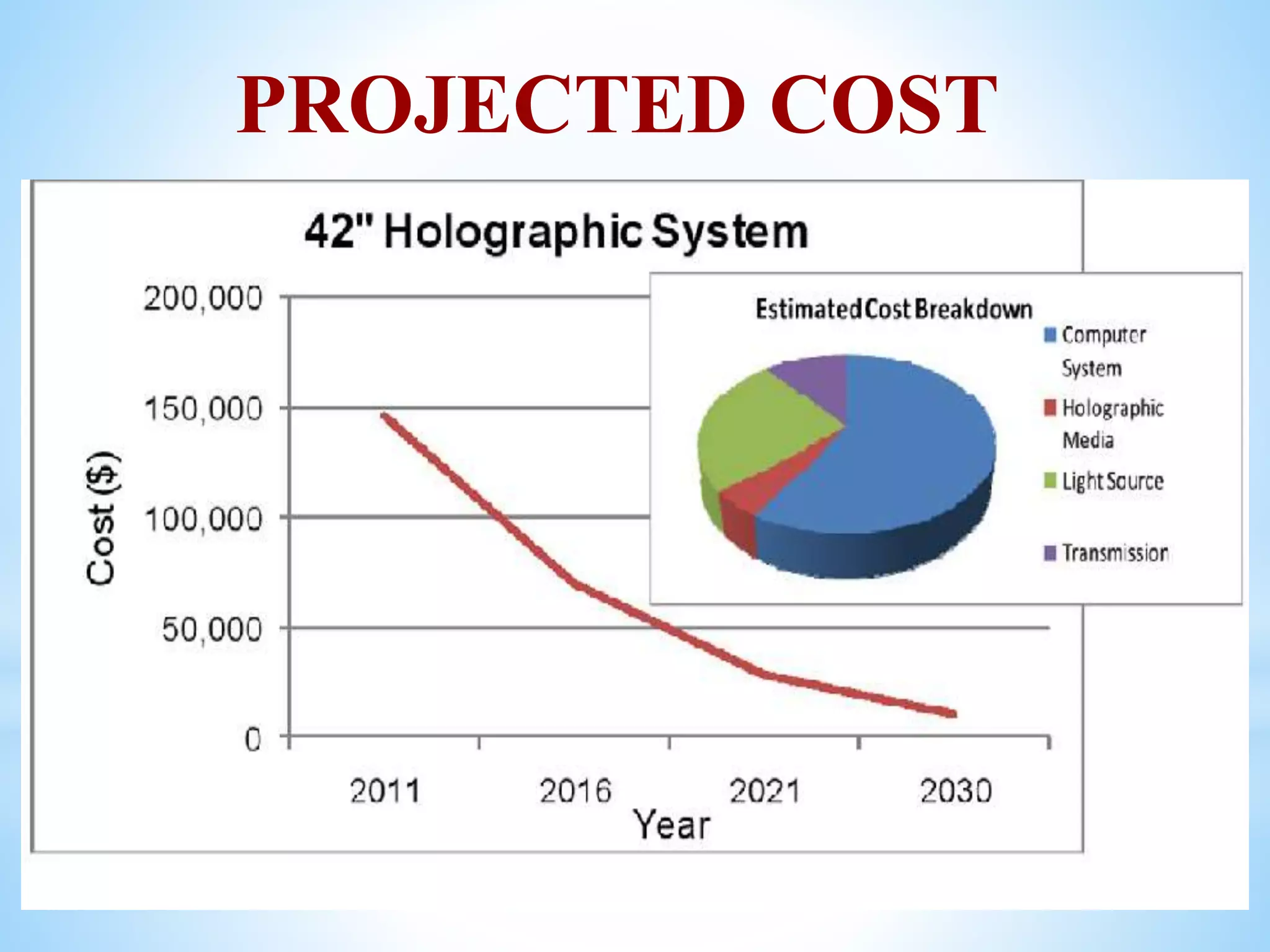
This technical presentation provides an overview of holography, including its history, properties, working principles, and applications. Holography allows the recording and reconstruction of 3D images through the interference and diffraction of light. Key points covered include the timeline of holography's development, the different types of holograms (reflection and transmission), how holograms are recorded and reconstructed using lasers, and their current and future uses in areas such as medical imaging, entertainment, and virtual communication. The document concludes that holographic technology has many potential applications limited only by the human imagination.