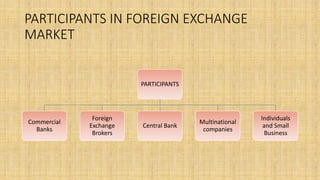
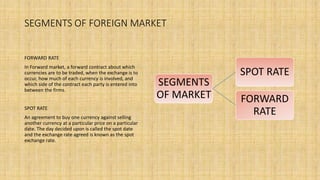
The document provides an overview of the foreign exchange (forex) market. It discusses key terms like foreign currency and exchange rate. The forex market allows participants to buy and sell currencies and includes banks, investment firms, central banks, and retail investors. It is the largest financial market in the world by trading volume. The main segments are the spot market for immediate exchanges and forward market for exchanges at a future date. Major participants include commercial banks, brokers, central banks, and multinational companies. The forex market facilitates international trade and investment by transferring purchasing power across countries and setting currency prices.