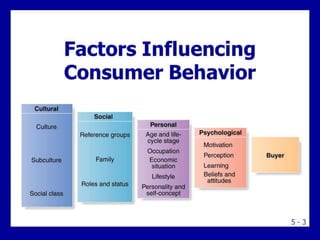
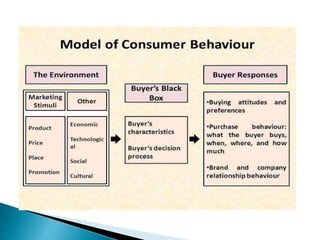
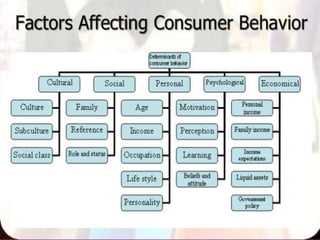
This document summarizes consumer behavior and the factors that influence it. It discusses that consumer behavior is the study of how individuals select, buy, use, and dispose of goods and services. It is influenced by cultural, social, personal, and psychological factors. The major theories of consumer behavior are economic, psychological, psychoanalytical, and sociocultural theories. The document also examines the consumer buying process and models used to understand it.