Embed presentation
Download to read offline




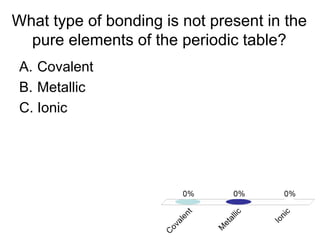
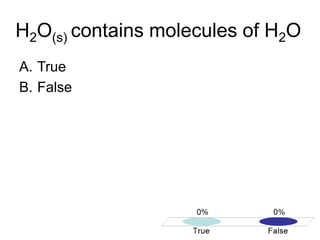
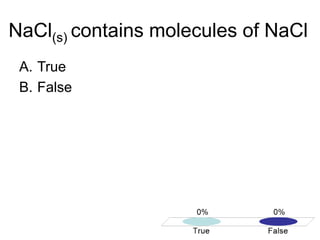
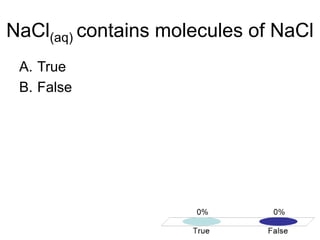

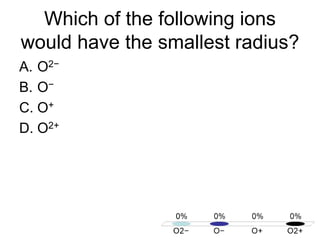
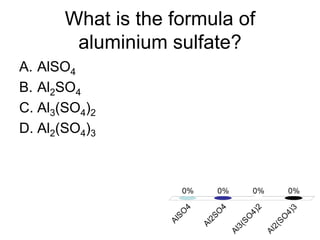
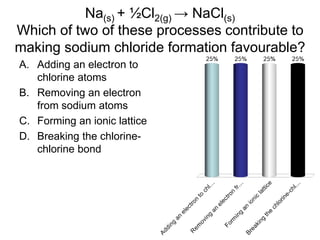

This document discusses different types of bonding between atoms, including ionic and covalent bonding. It addresses why atoms form bonds, the types of bonds present in pure elements versus compounds, and examples of ionic compounds like NaCl, H2O and their structures. Multiple choice questions are also included to test understanding of ion formation, ionic compound formulas, and which processes contribute to making ionic bond formation energetically favorable.











