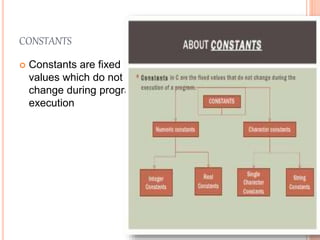
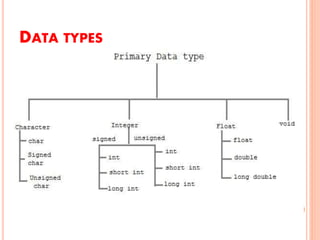
C is a powerful, structured programming language developed by Dennis Ritchie. It is a high-level language with low-level features that provides easy readability through comments. A C program is written, saved, compiled to check for errors, and then executed. There are six types of tokens in C - keywords, identifiers, constants, strings, special symbols, and operators - which are the smallest units that make up a C program. Variables are used to store values that can change during program execution, while constants represent fixed values. C supports several data types including integers, characters, floating-point numbers, and void.




![There are 6 different types of token in
c
Keywords (float,int,while etc)
Identifiers(main ,amount etc)
Constants ( 17.5 , -23.4 etc)
Strings ( “hello” , “lets go” )
Special symbols ( {},[],& )
Operators ( +,-,*,/ )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontocprogramming-151029154937-lva1-app6892/85/Introduction-to-c-programming-5-320.jpg)