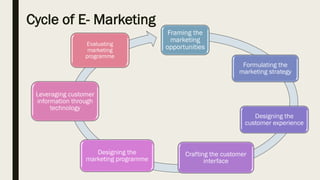
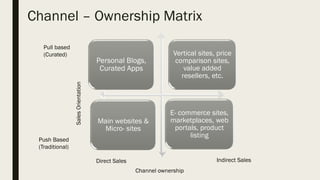
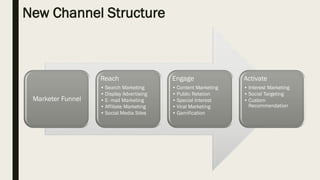
This document discusses digital marketing strategies and concepts. It covers the cycle of e-marketing, including framing opportunities, formulating strategies, designing customer experiences, crafting interfaces, designing programs, and evaluating performance. It also discusses product strategies like product mix, mass customization, and bundling. Additionally, it outlines strategies for online branding, pricing, distribution channels, and the importance of people, processes, programs, and performance metrics in digital marketing.