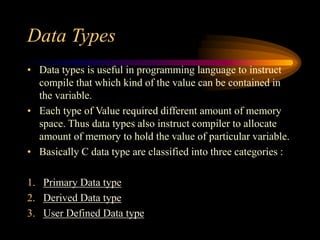
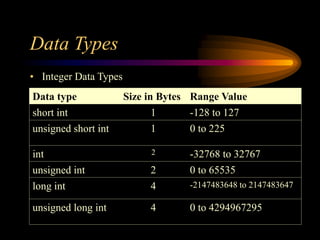
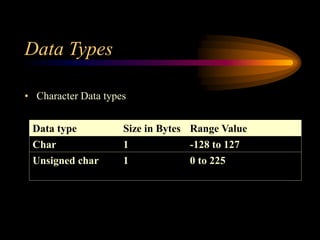
This document provides an overview of the basics of the C programming language, including its character set, tokens, symbolic constants, and data types. The character set of C consists of letters, digits, whitespace, and special symbols. The smallest units of a C program are tokens, which include keywords, identifiers, constants, operators, strings, and special symbols. Symbolic constants are user-defined names for fixed values, defined using the #define preprocessor directive. C supports primary, derived, and user-defined data types, including integer, floating-point, character, and other types that specify the size and range of variable values.


![Character Set
• Character set is a collection of characters that can be used
to write a program of particular language.
• Every language having their own set of characters.
• Character set of c consist of letters, digits, white space and
special symbols
• Letters : A-Z , a-z
• Digits : 0-9
• White spaces : Blank space, tab, new line,form feed,
carriage return
• Special symbols : # + - * / % & ! , . : ; $ ^ | ~ () {} [] <> =
_ “ ‘ ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cppresentation-190717151902/85/Cp-presentation-3-320.jpg)



![C Tokens
5. String :
• A string is a sequence of characters that is enclosed
between double quotation marks.
• FOR EXAMPLE : “Hello”
6. Special Symbols :
• Following are the special Symbols used in c language :
• # ,+,-,*,/,%,&,| ,~,`,”,:,;,!,?,/,_(),{},[],<>,=,
• The C program consists of different types of tokens.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cppresentation-190717151902/85/Cp-presentation-7-320.jpg)