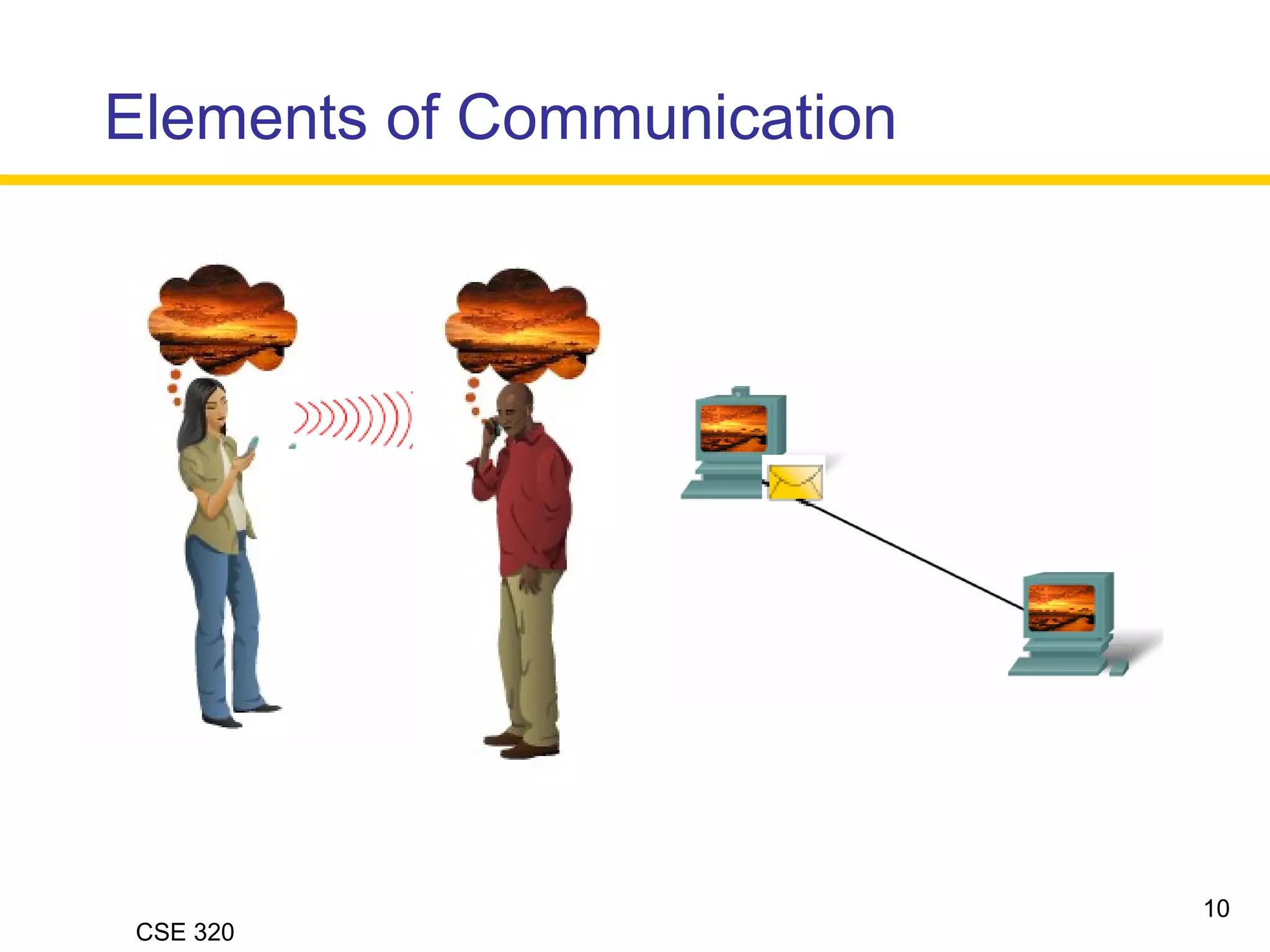
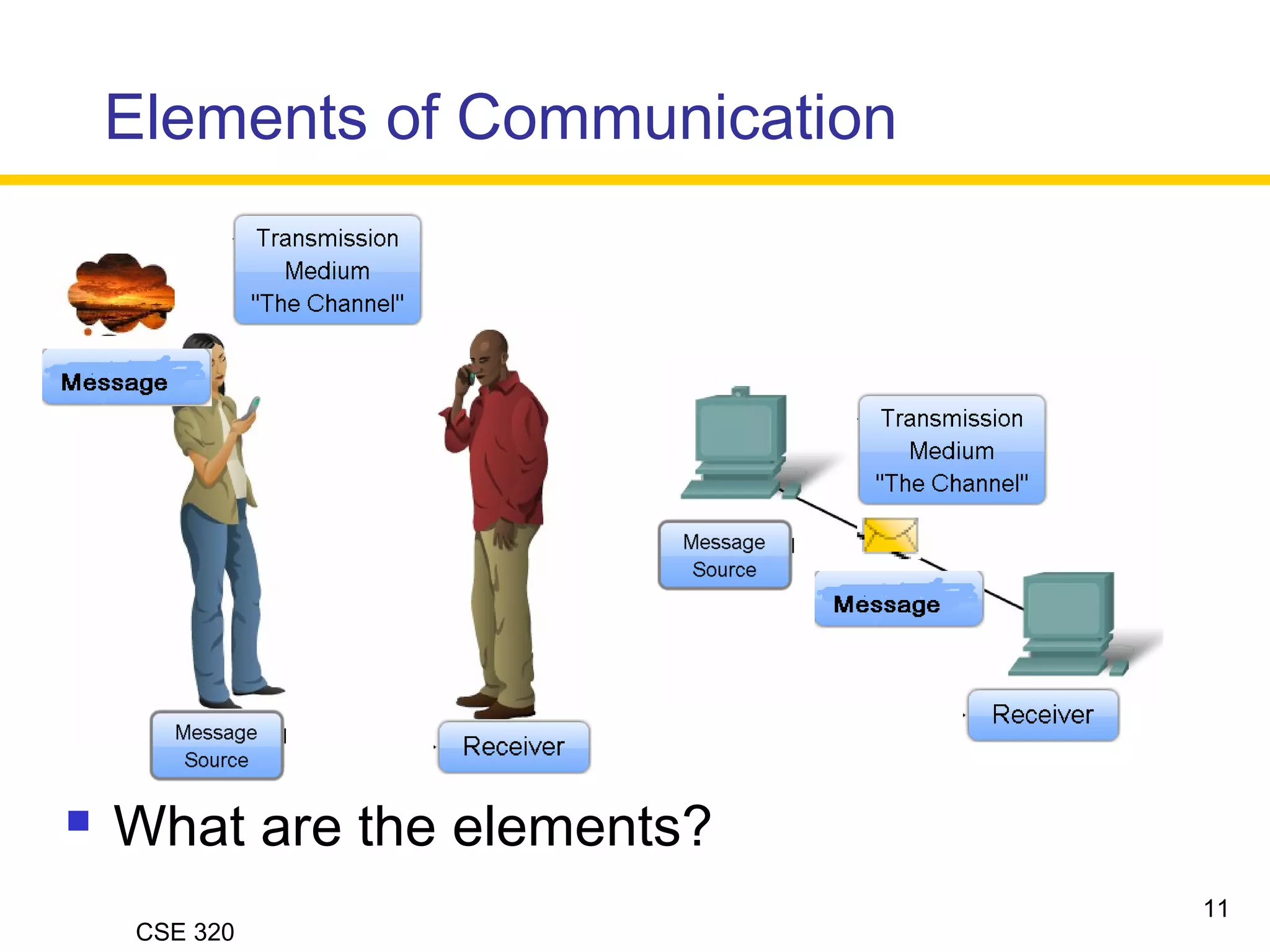
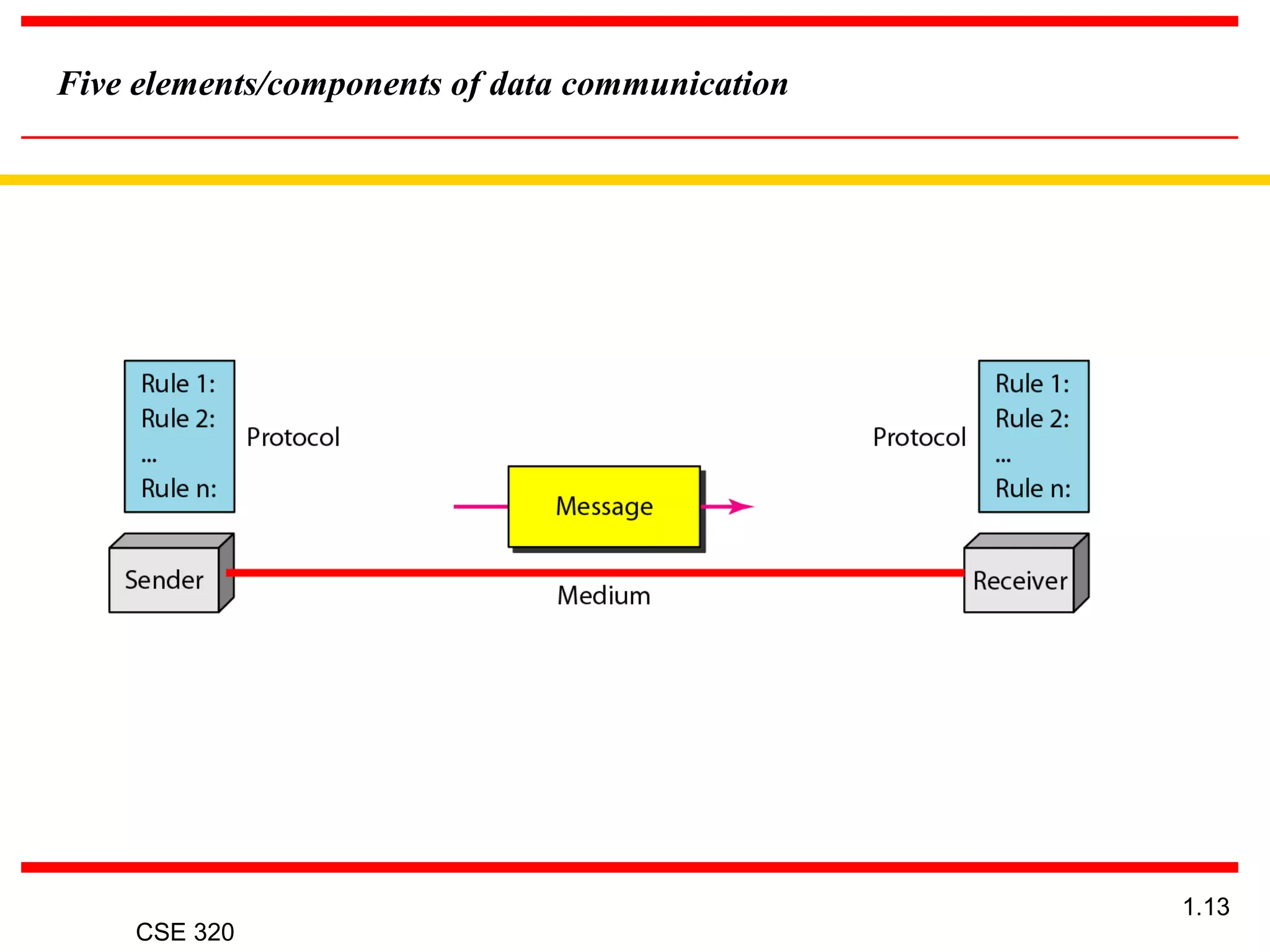
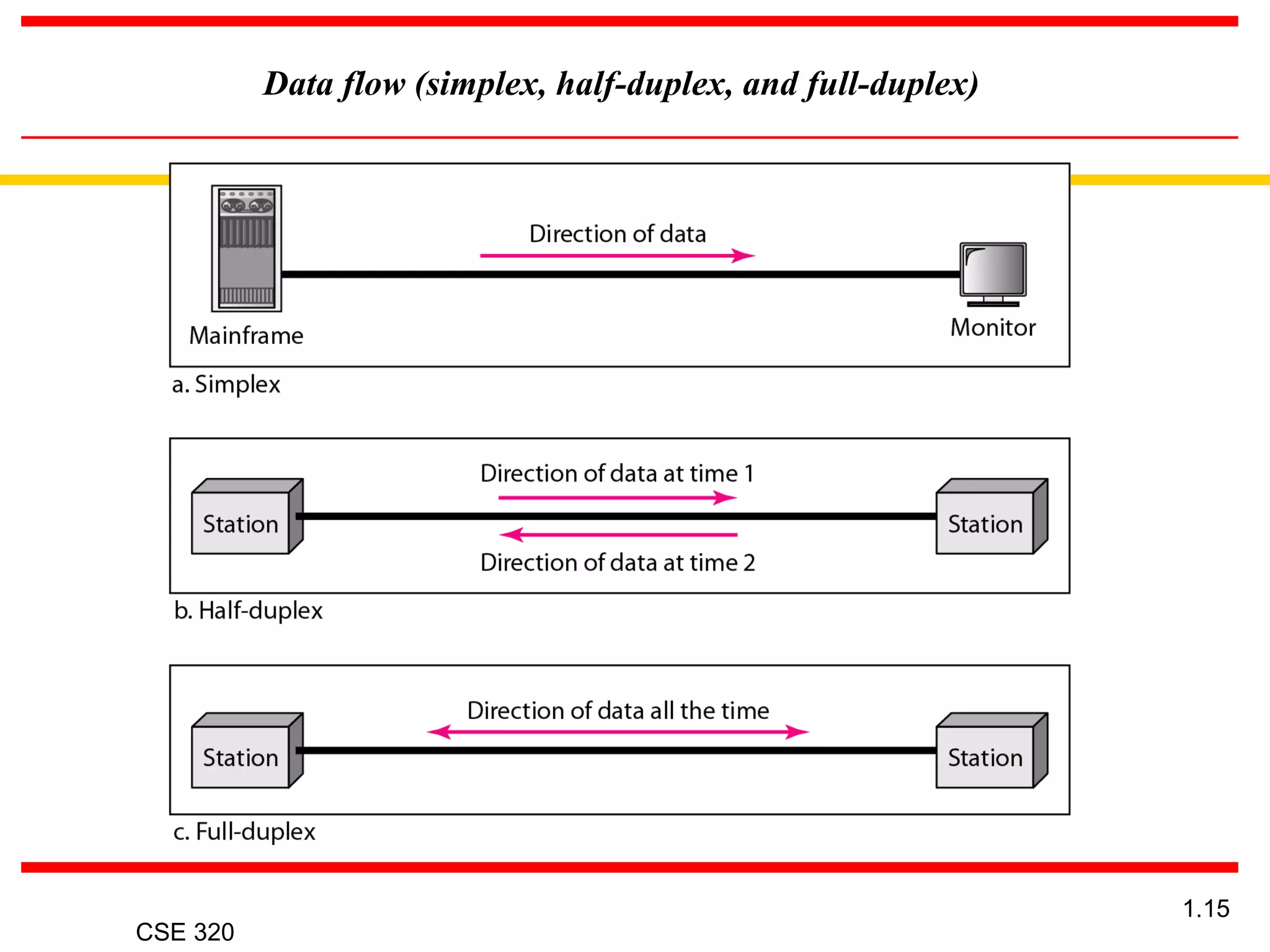
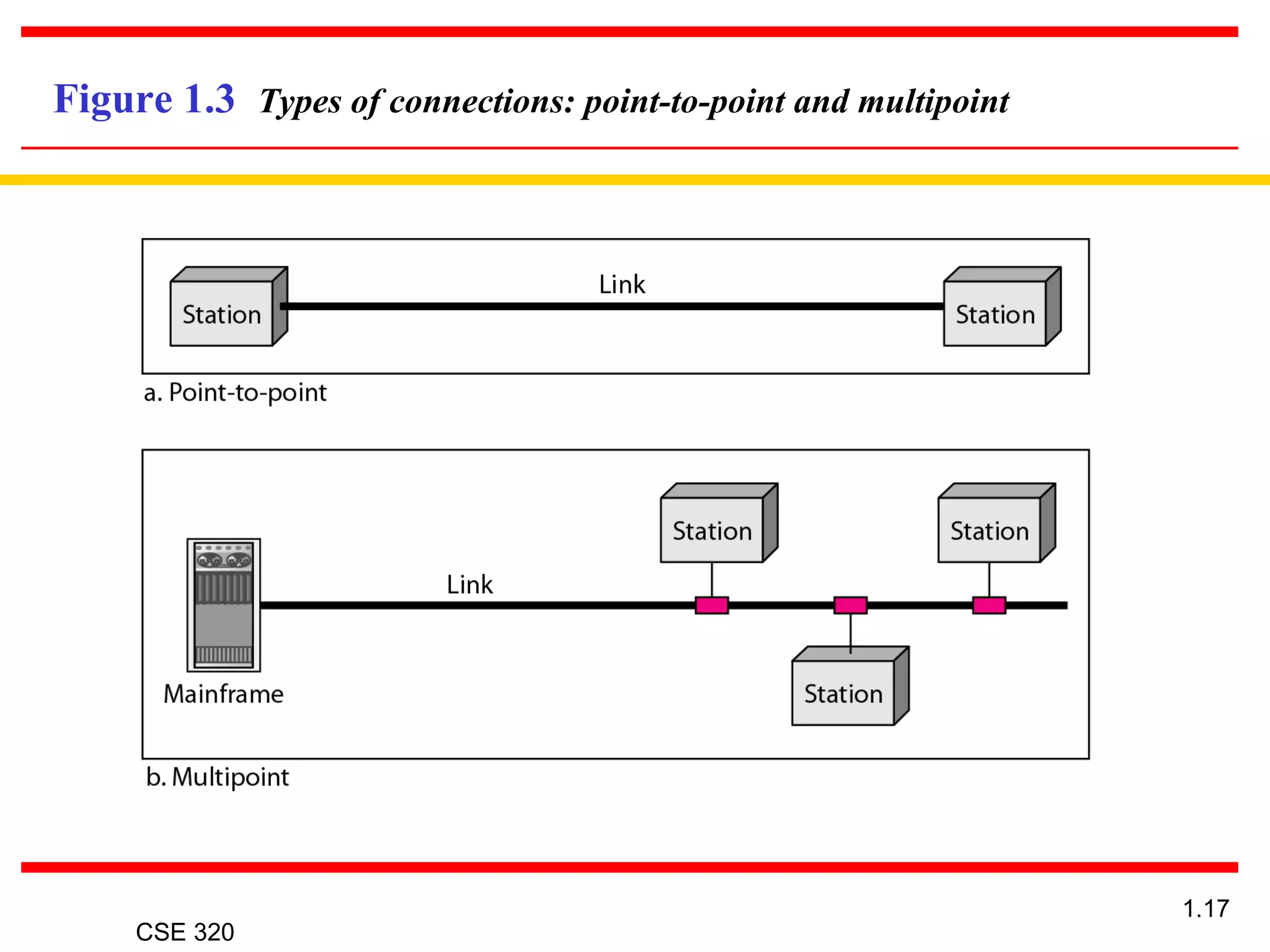
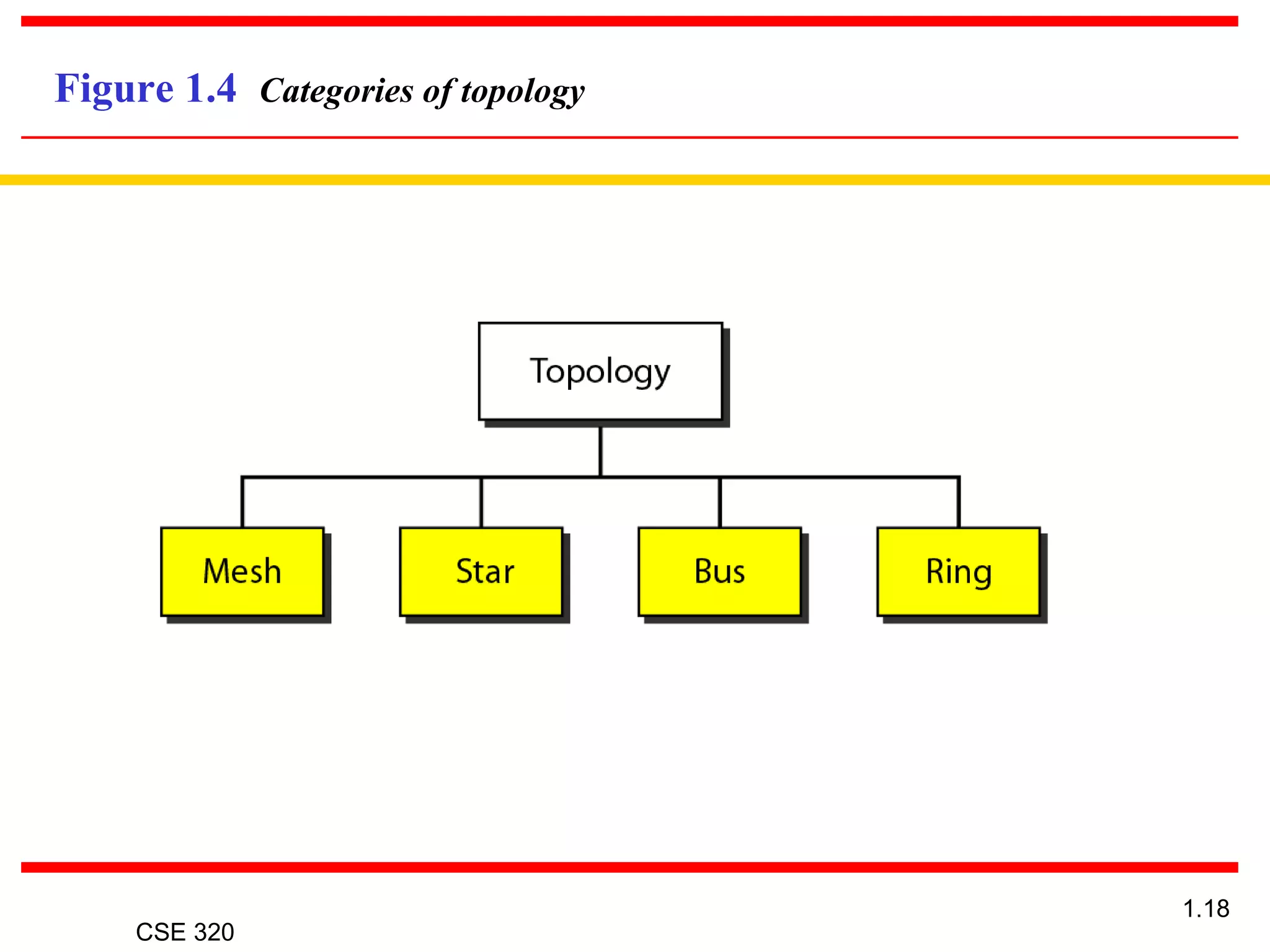
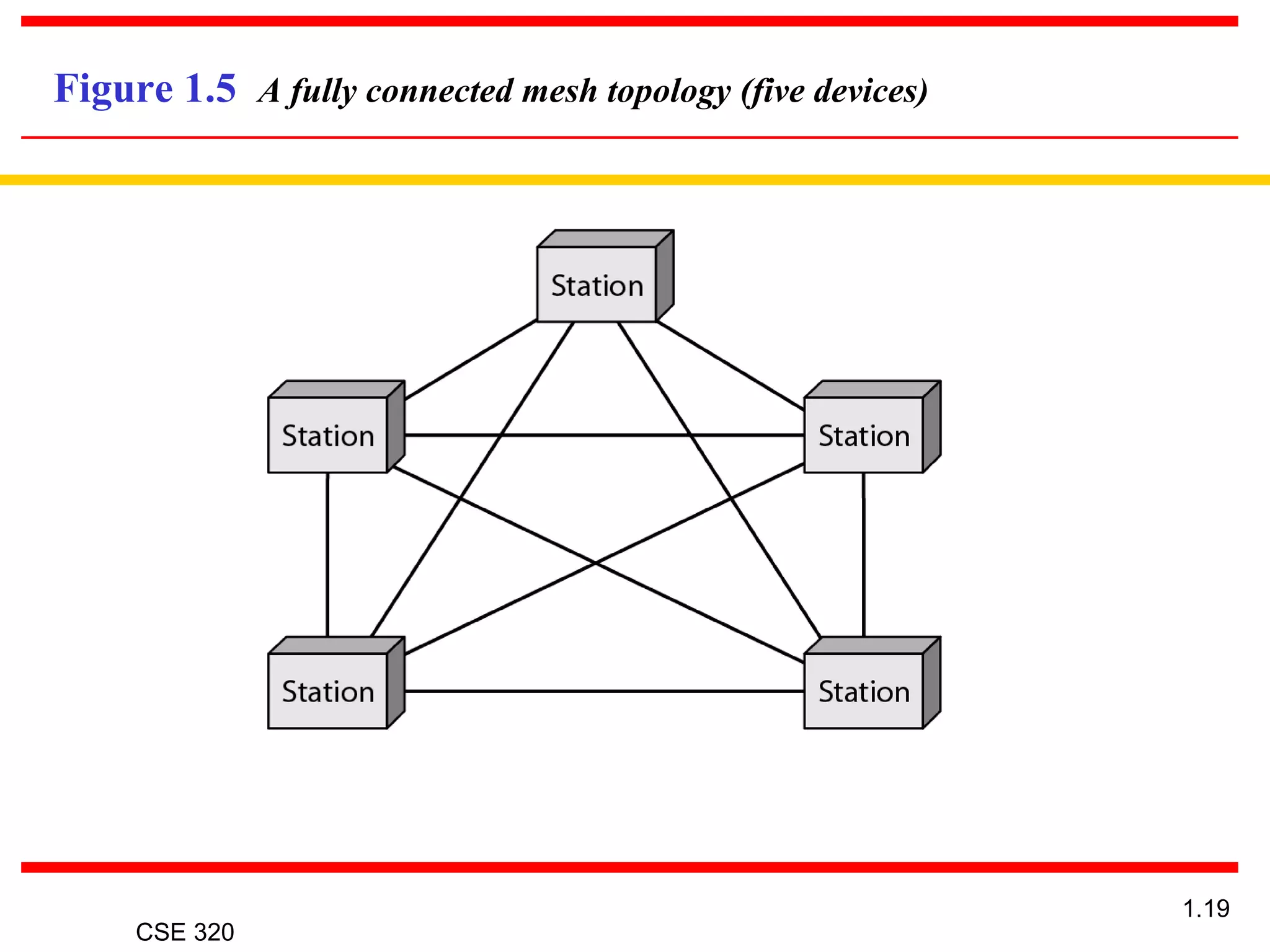
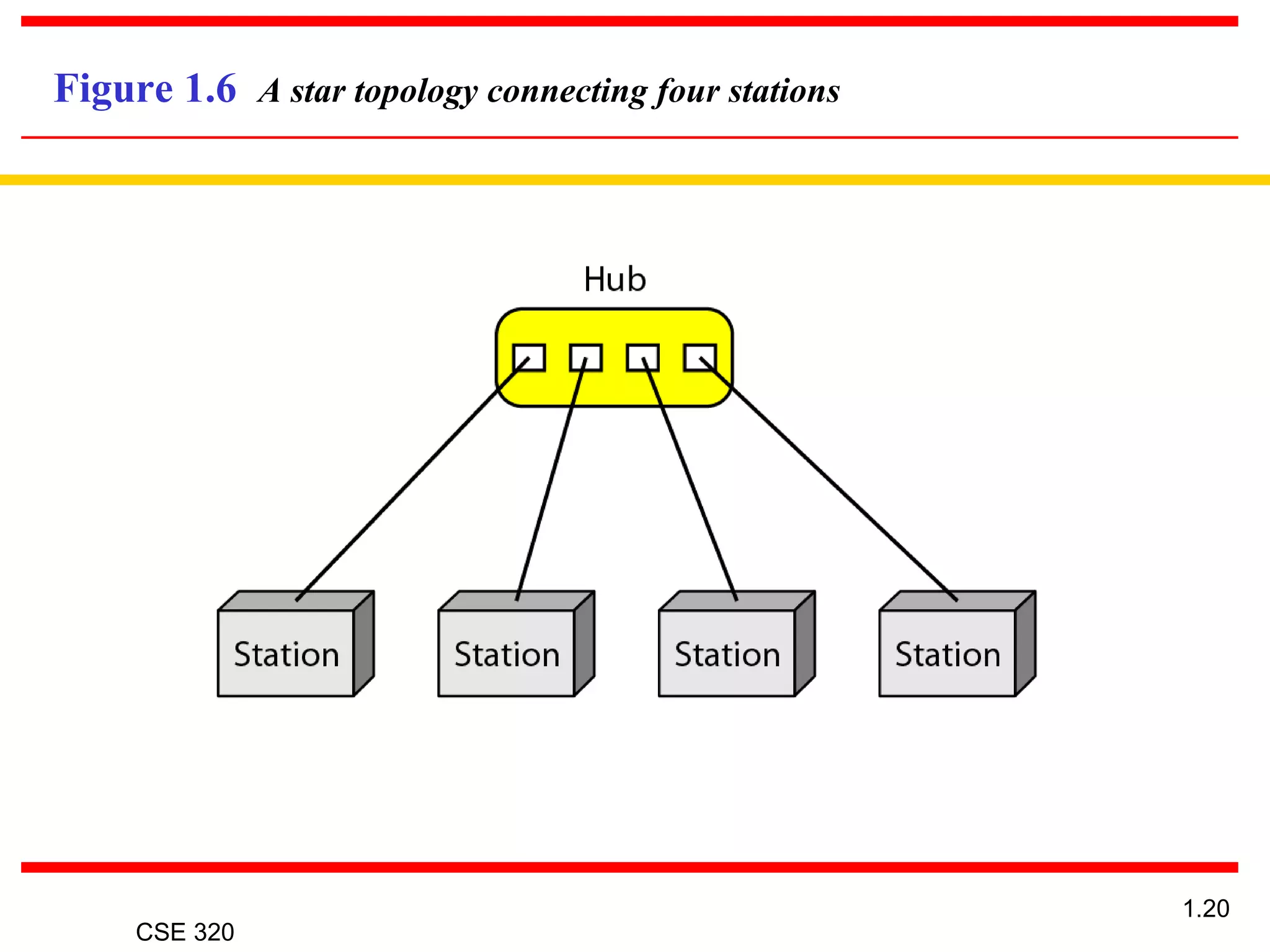
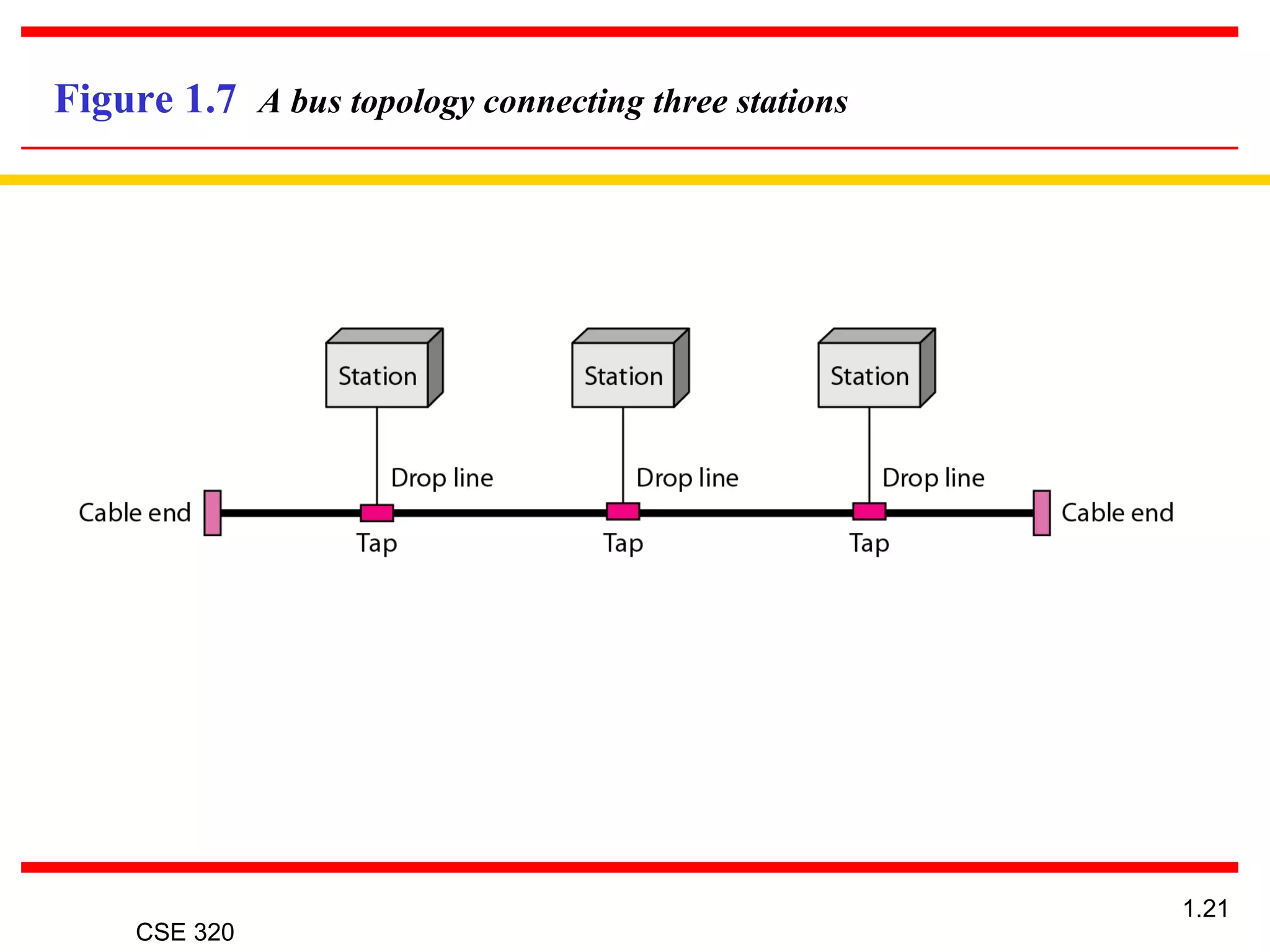
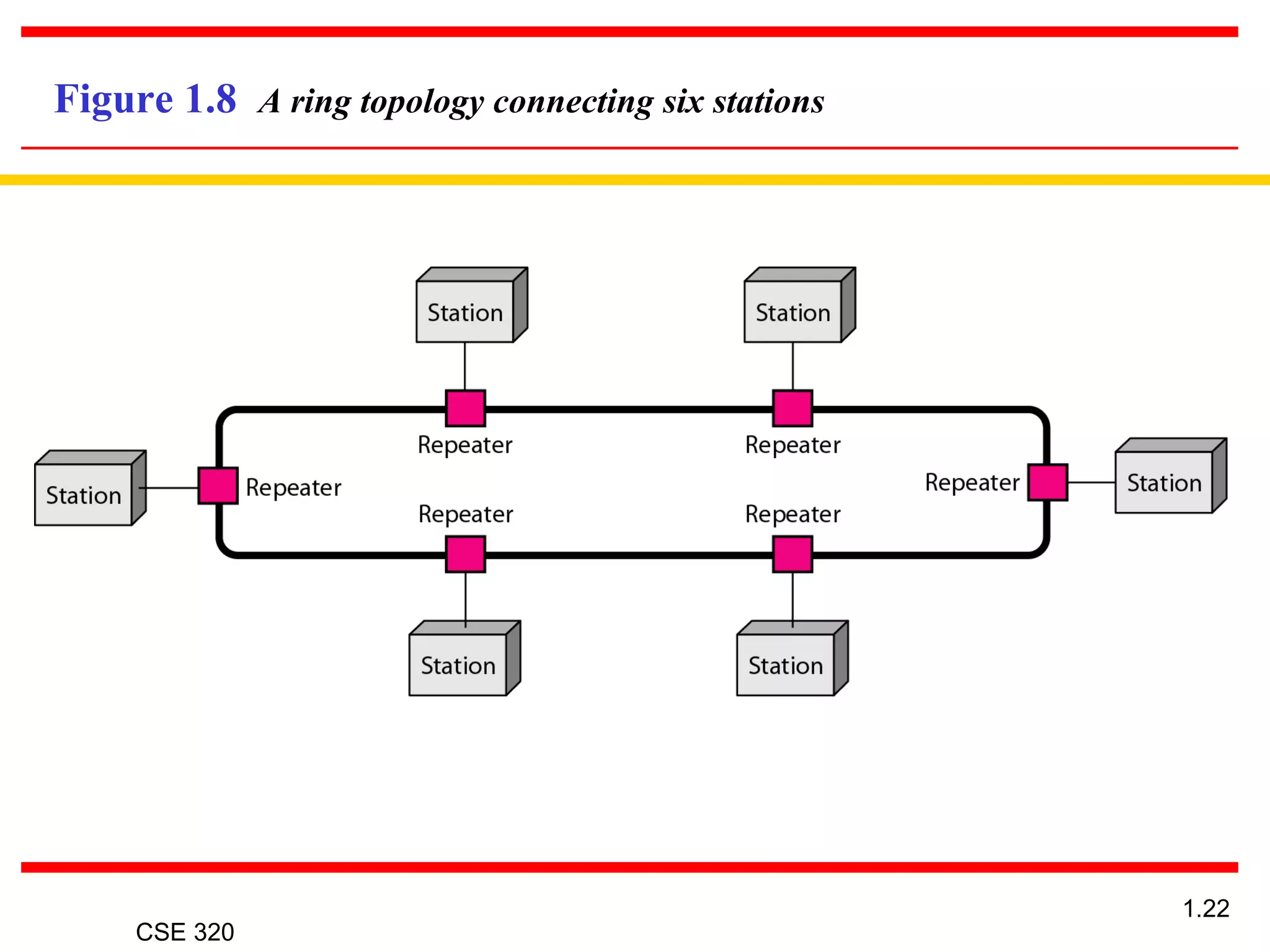
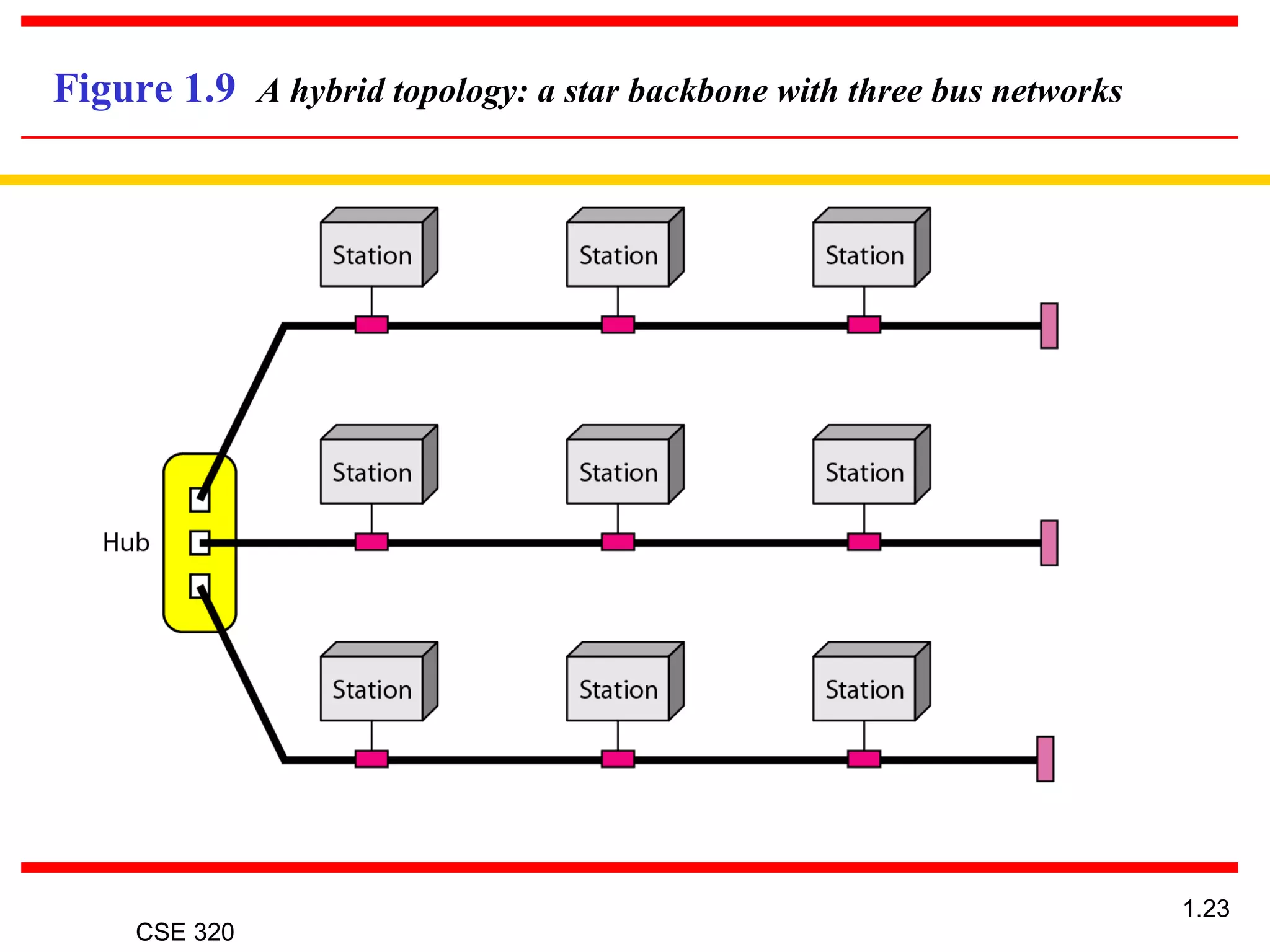
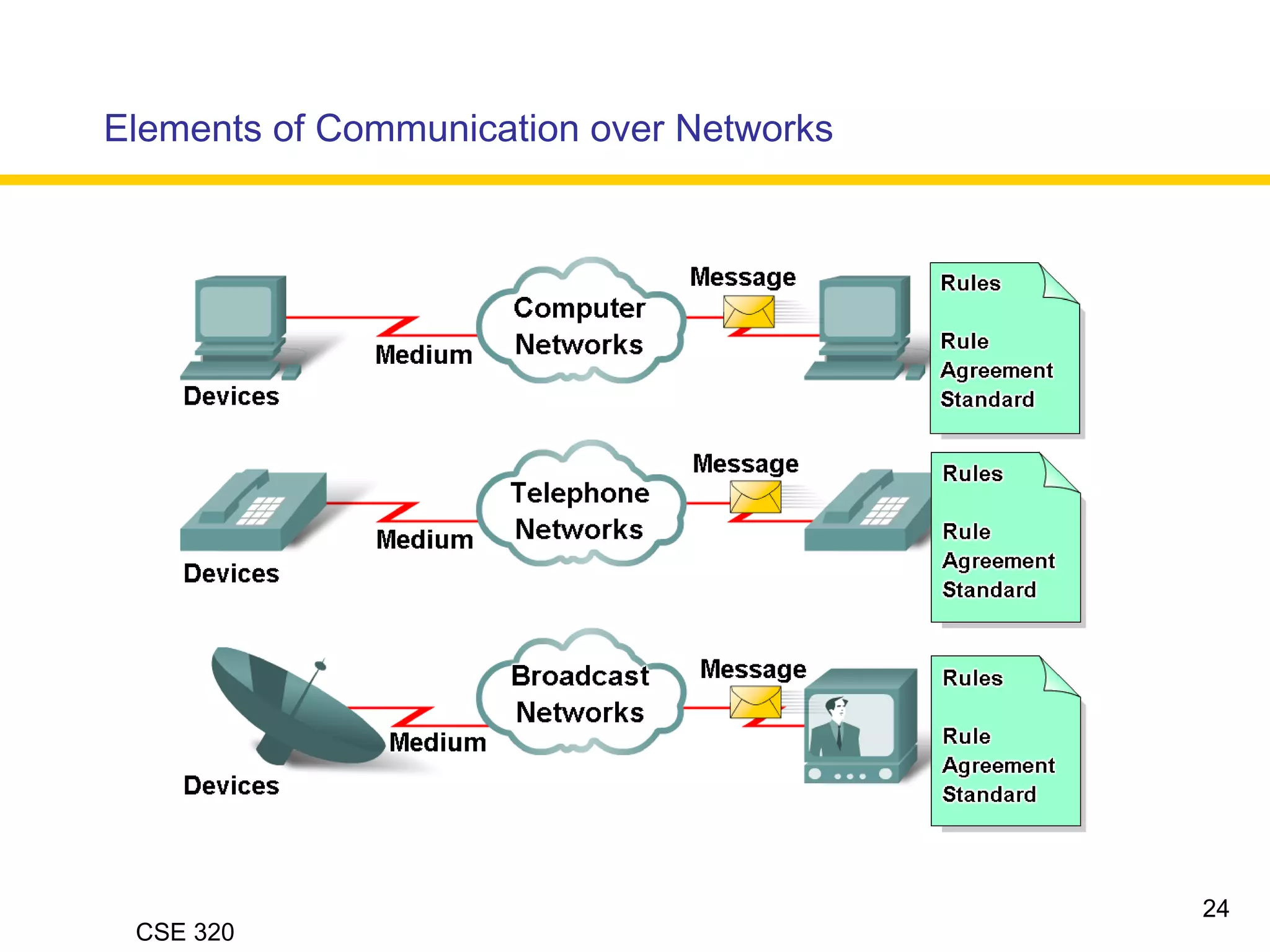
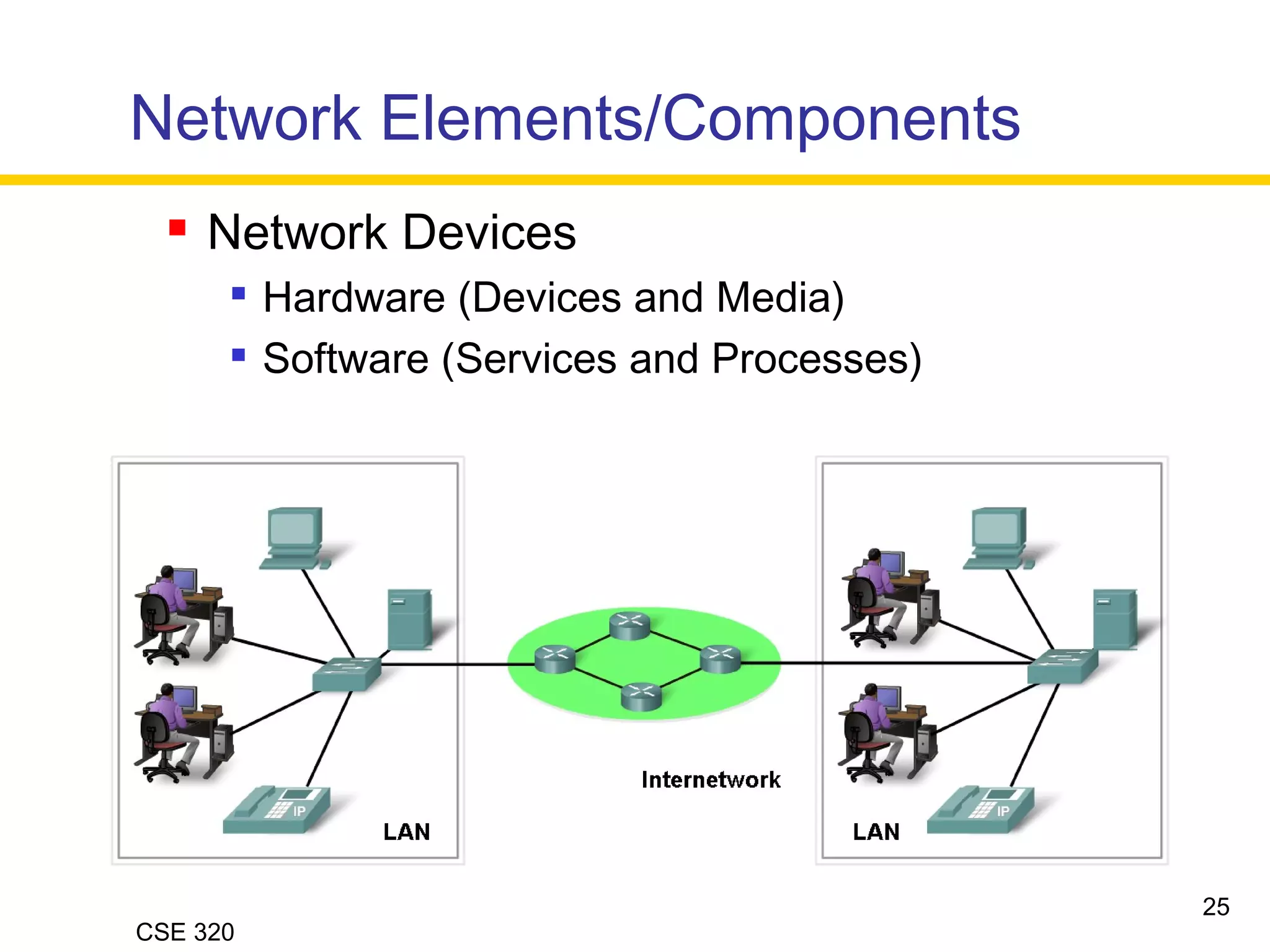
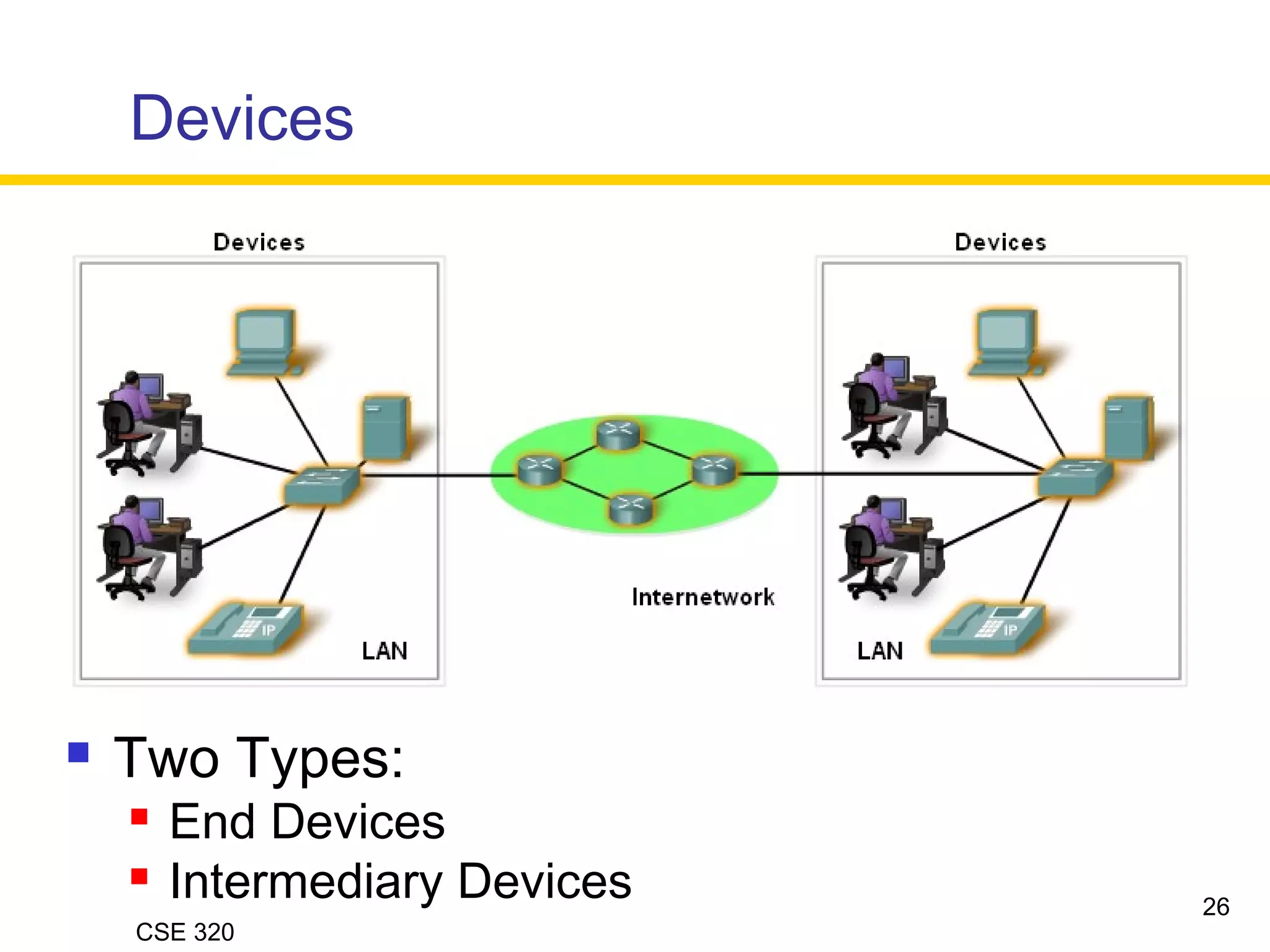
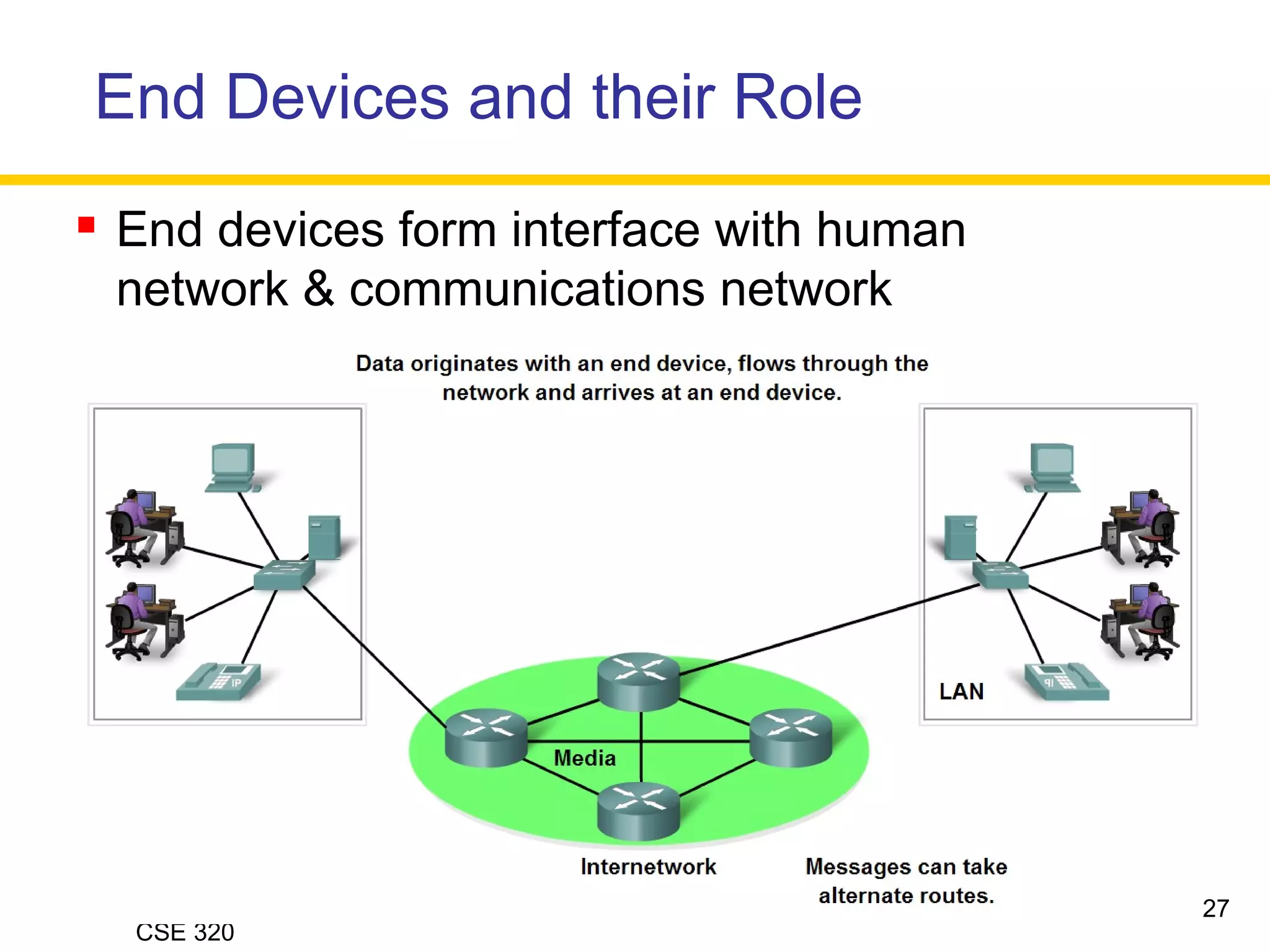
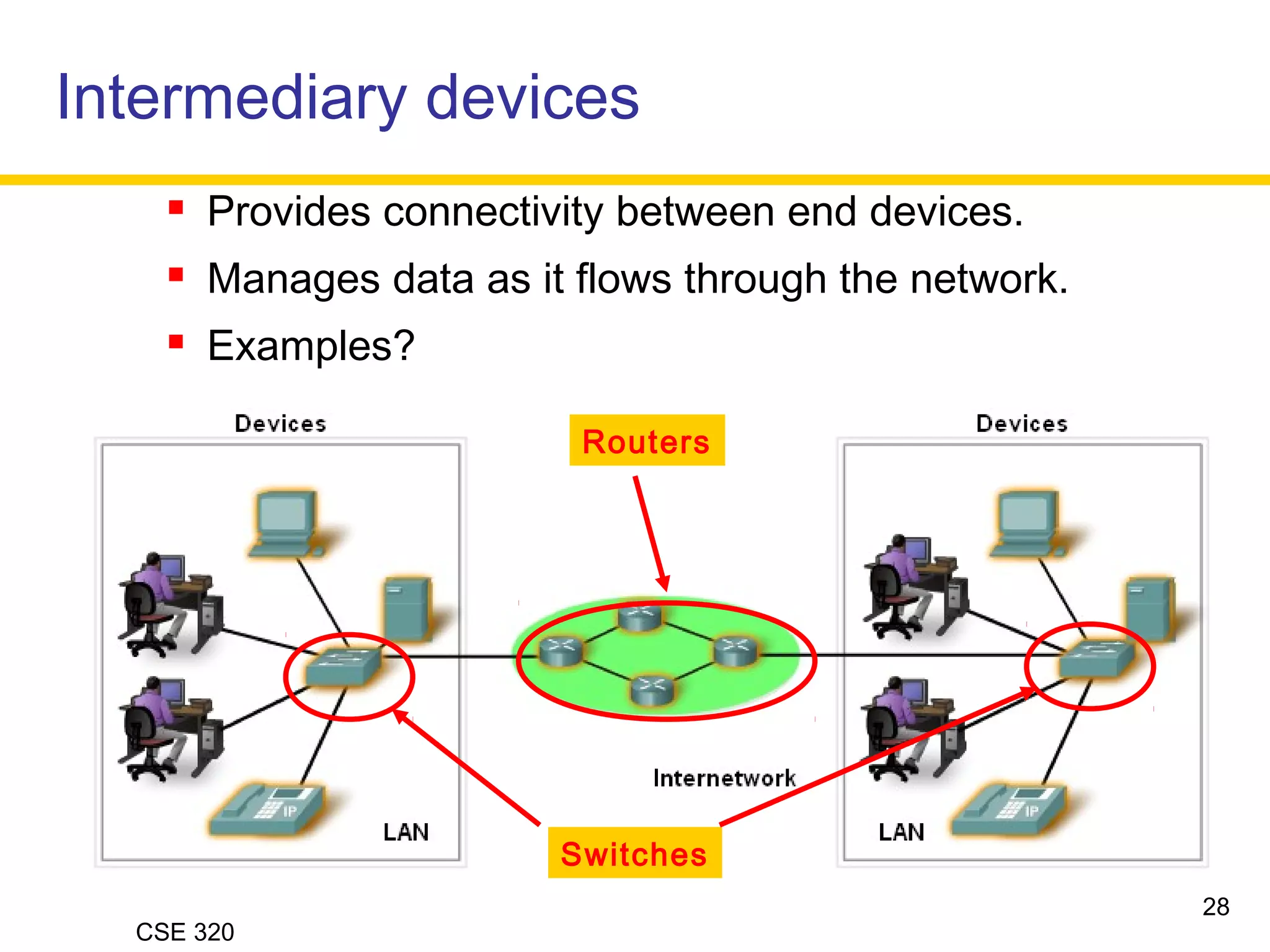
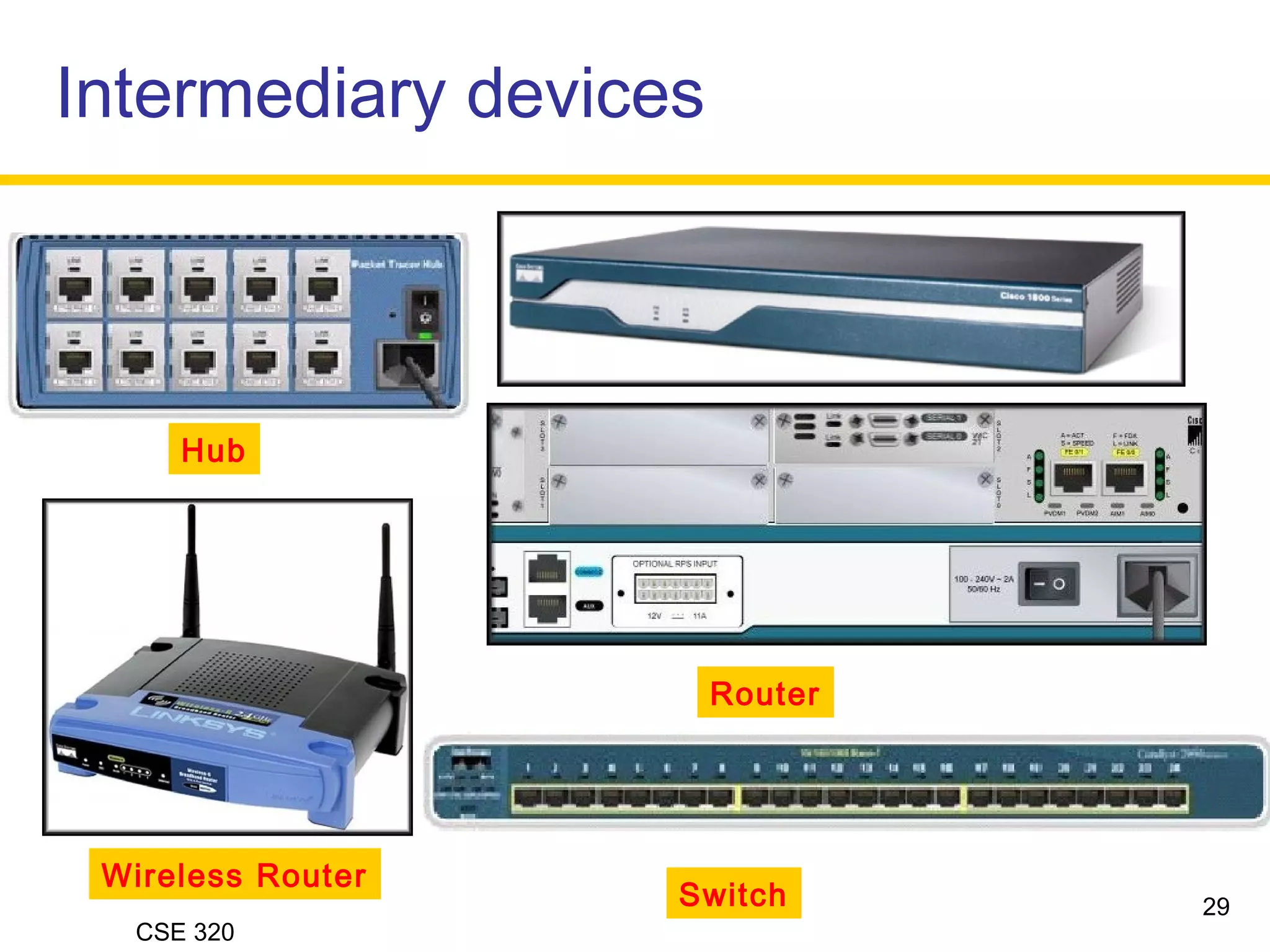
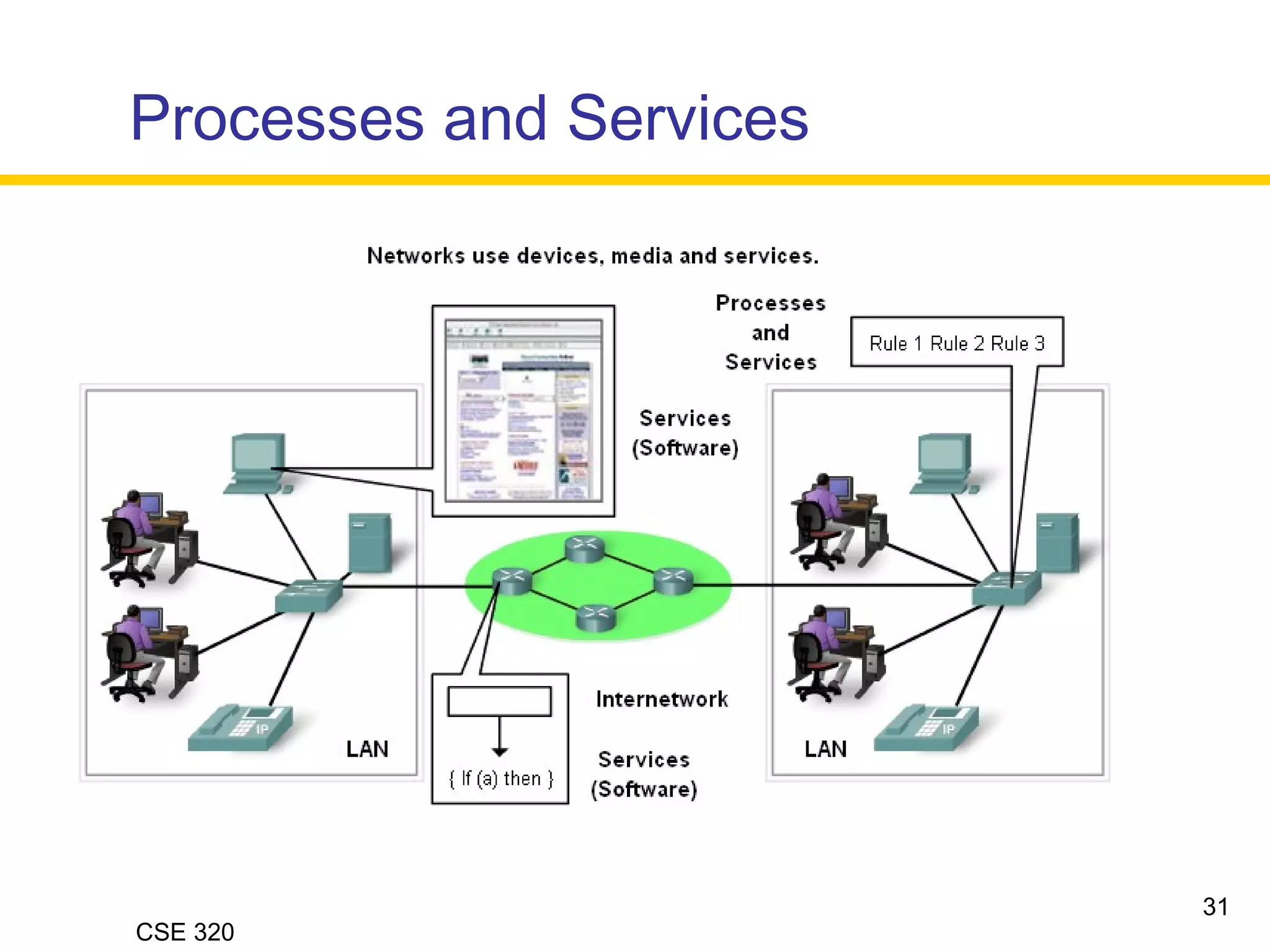
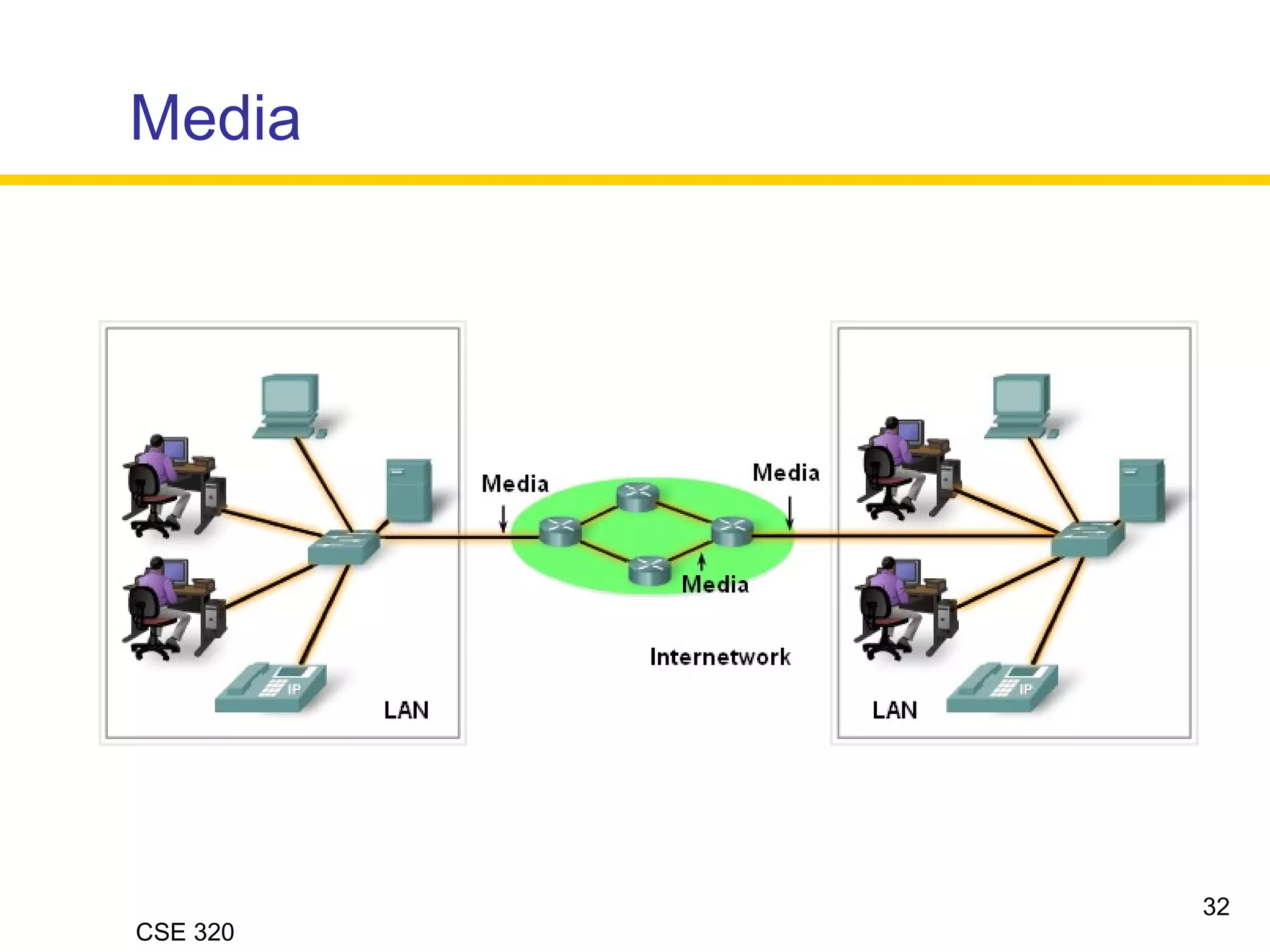
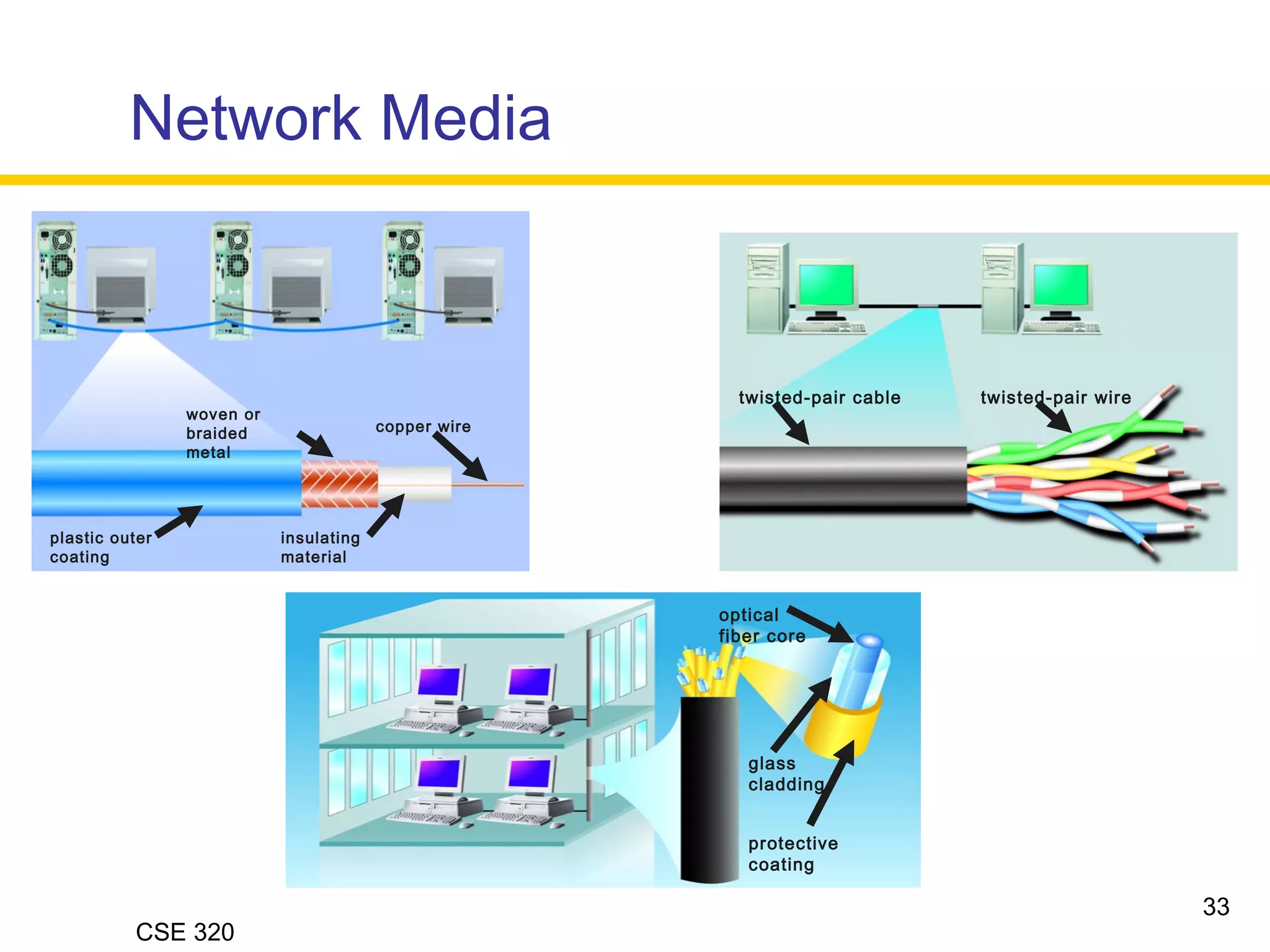
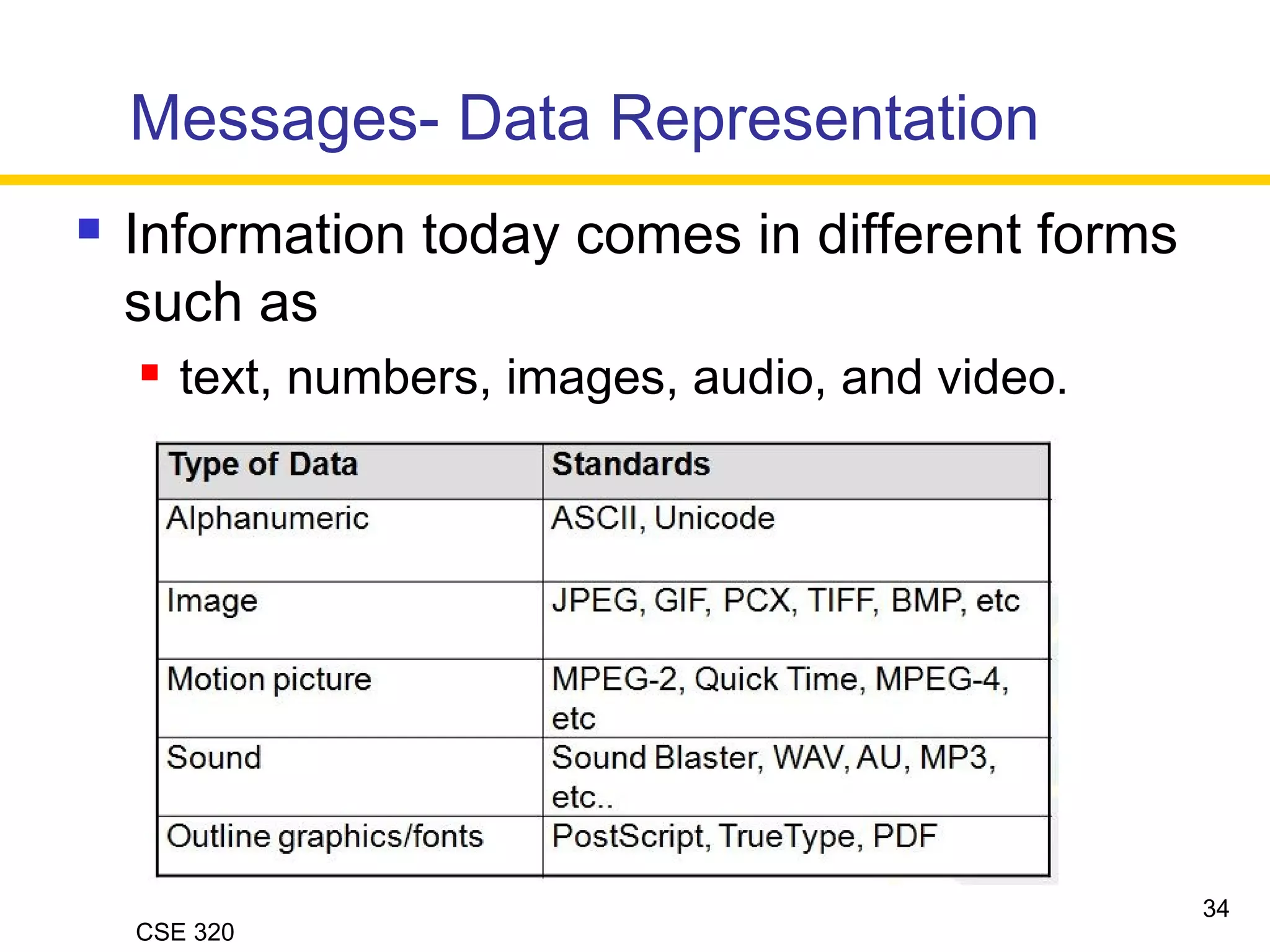
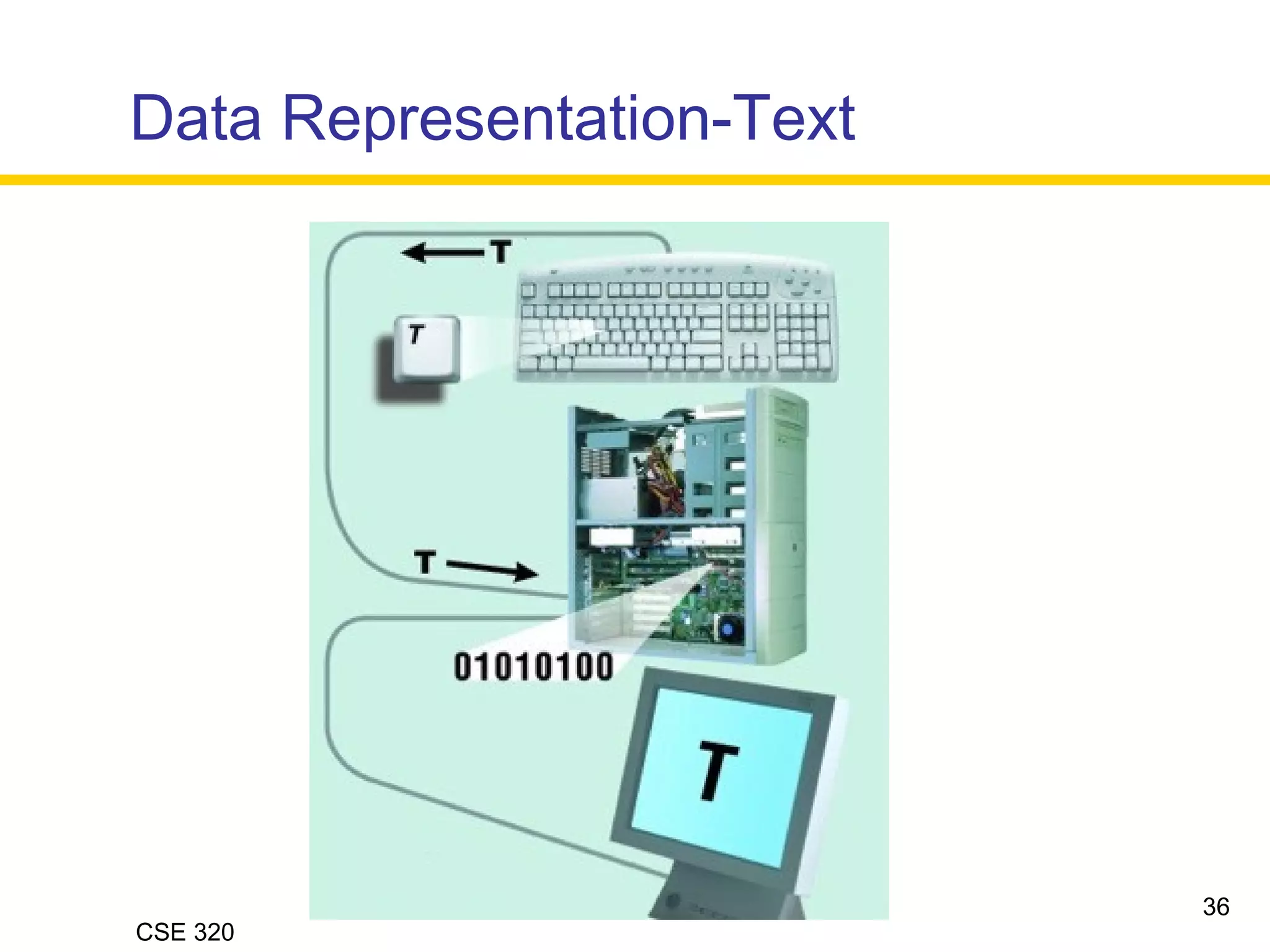
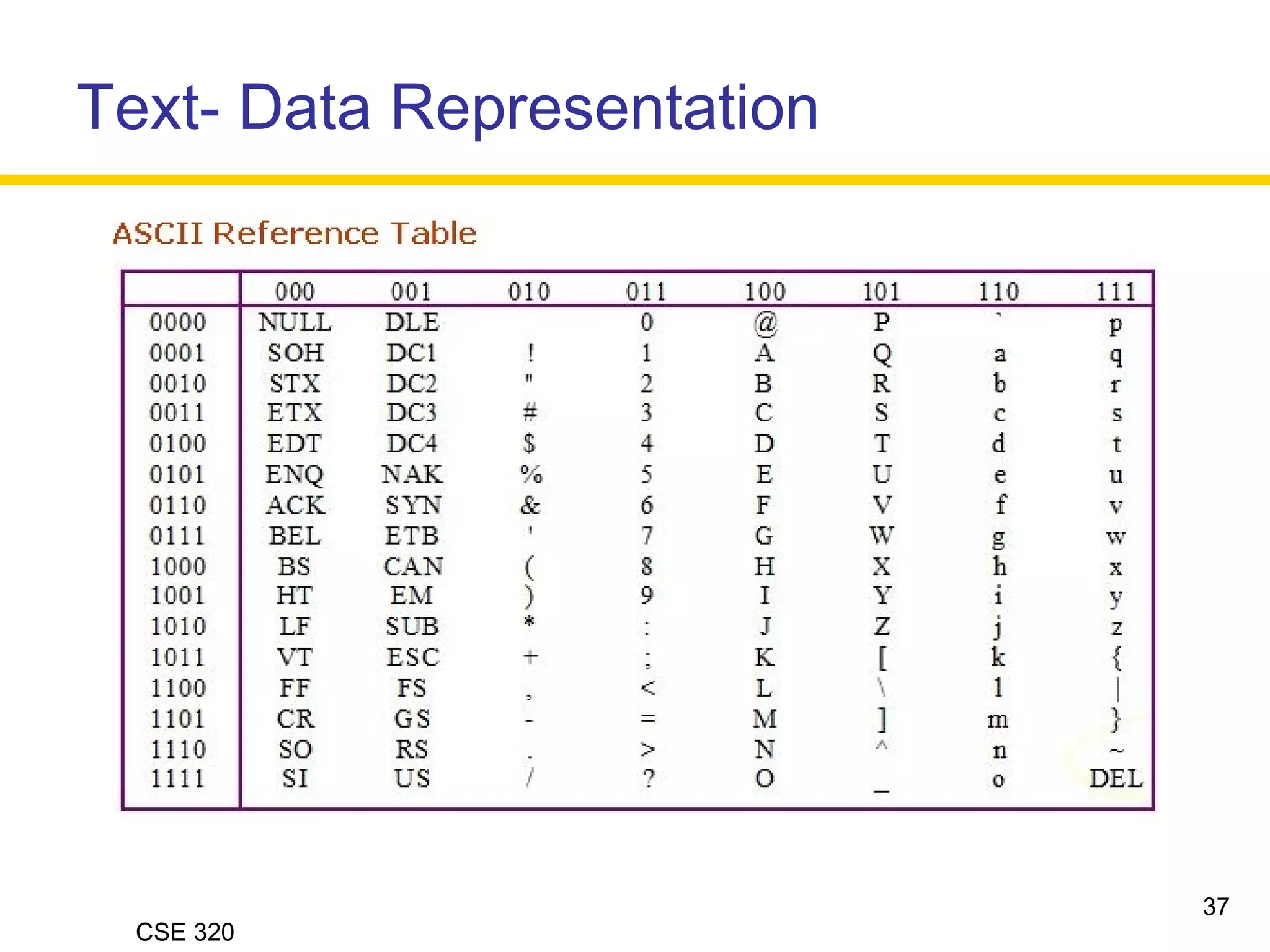
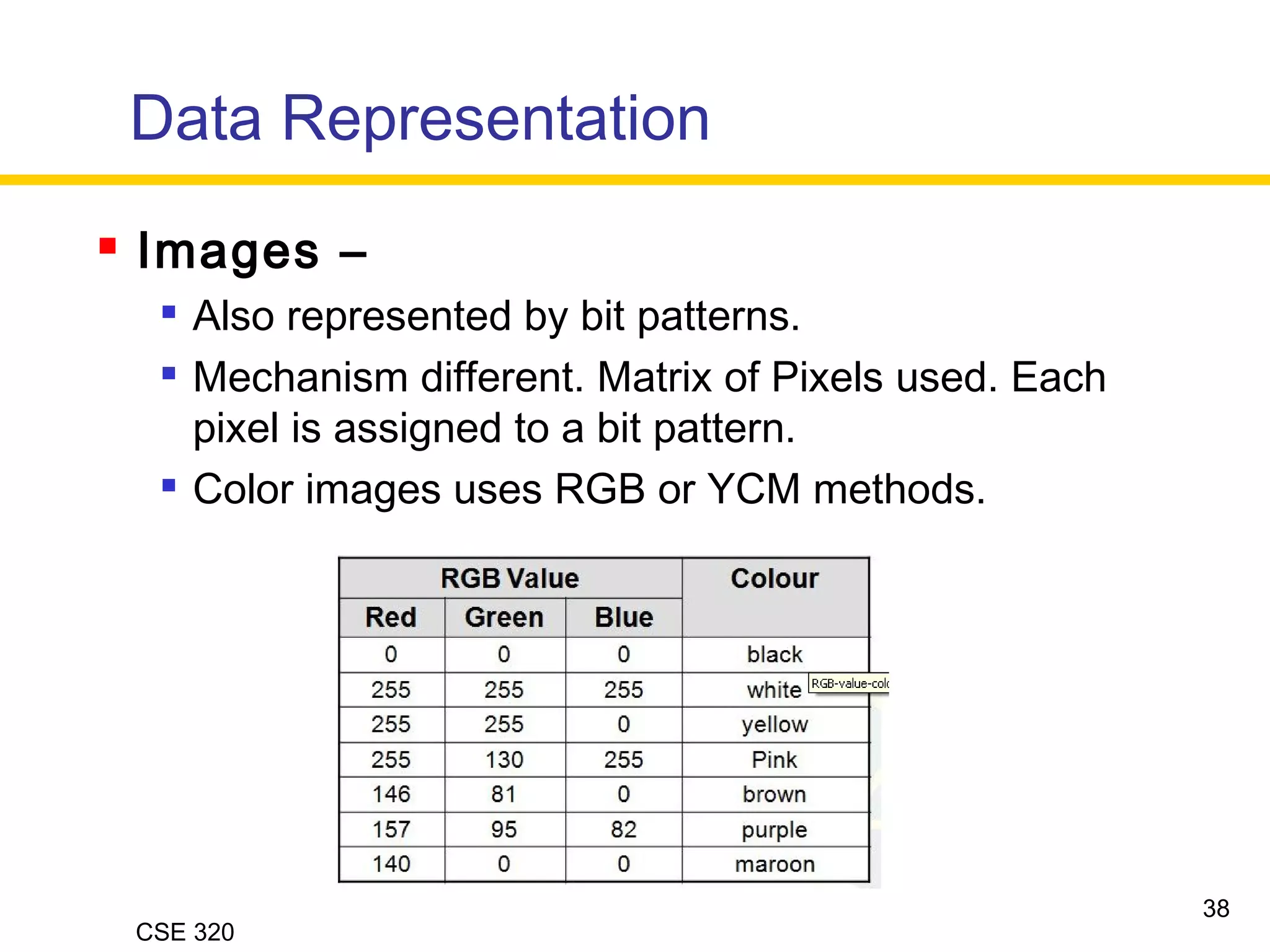
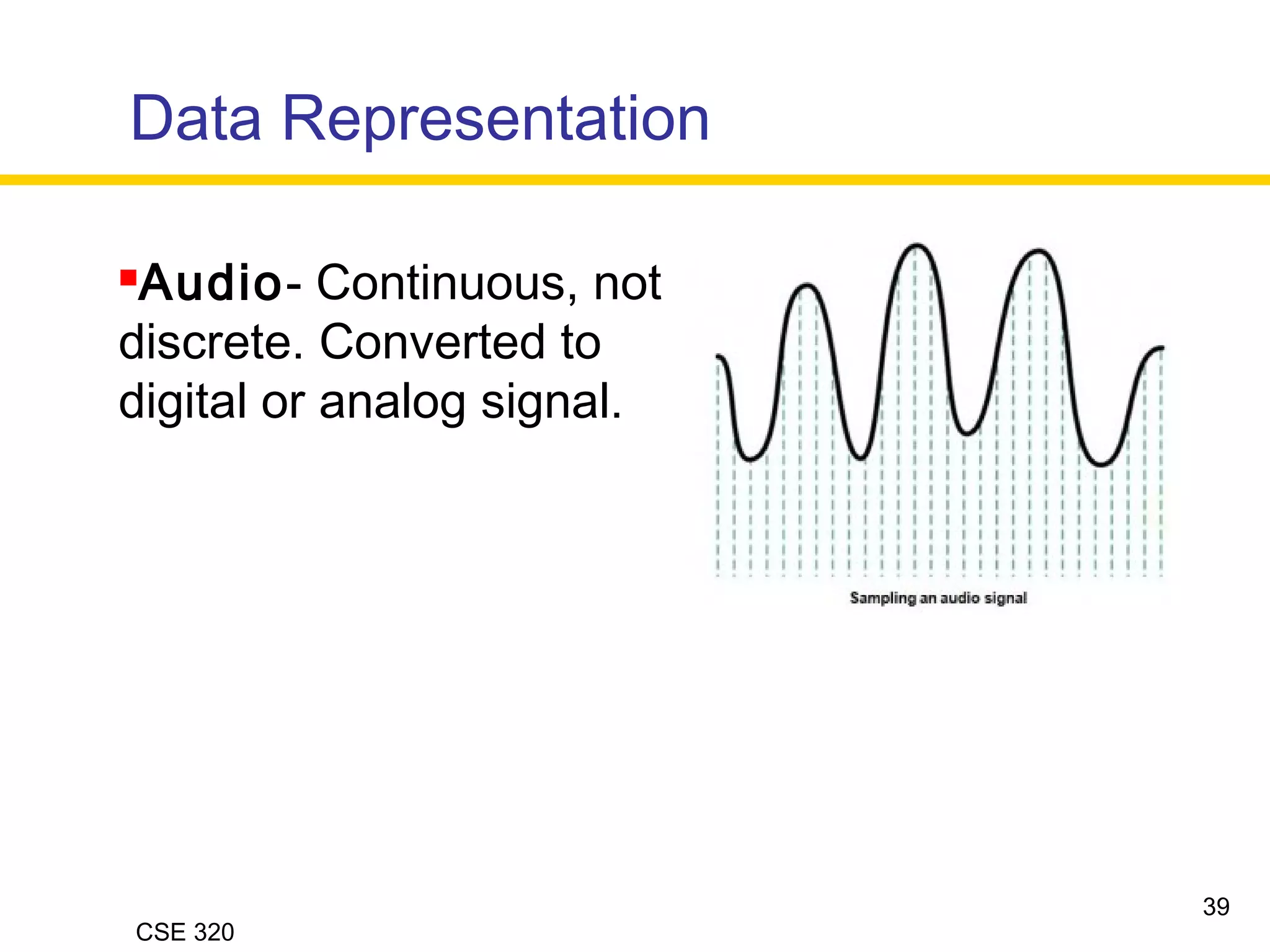
The document discusses the key elements of data communication, including:
1) Devices that exchange data via a transmission medium, such as computers.
2) The medium that allows devices to connect and exchange data, such as cables or wireless signals.
3) Messages in the form of data (zeros and ones) that travel over the medium.
4) Protocols that govern how messages flow across networks by establishing rules for communication.