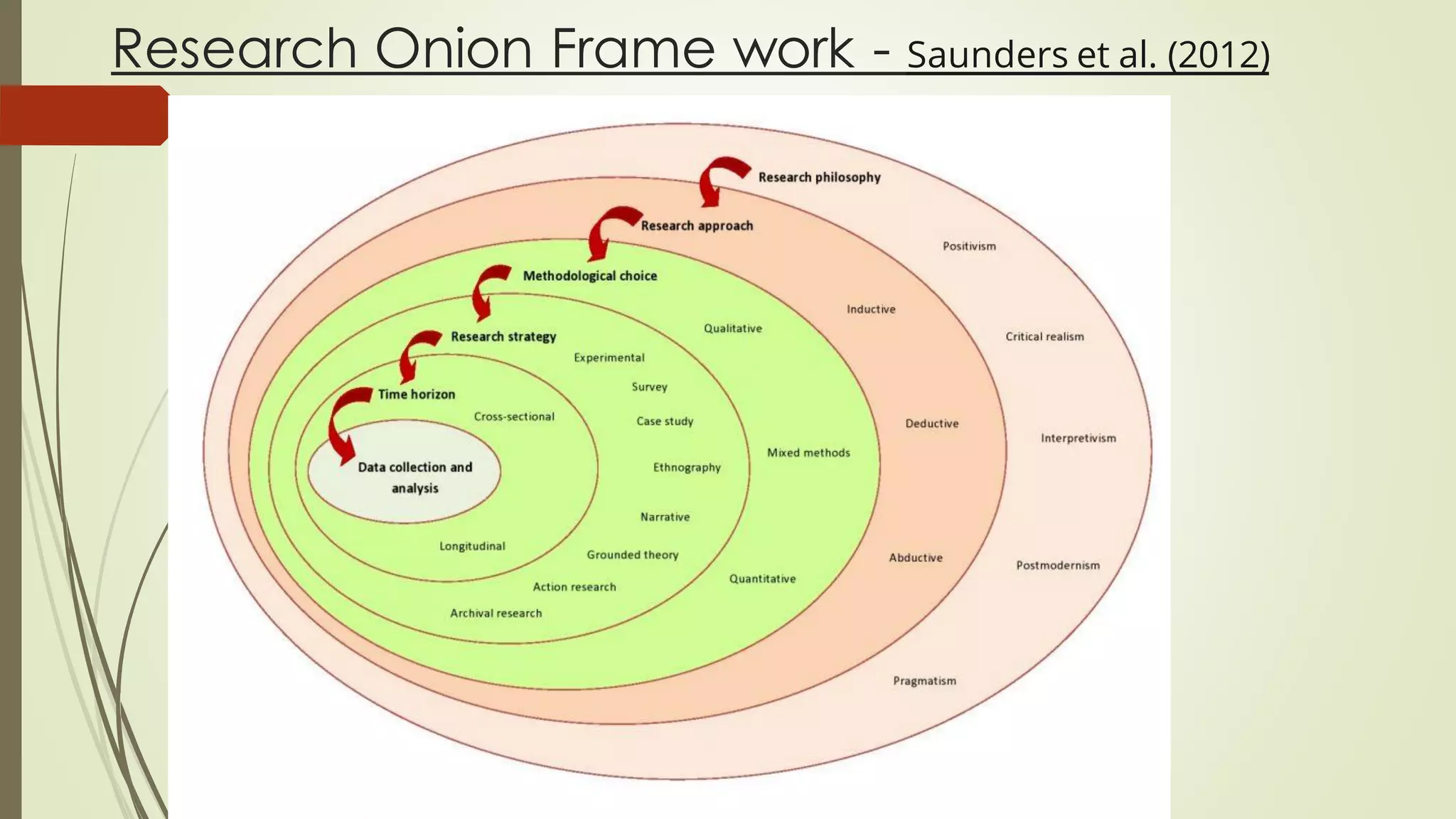
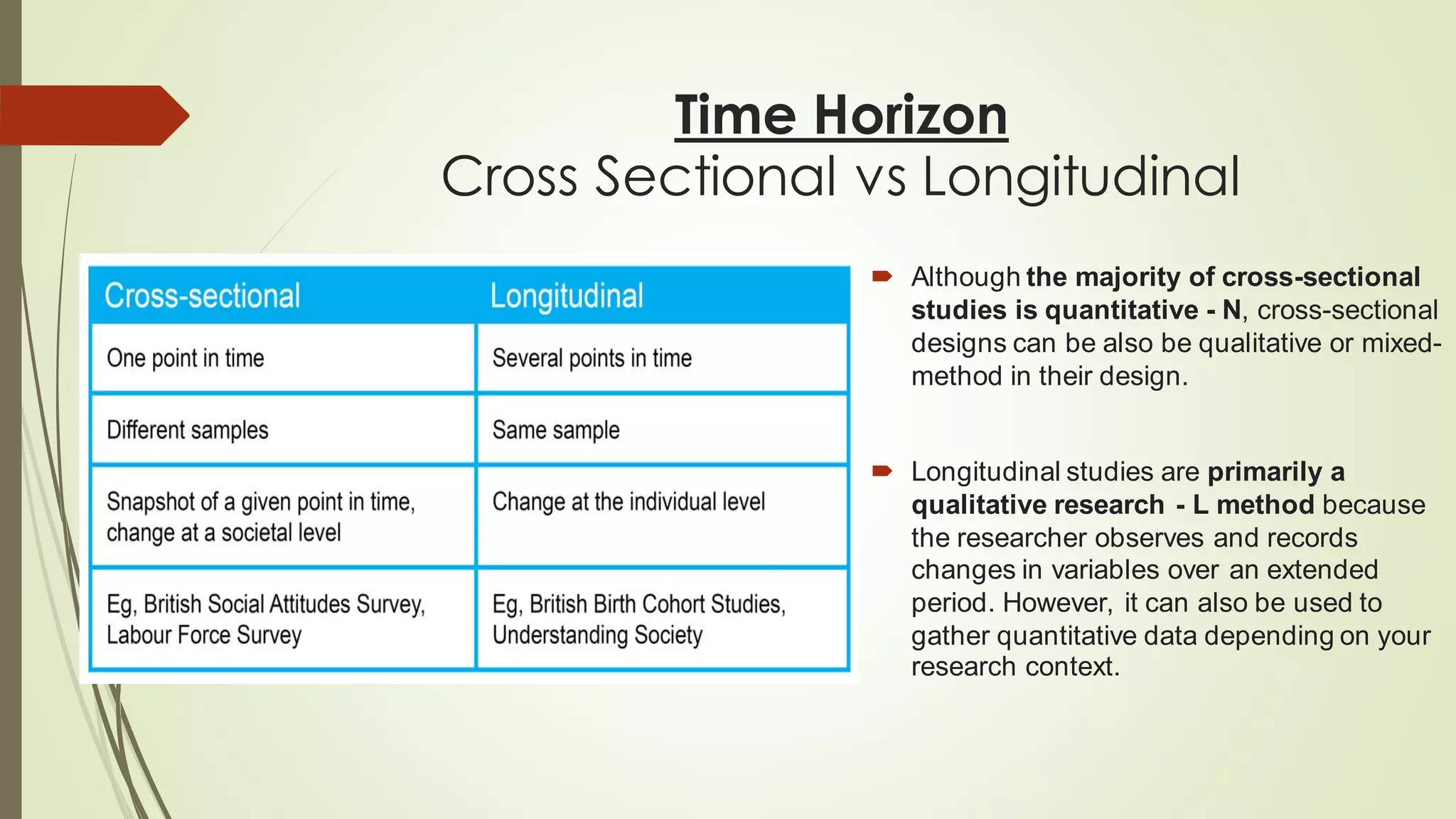
This document provides an overview of research methodology basics. It defines research and the scientific method. There are several key steps in the scientific method including making observations, asking questions, designing a study, and analyzing results. The document also discusses different research philosophies like positivism and interpretivism. Common research strategies are described such as experimental, case study, and survey methods. Research can have a cross-sectional or longitudinal time horizon and employ qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods. Understanding research methodology foundations helps researchers design effective studies.