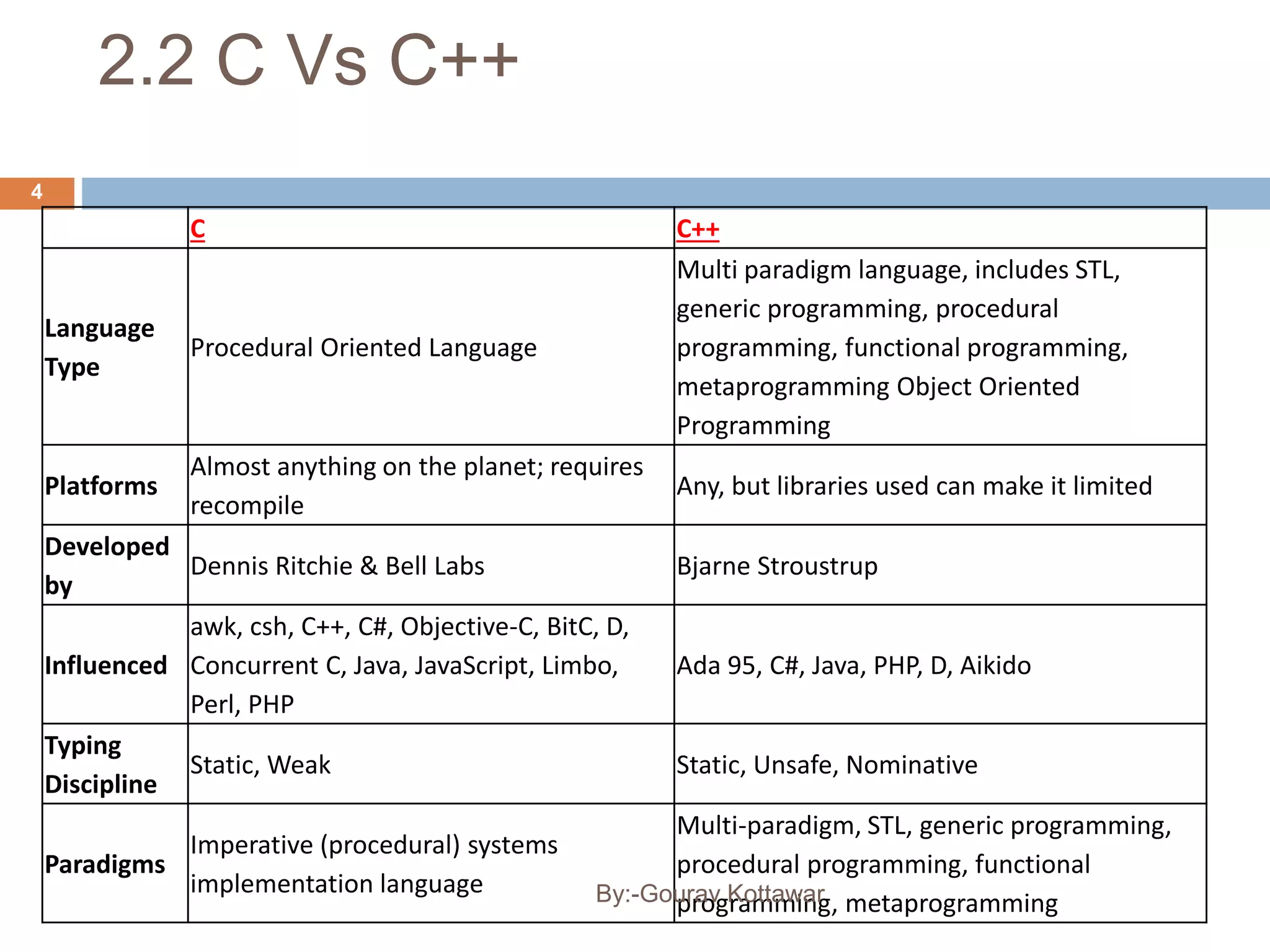
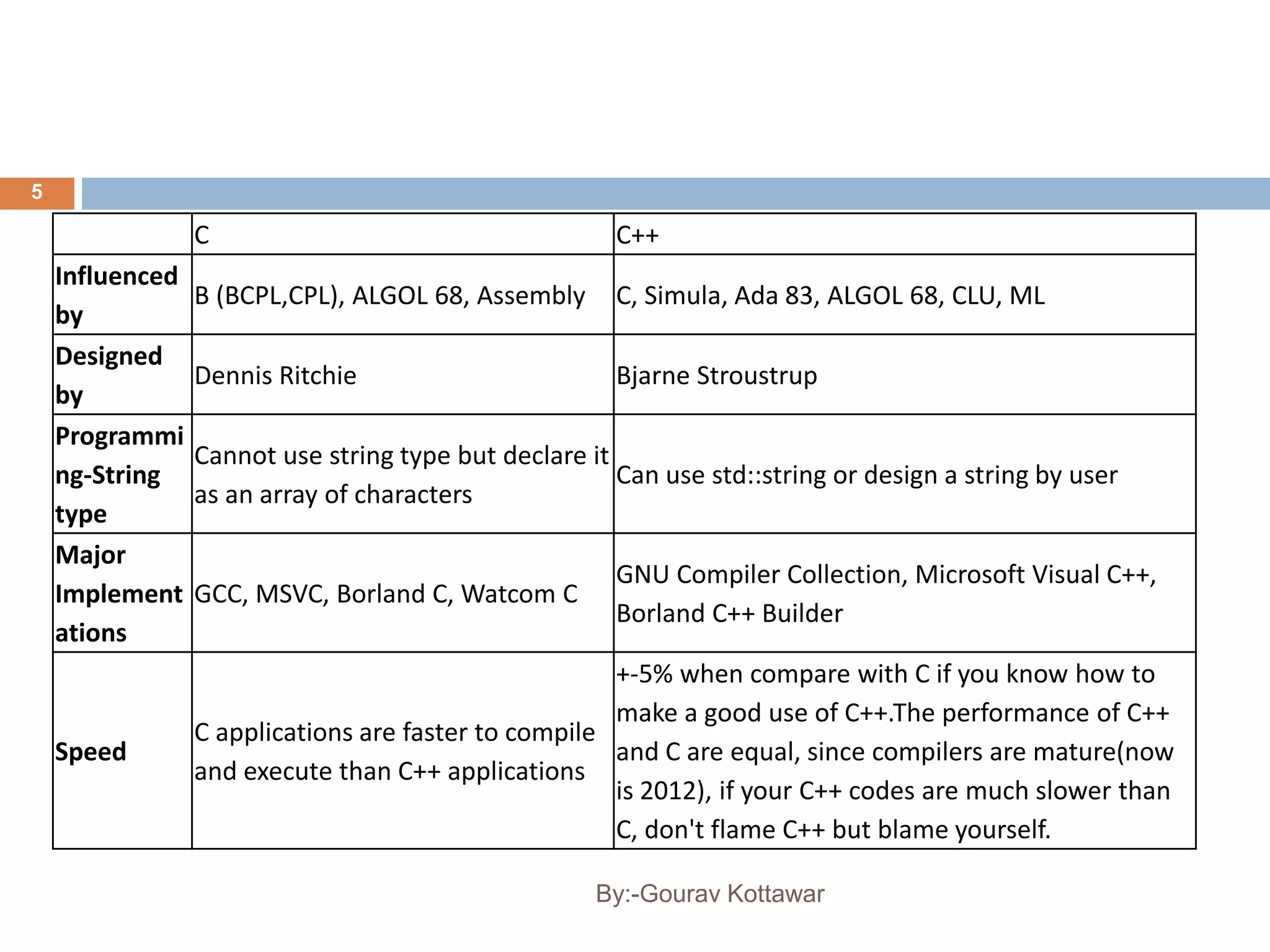
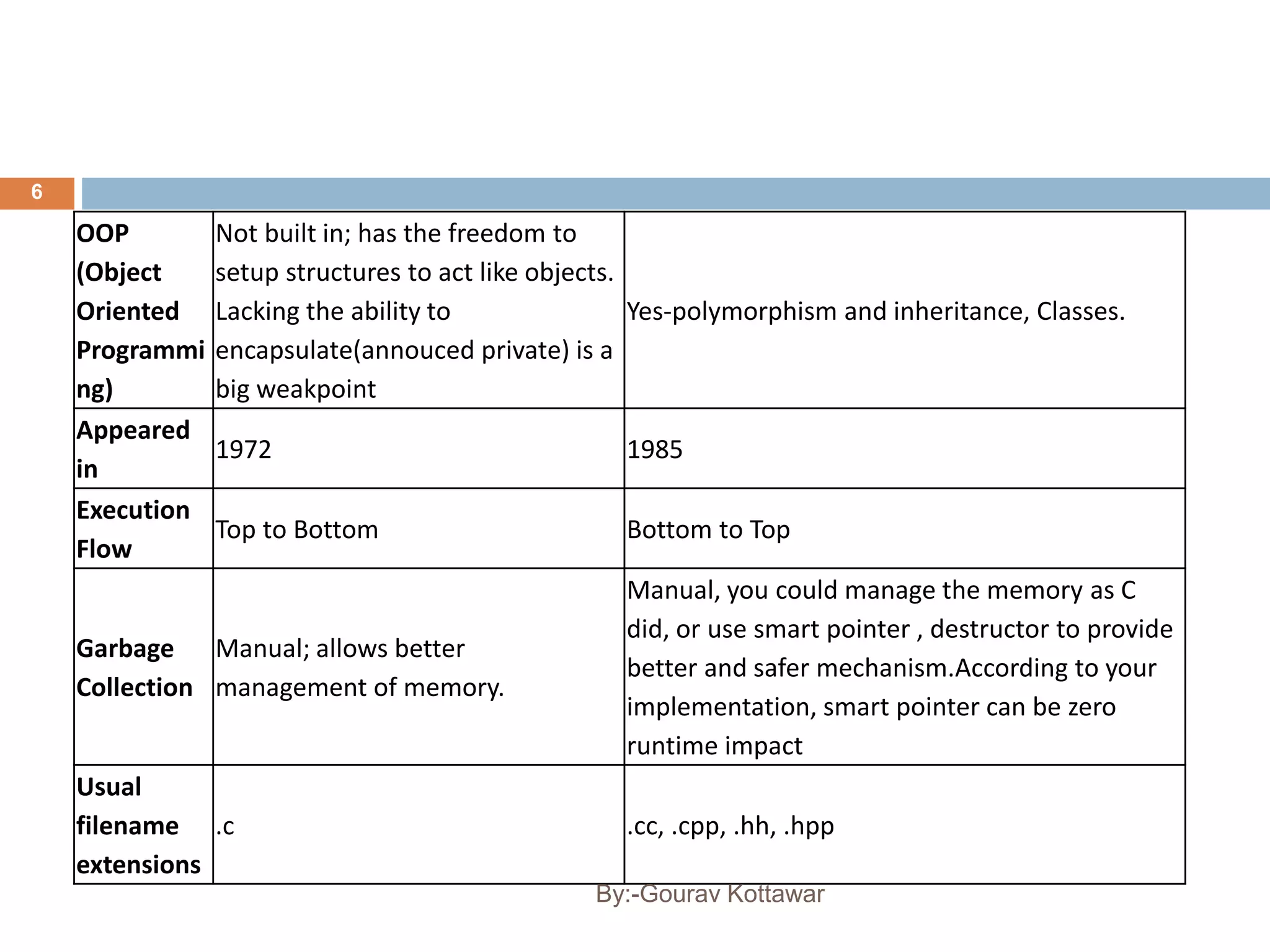
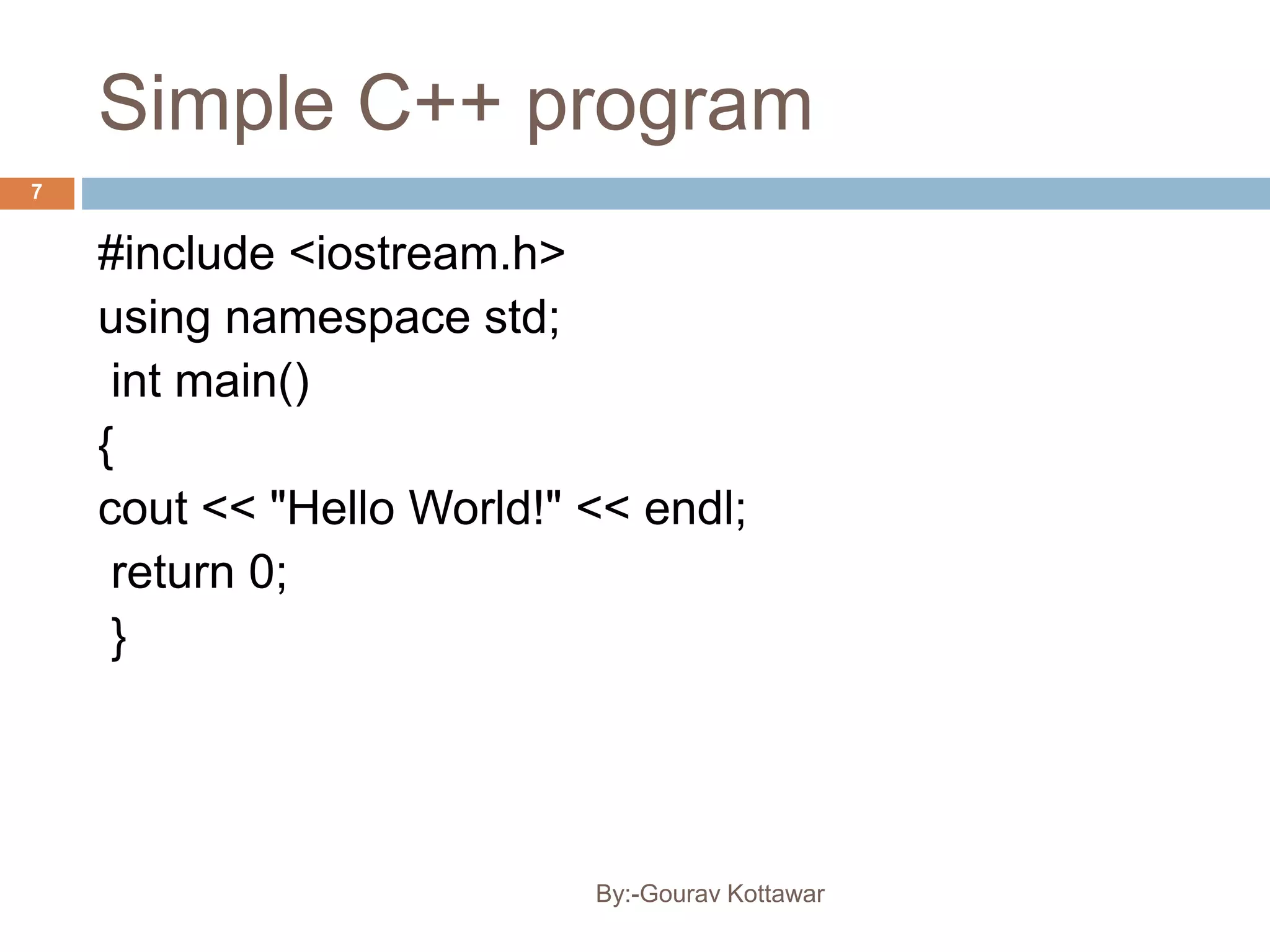
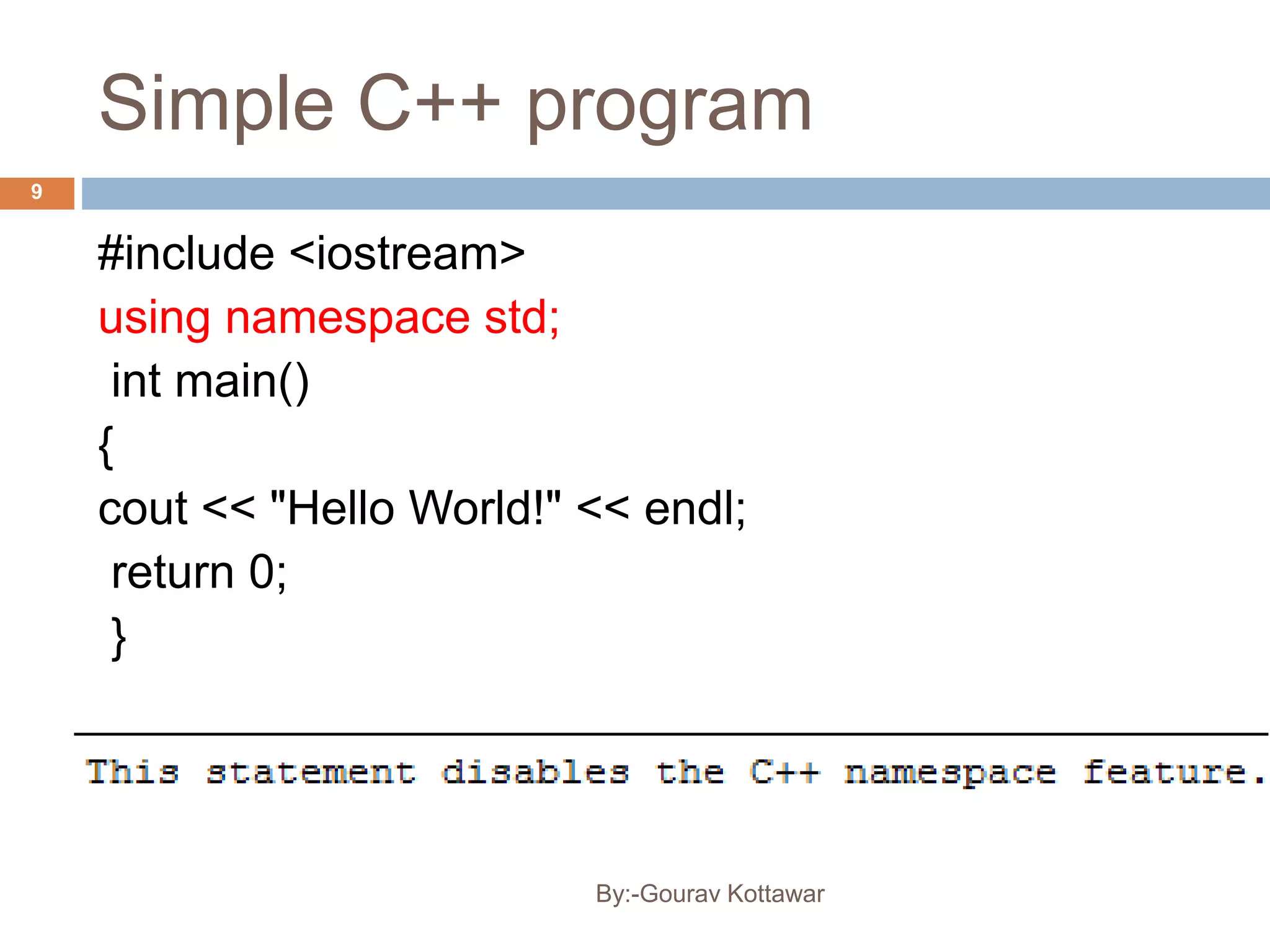
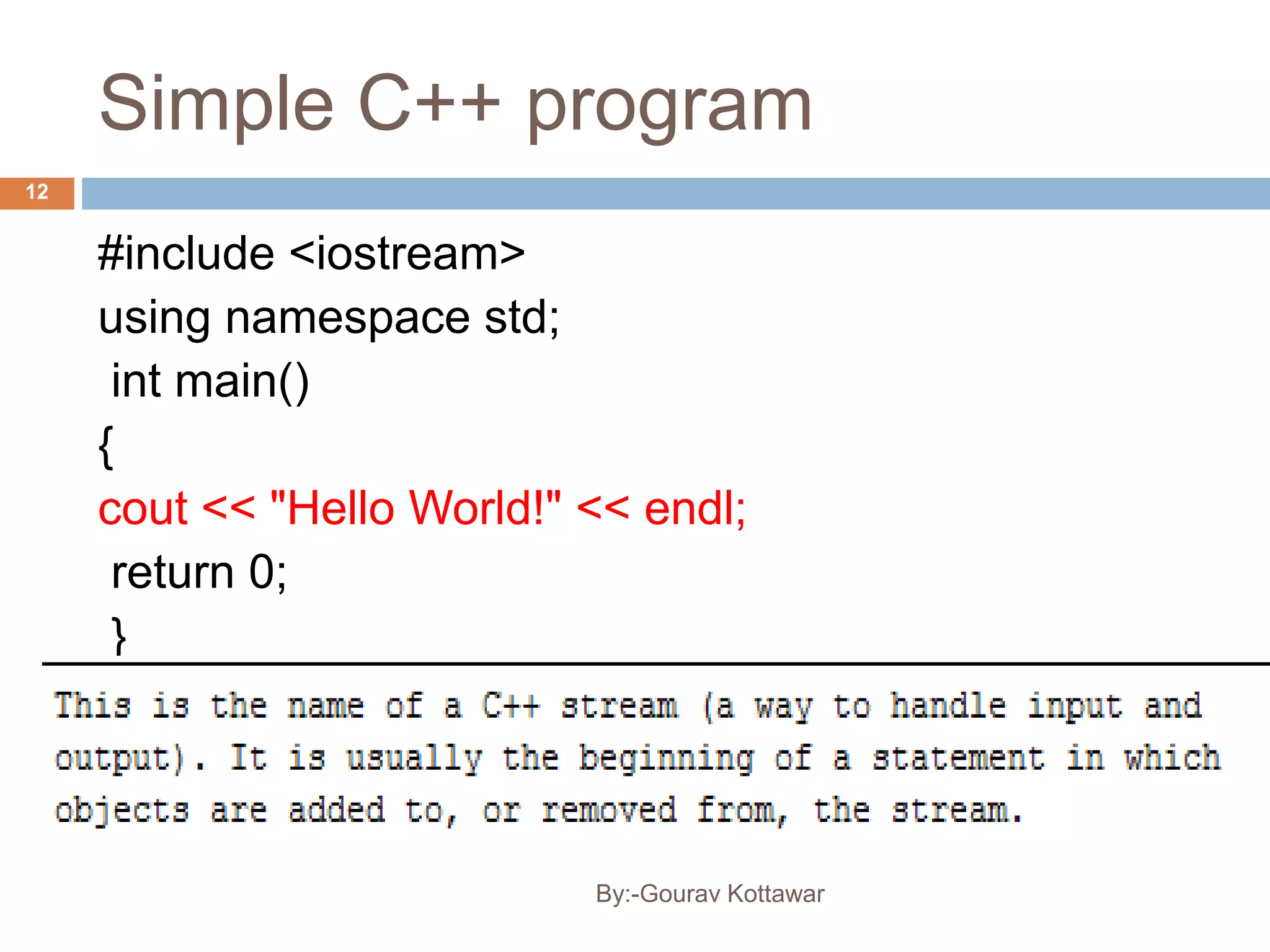
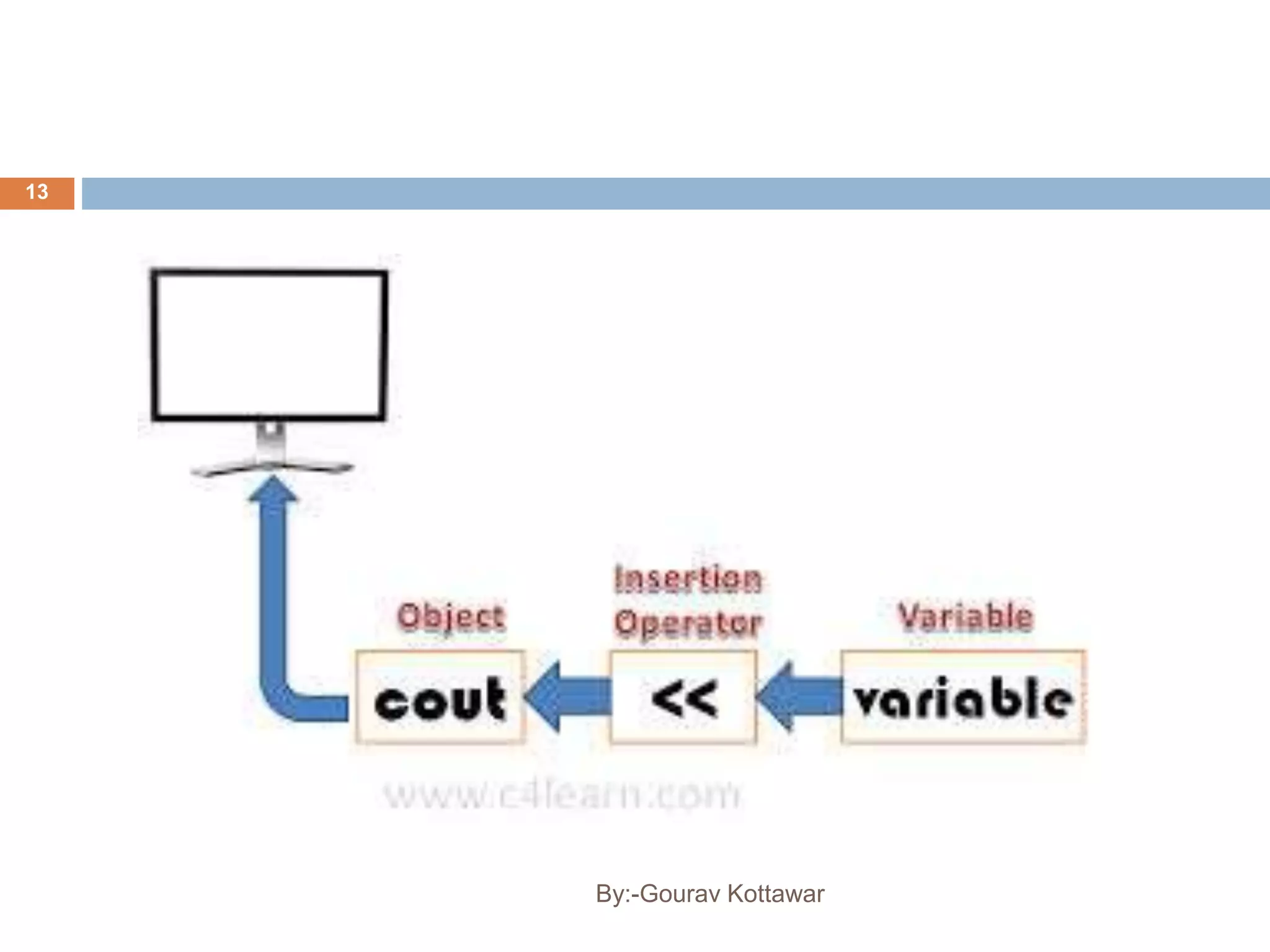
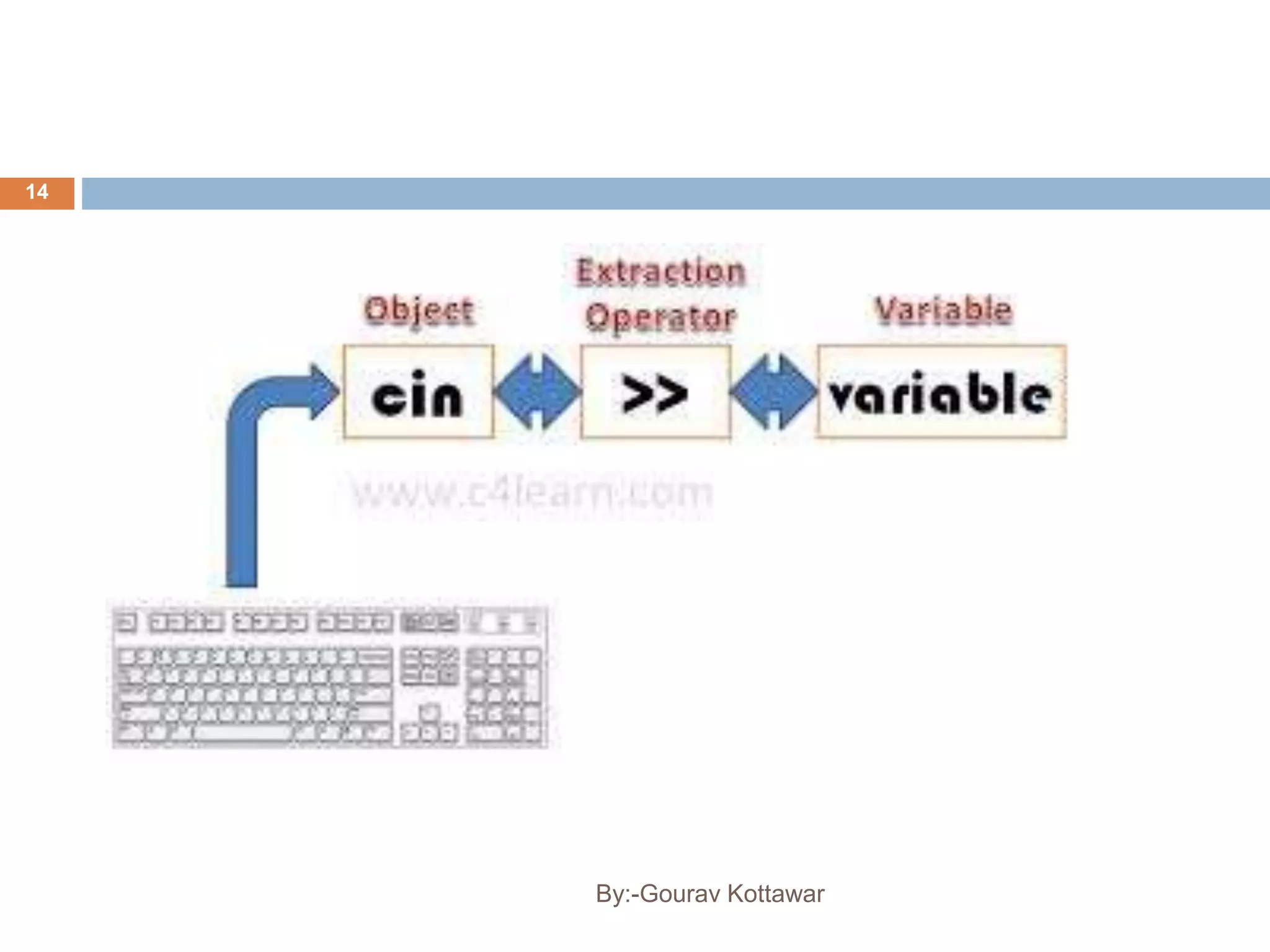
The document provides an introduction to the basics of C++, including a brief history of C and C++, comparing C and C++, and providing a simple C++ "Hello World" program example. C++ was created by Bjarne Stroustrup in 1979 as an enhancement to the C language by adding object-oriented programming capabilities while still maintaining efficiency and flexibility. The document outlines some key differences between C and C++, such as C++ supporting object-oriented programming, classes, and templates while maintaining similar performance to C.