This document provides an overview of e-marketing. It defines e-marketing as the process of advertising and selling products online using electronic technologies. The key points covered include:
- E-marketing strategies aim to connect businesses to customers using a range of online technologies. It includes both direct and indirect response marketing.
- The scope of e-marketing includes distribution, customer relationship management, money collection, lead generation, advertising, and feedback.
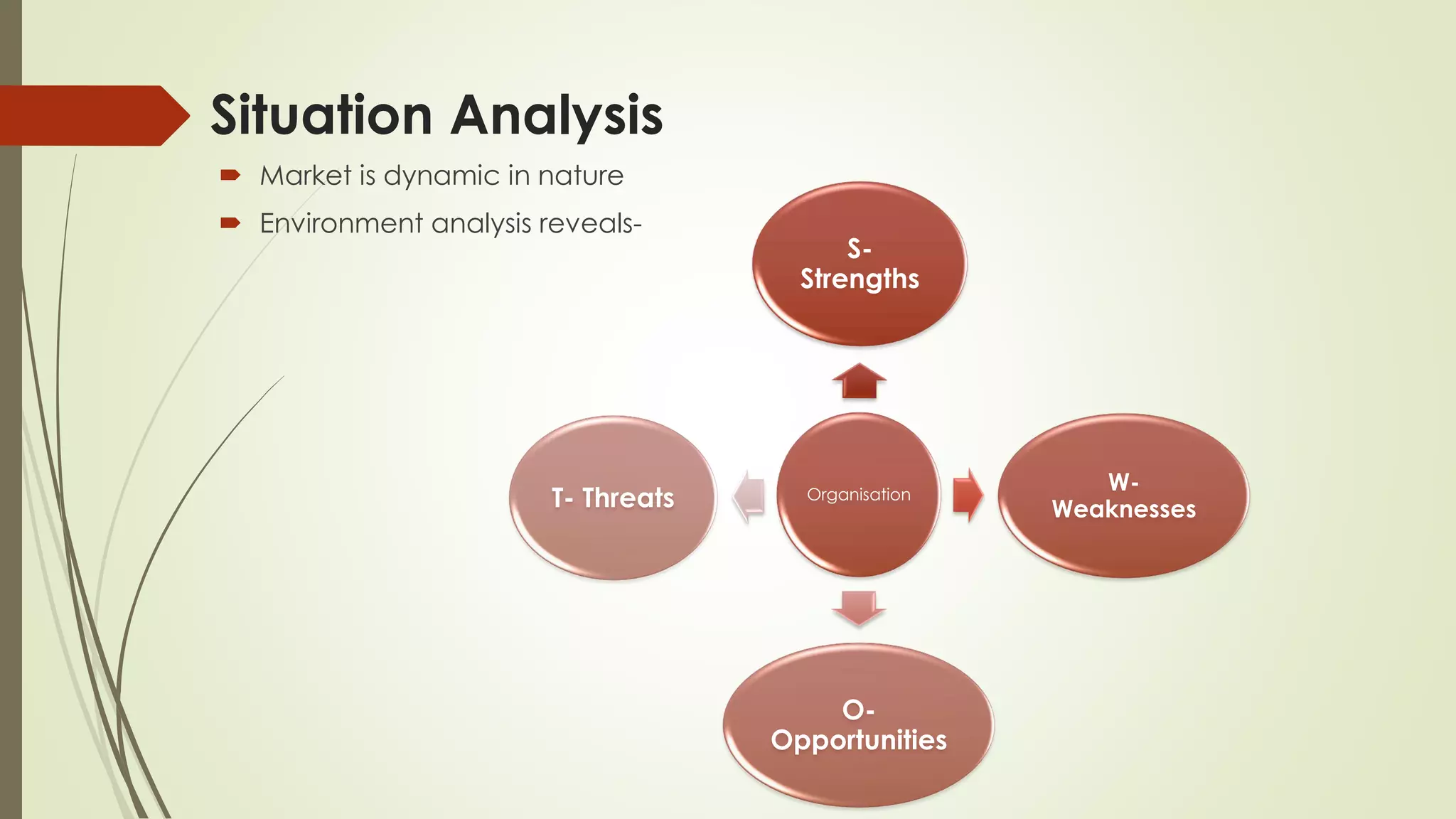
- Developing an e-marketing plan involves situation analysis, strategic planning, setting objectives and strategies, implementation plans, budgets, and evaluation.
- Segmentation, targeting, differentiation, and positioning are important aspects of e-marketing strategic planning.