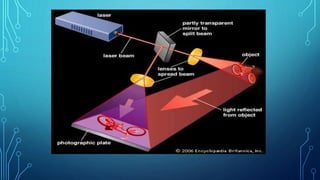
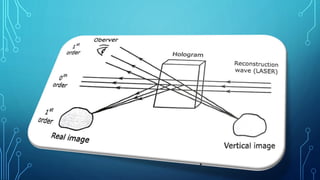
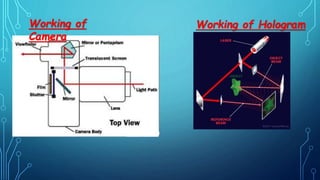
The document discusses hologram technology, defining holograms as physical structures that diffract light into images and detailing the science of holography. It covers the history, working processes, classifications, and applications of holograms, highlighting their differences from photography. Holograms have potential in various fields including art, data storage, and security, and are depicted in fiction as transformative technology.