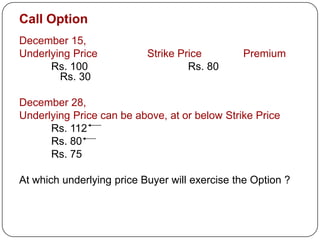
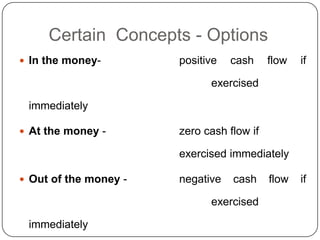
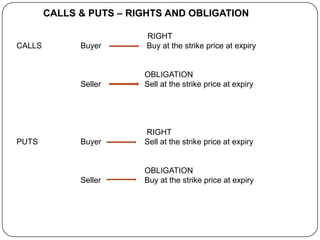
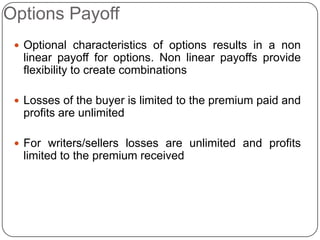
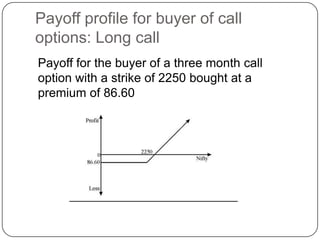
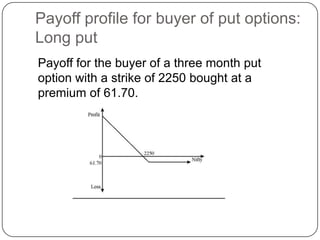
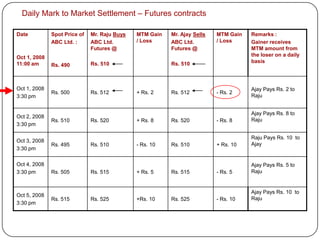
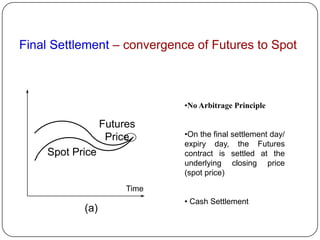
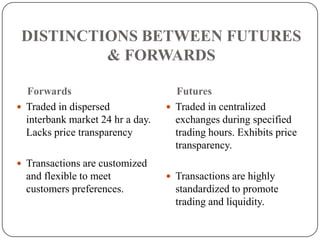
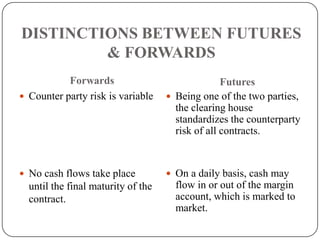
This document provides an introduction to derivatives. It defines derivatives as financial instruments whose value is derived from an underlying asset. The three main types of derivatives discussed are forwards, futures, and options. Forwards are customized bilateral contracts to buy or sell an asset in the future at a predetermined price. Futures are standardized exchange-traded versions of forwards that have no counterparty risk. Daily mark-to-market settlements determine profits and losses on futures positions. Options provide the right but not the obligation to buy or sell an asset at a future date.























![Points to remember……….
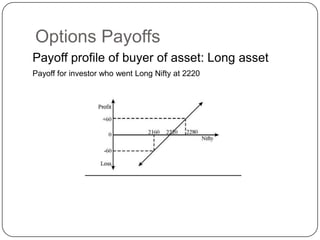
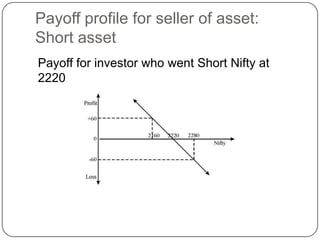
Long – Buy …(going long) [Bullish view]
Short – Sell …(going short) [Bearish view]
Squaring off (turn around trades) – opposite
transaction to the previous one
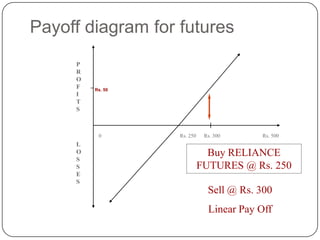
Buy low, sell high - gives a profit
Sell high, buy low - also gives a profit
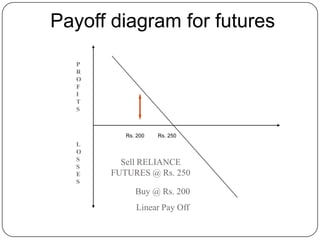
Sell low, buy high – gives a loss
Buy high, sell low – also gives a loss](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoderivatives-120812134457-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-derivatives-32-320.jpg)


![Options
Example :-
TATA is launching a car – Nano
Price is Rs. 1Lakh. [Purchase price]
You can book the car by paying Rs. 20,000 [deposit]
By booking the car, what have you bought?
o A RIGHT to buy the car
When booking matures, can TATA force you to buy
Nano?
o TATA has only OBLIGATION
Can you force TATA to sell Nano?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoderivatives-120812134457-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-derivatives-41-320.jpg)