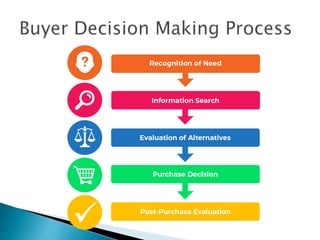
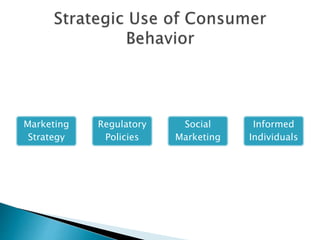
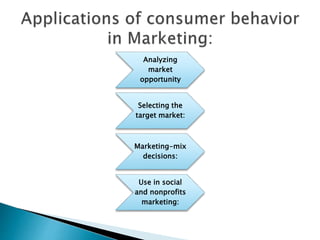
The document discusses various topics related to consumer behavior including the difference between consumer and organizational buying, factors that influence consumer behavior, and the importance of understanding consumer behavior for marketing and public policy decisions. It provides definitions of key terms, describes the consumer decision making process, and explains how knowledge of consumer behavior can benefit companies, regulators, and social marketing programs.