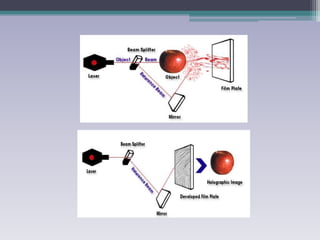
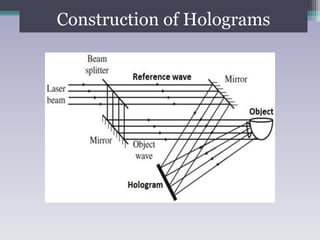
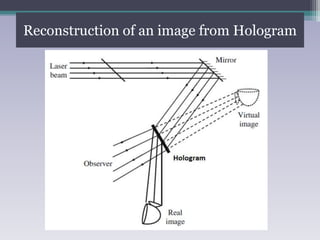
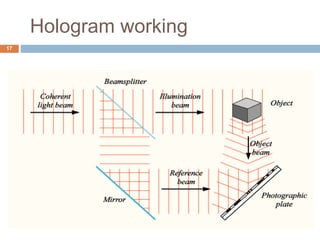
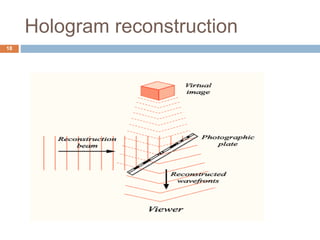
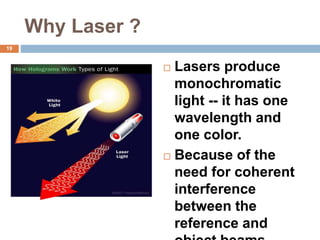
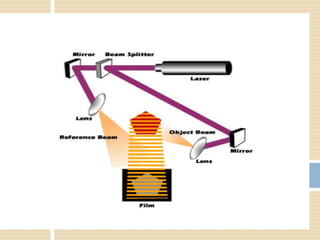
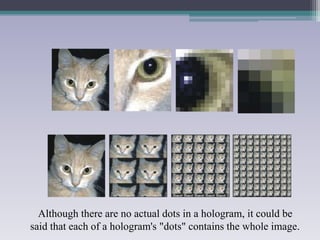
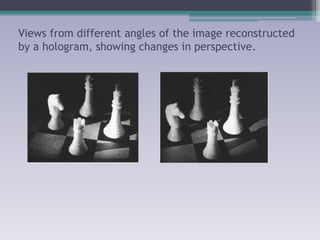
Holography is a technique that uses the properties of light interference and diffraction to record three-dimensional images of objects. A hologram is produced by interfering a reference beam of laser light with light scattered from the object being recorded to form an interference pattern, which is recorded on film or other media. When the hologram is later illuminated with only the reference beam, a three-dimensional image of the original object is reconstructed which can be viewed from different angles. Holography has applications in authentication, virtual displays, optical data storage, and medical and industrial imaging due to its ability to capture and reconstruct true three-dimensional images.