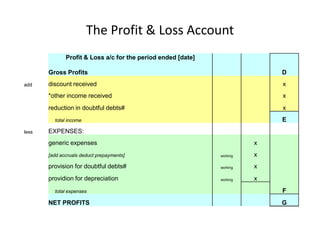
This document introduces the key financial statements prepared at the end of an accounting period: the trading account, profit and loss account, and balance sheet. It explains that the trial balance is prepared first using debit and credit columns to show asset/expense and liability/income balances. The trading account calculates gross profit by subtracting the cost of goods sold from net sales. The profit and loss account then calculates net profit by subtracting total expenses from total profits including gross profit and other income. Finally, the balance sheet presents the financial position by showing assets, liabilities, and capital/net assets.



![The Trial BalanceIs a list of all the balances in the ledgers at the end of the period in review.It uses two monetary columns [debit, credit]The debit column displays the assets and paid up expenses [A + E ] as at the date of review;The credit column displays the liabilities and income gained [L + C] as at the date of reviewTrial Balance formula.. A + E = L + C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontofinalaccounts-110908225033-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-final-accounts-4-320.jpg)
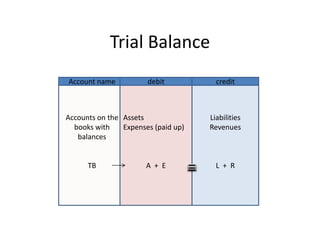
![Trial Balance as on …The Bal c/d on the account should be posted to the opposing column on the Trial Balance [eg if the Cash bal c/d fell on the credit side then it should be recorded in the debit column of the Trial Balance]Assets, Expenses Liabilities, Income](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontofinalaccounts-110908225033-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-final-accounts-6-320.jpg)
![Creditors’ figure(the summary total of the amounts owing to the suppliers recorded in this ledger)Debtors’ figure(the summary total of the amounts owed by the customers recorded in this ledger)Posting – transfer data from the journals [Day Books] to the ledgersBalance off – the act of finding the figure that makes both side equalDebit – the act of recording data on the left hand side of the accountCredit – the act of recording data on the right hand side of the account](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontofinalaccounts-110908225033-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-final-accounts-7-320.jpg)



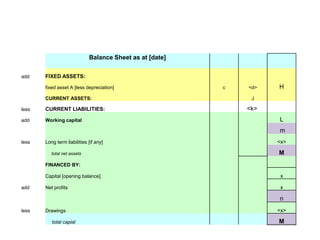
![The Balance Sheet This shows the financial status of the business at a given date. It reveals the value of the assets, liabilities, and capital... such that -:Net Capital = Net Assets less long term liabilities [C = A – L]Net Assets = Fixed Assets plus Working CapitalWorking Capital = Current Assets less Current LiabilitiesLong term Liabilities = debts which become due after 1 yearORNet Capital = opening capital plus net profits less drawings](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontofinalaccounts-110908225033-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-final-accounts-12-320.jpg)