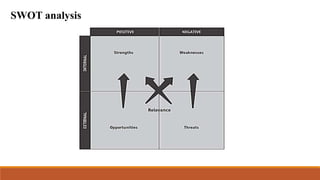
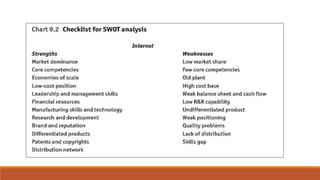
This document provides an overview of strategic planning and decision-making processes for organizations. It discusses strategic management, organizational goals and plans, the planning process, management by objectives (MBO), and SWOT analysis. Some key points covered include:
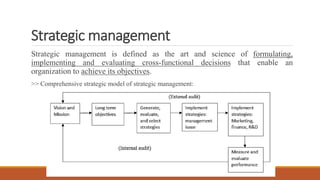
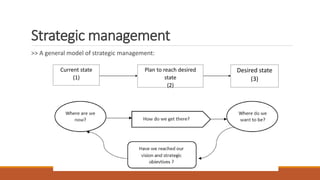
- Strategic management involves formulating, implementing, and evaluating cross-functional decisions to achieve organizational objectives.
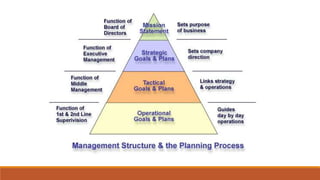
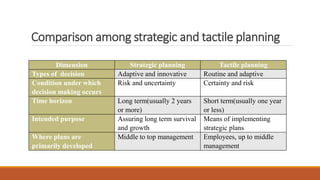
- Organizations establish strategic, tactical, and operational goals and plans at different levels. Strategic plans outline long-term decisions, tactical plans implement strategic plans, and operational plans focus on short-term goals.
- The planning process involves establishing objectives, developing premises, evaluating alternatives, selecting a course of action, and developing derivative plans.
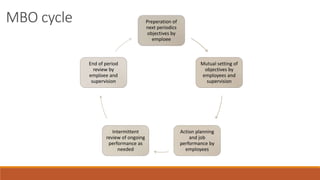
- M