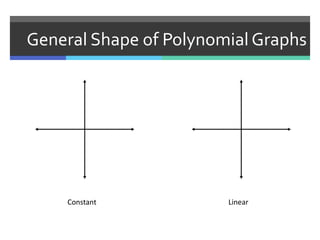
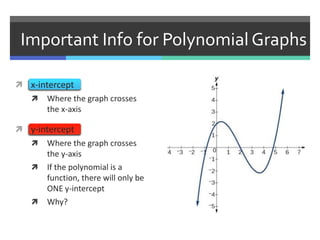
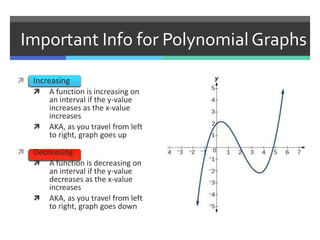
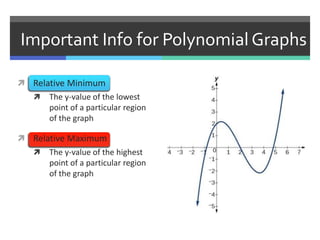
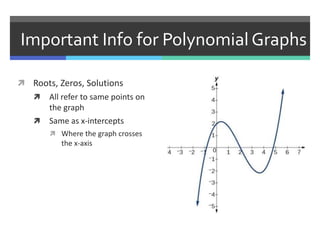
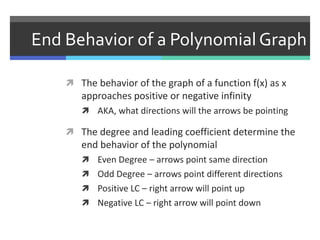
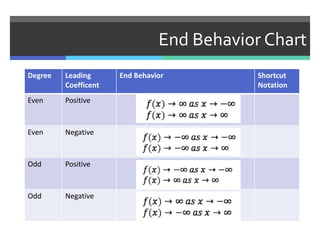
This document discusses polynomials and their graphs. It defines a polynomial as an expression with two or more algebraic terms separated by plus and minus signs. Polynomials are named based on their degree and number of terms, with the degree being the highest exponent of its terms. The general shapes of polynomial graphs are constant for linear polynomials, parabolic for quadratics, cubic for cubics, and so on. Important features of polynomial graphs discussed include x-intercepts, y-intercepts, regions of increase/decrease, relative maxima/minima, and end behavior determined by degree and leading coefficient.