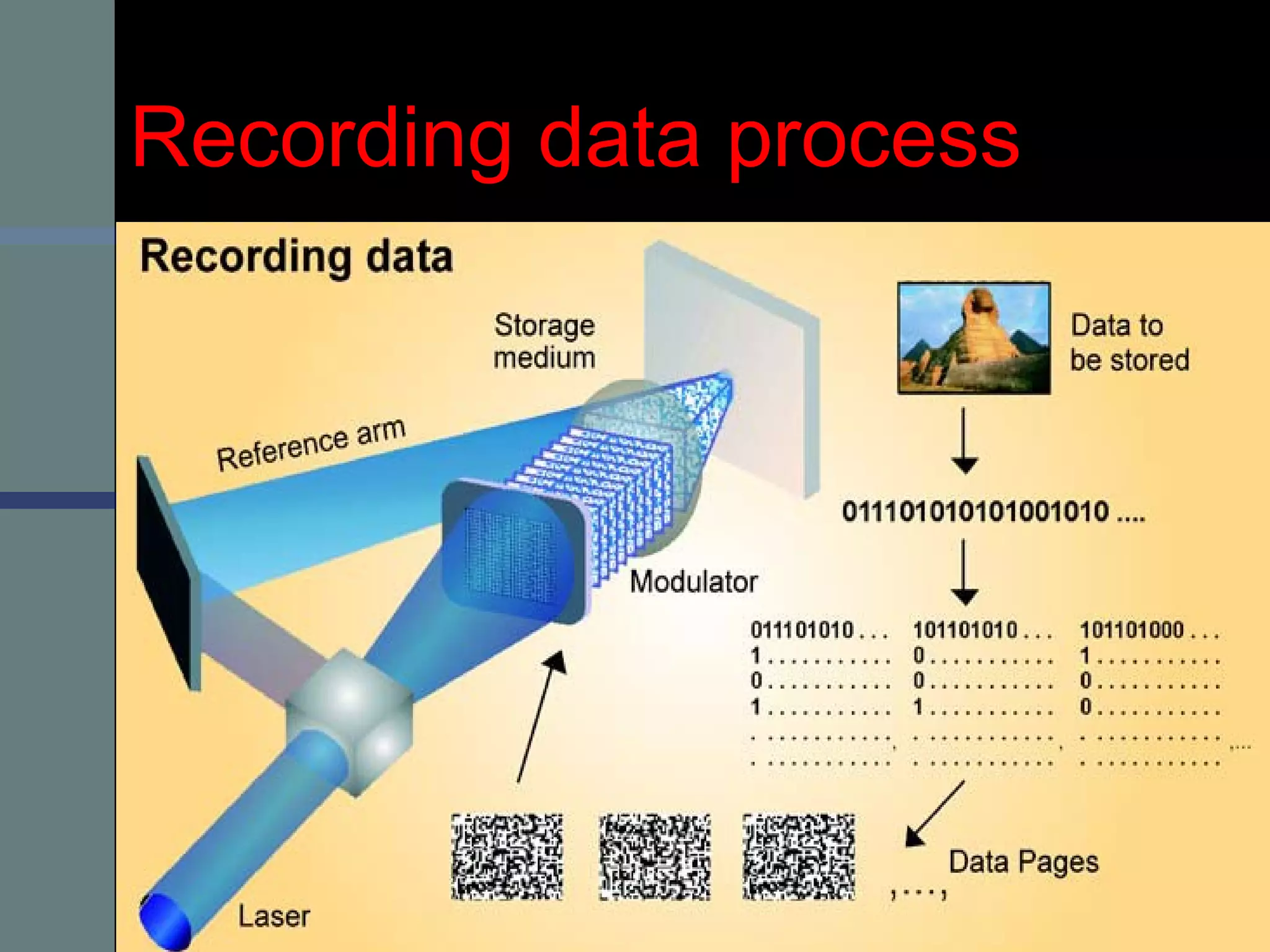
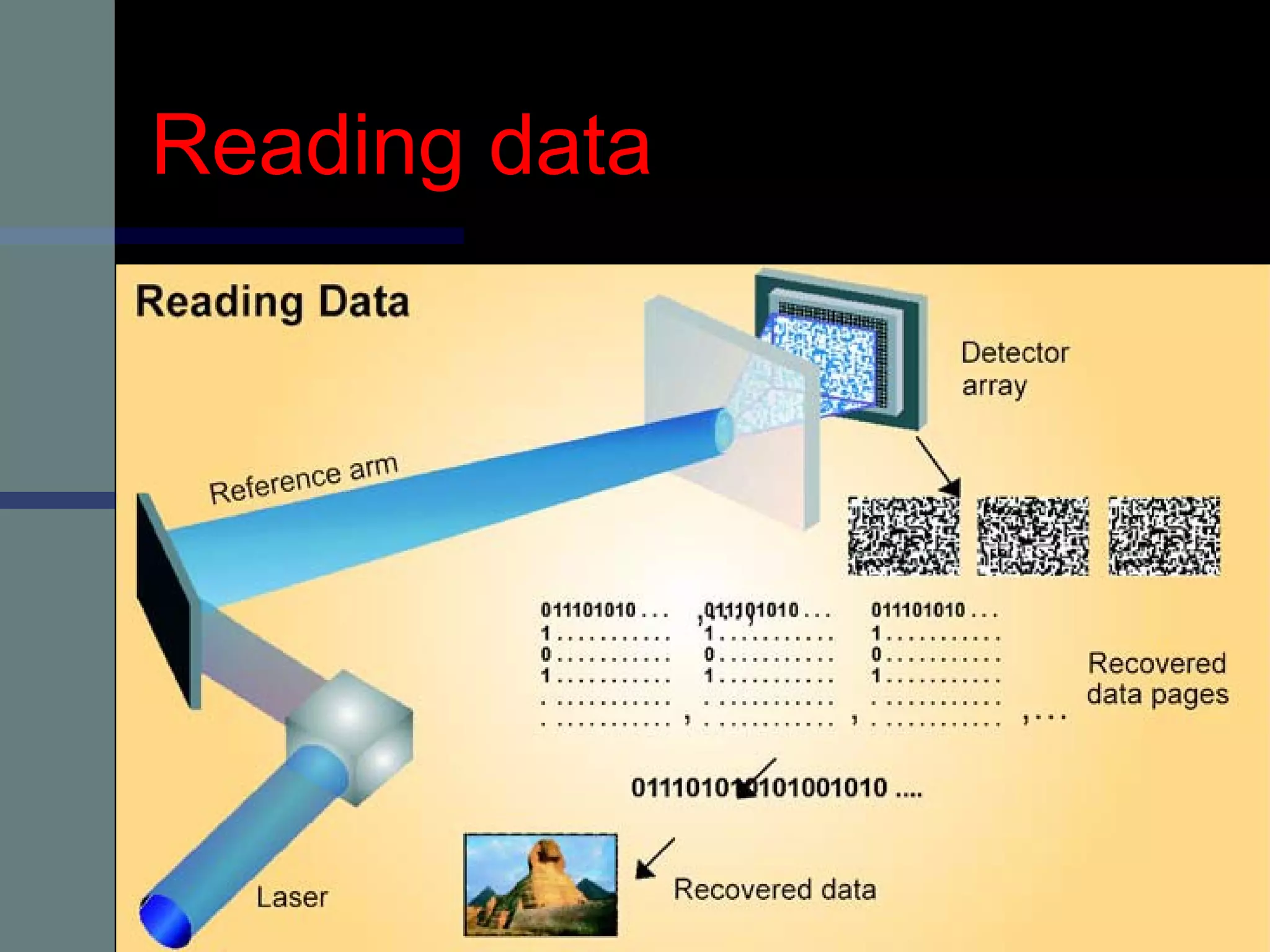
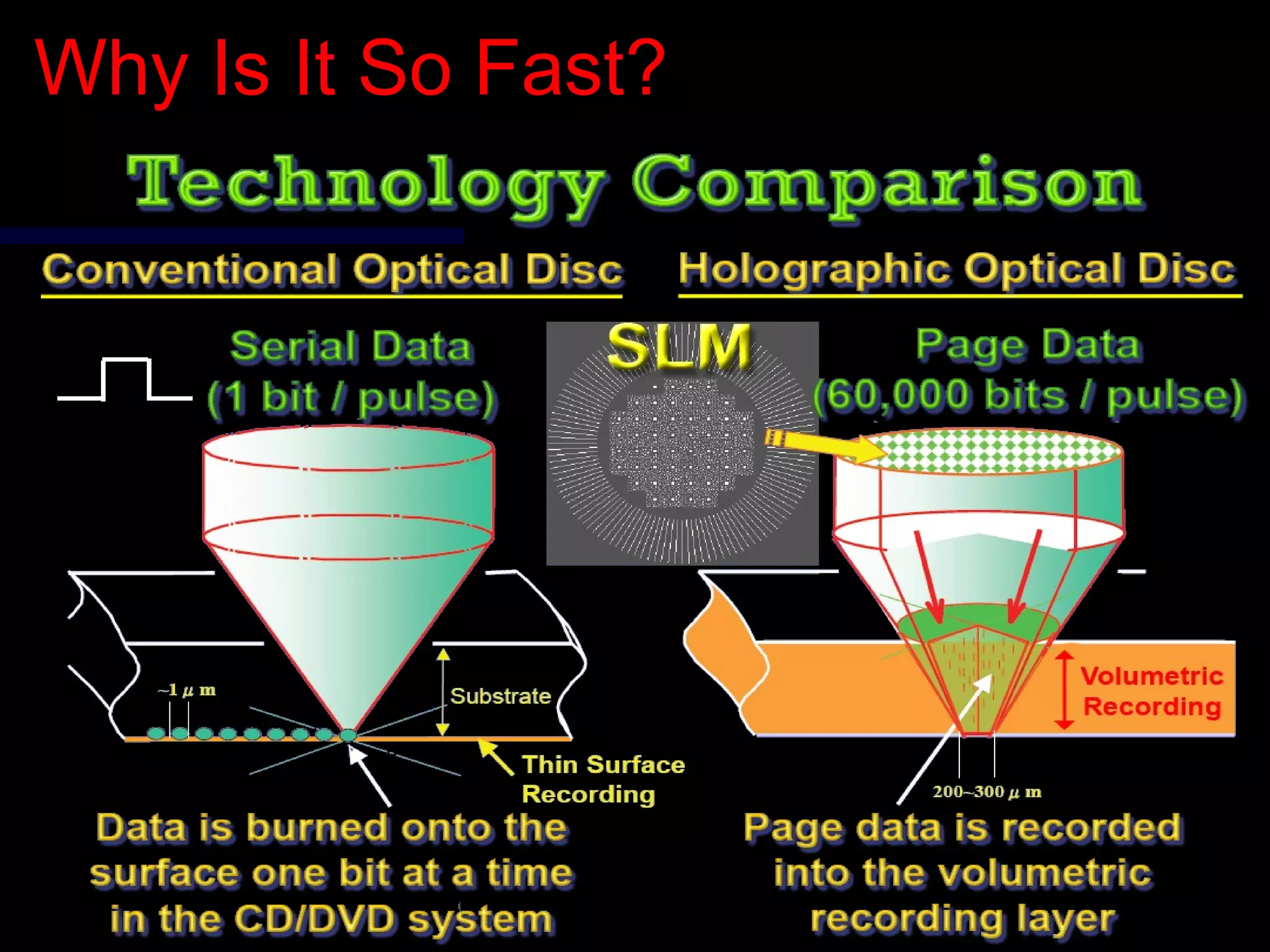
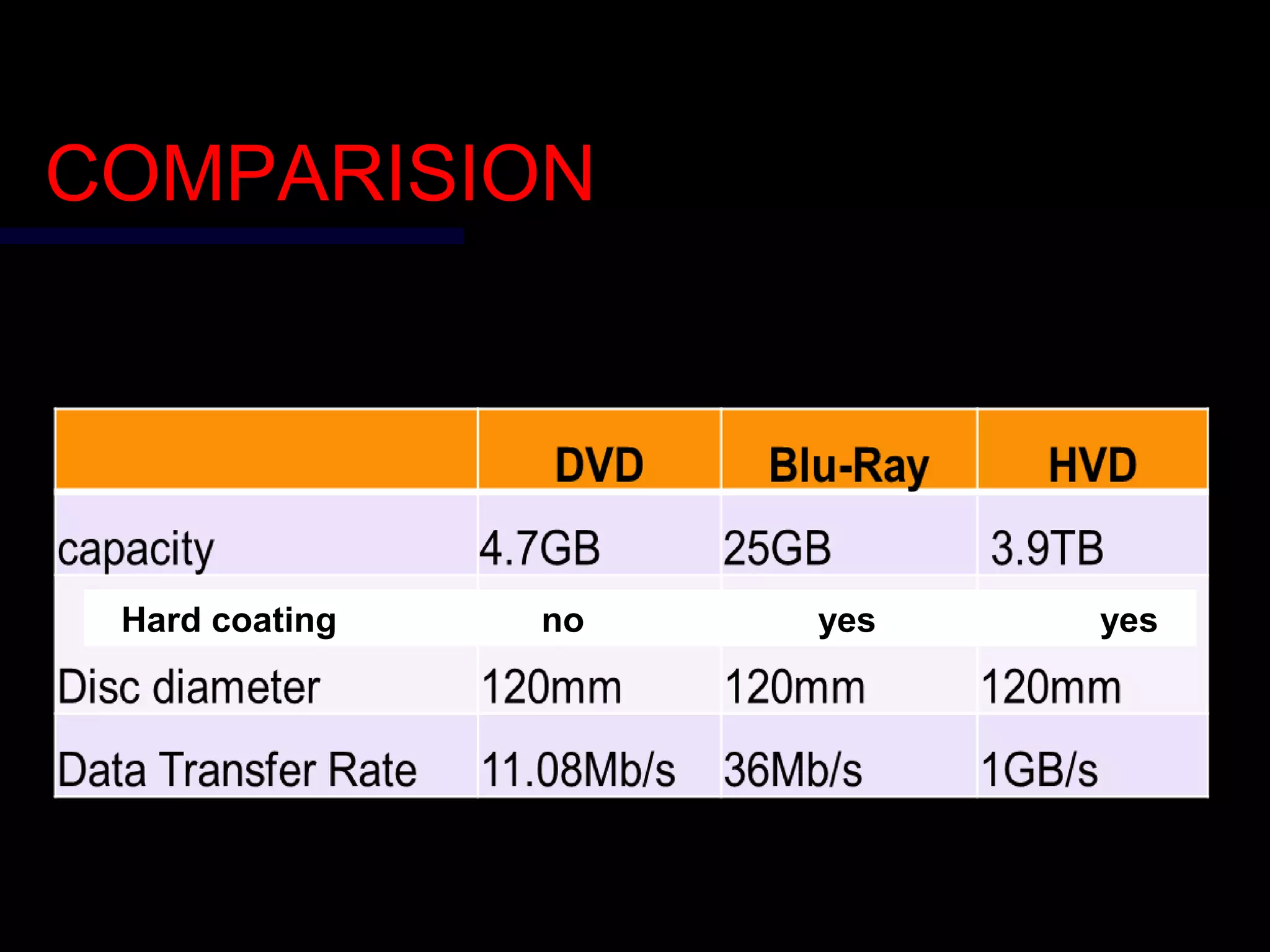
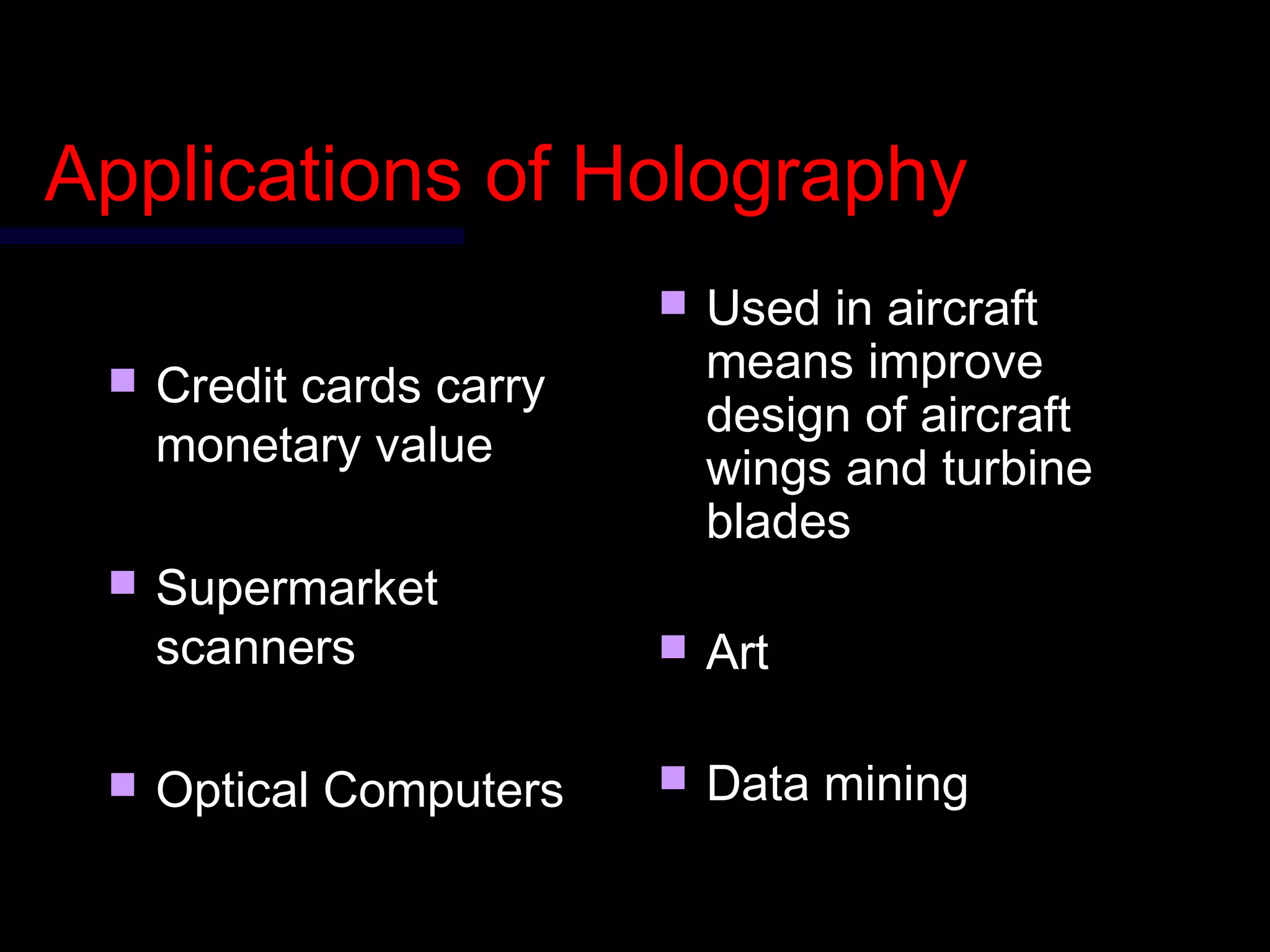
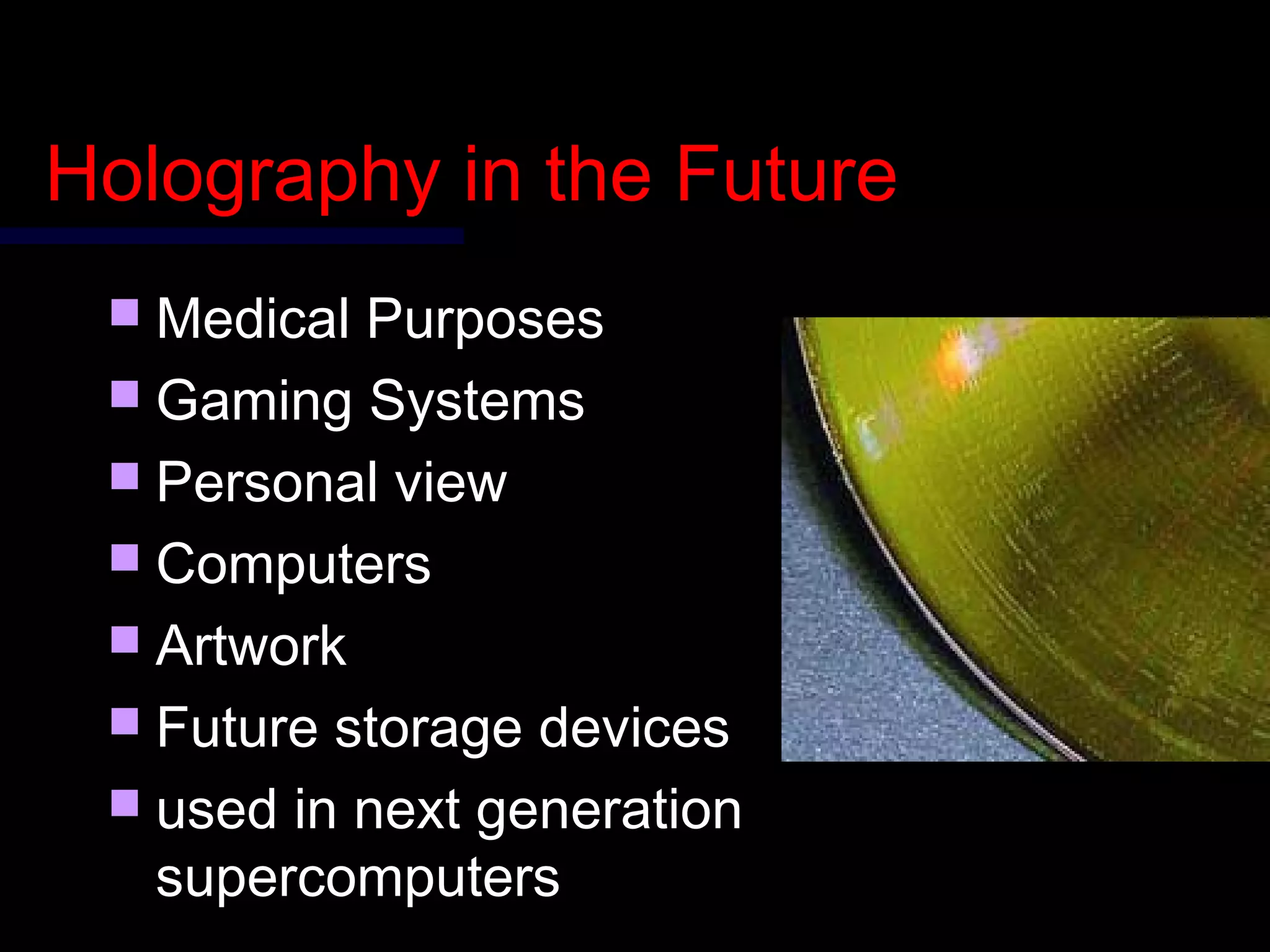
This document provides an introduction to holography and holographic data storage. Holography was developed in 1947 by Dennis Gabor and involves recording interference patterns of light to reproduce a 3D object. Holographic data storage uses a reference beam and information beam to record data as an interference pattern in a storage medium, allowing the data to be read quickly using only the reference beam. Holographic data storage offers significantly higher storage capacity than technologies like CDs and DVDs, with the potential to store 3.9 terabytes in a single disk.