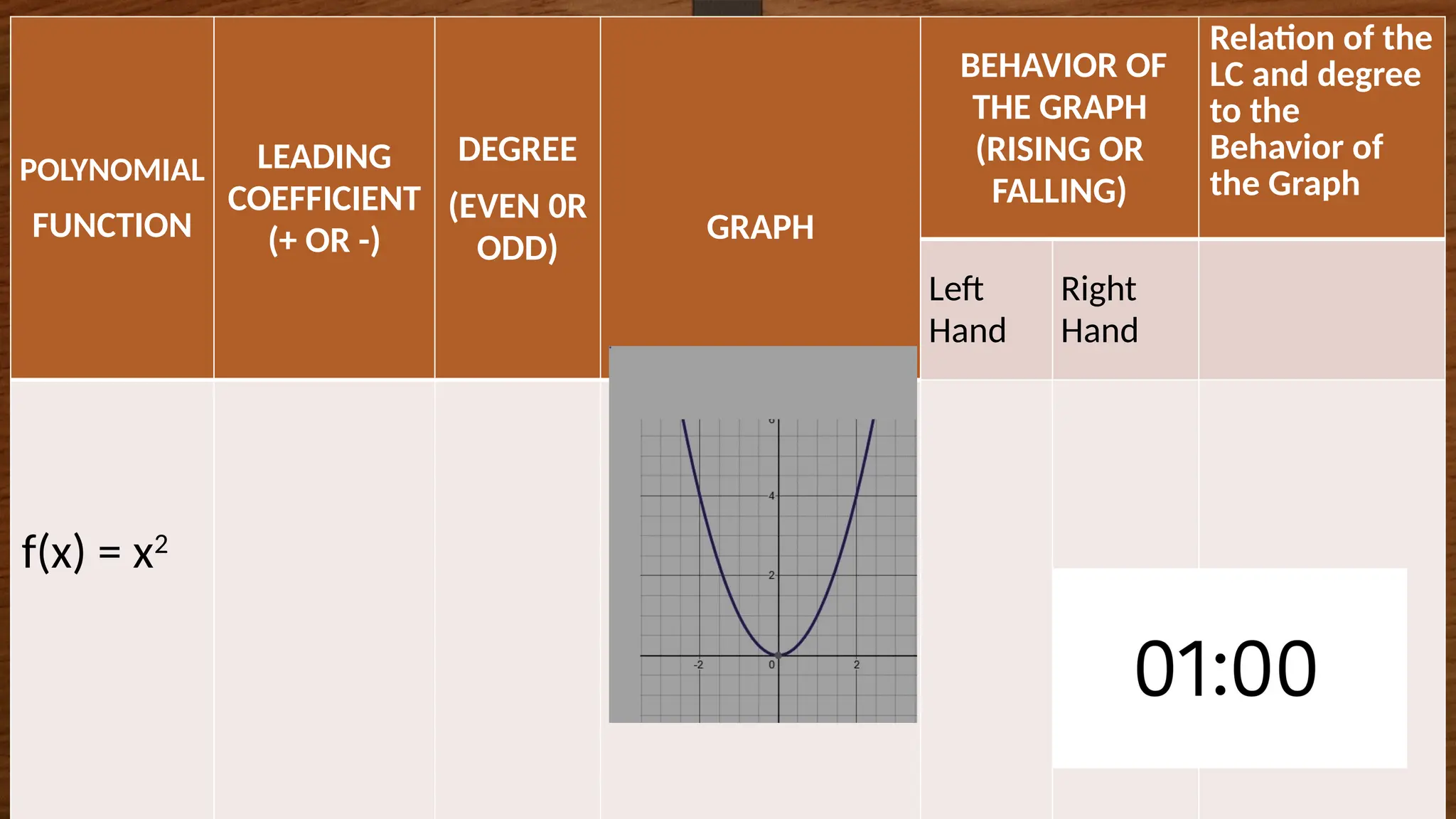
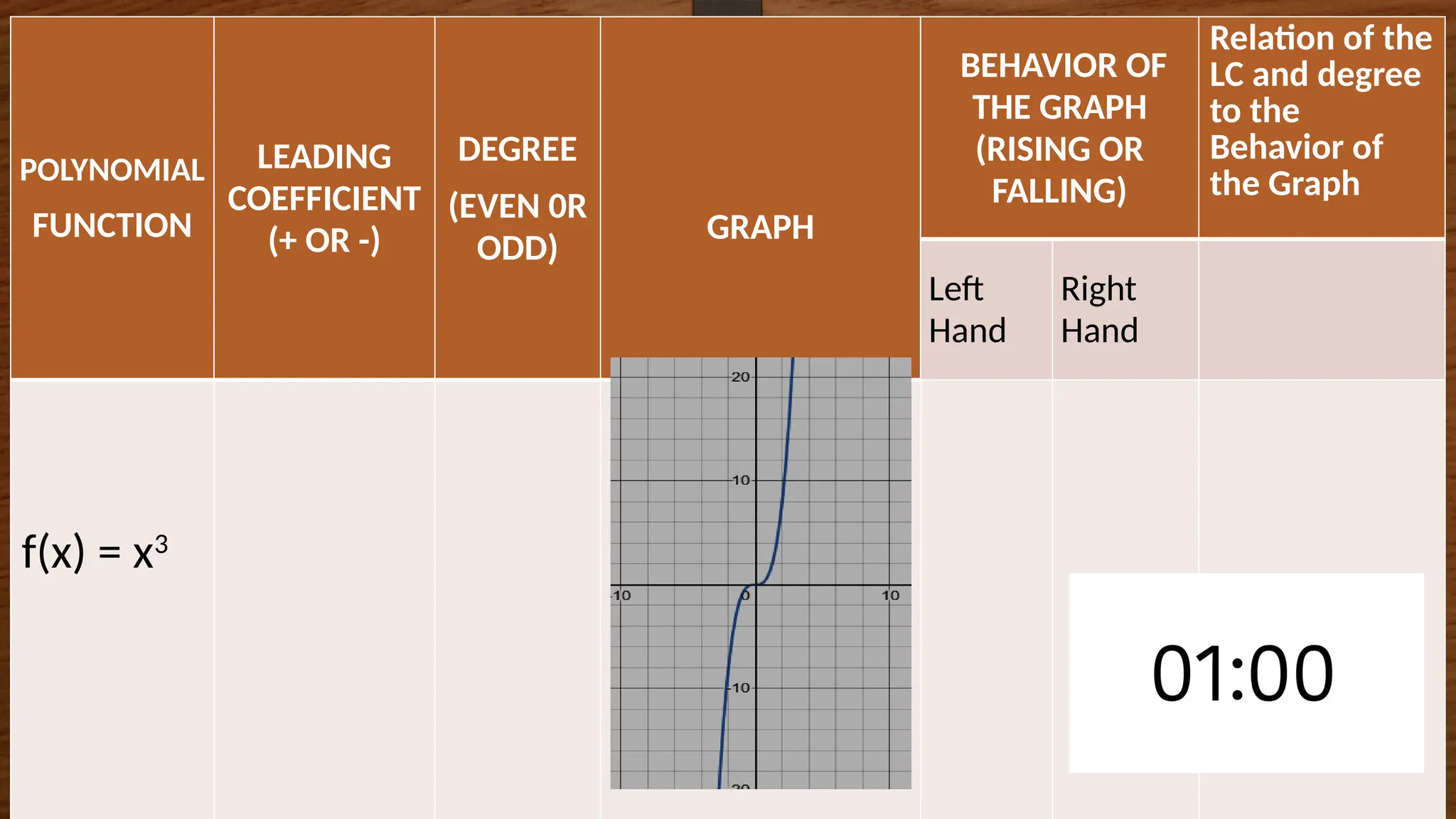
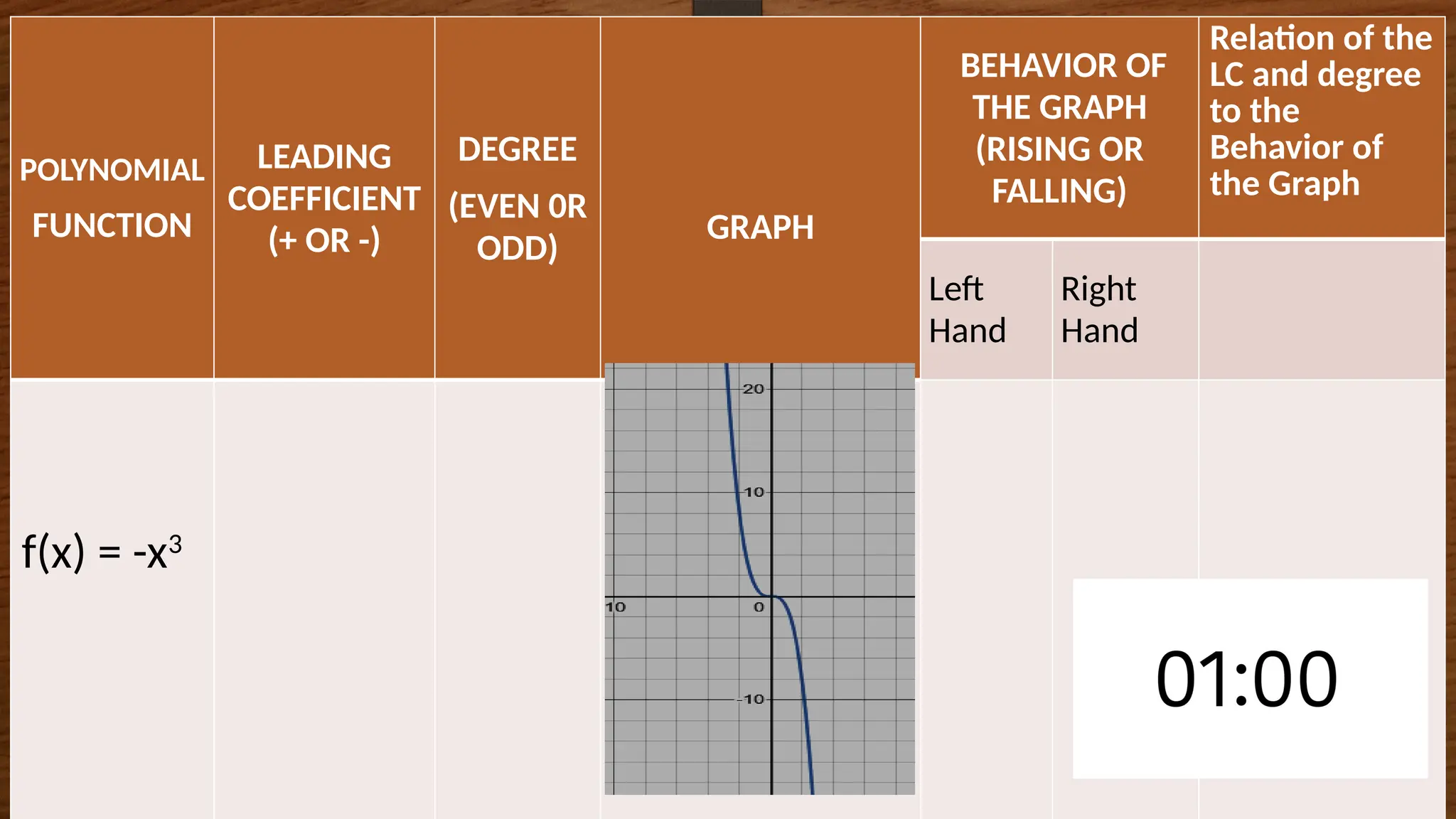
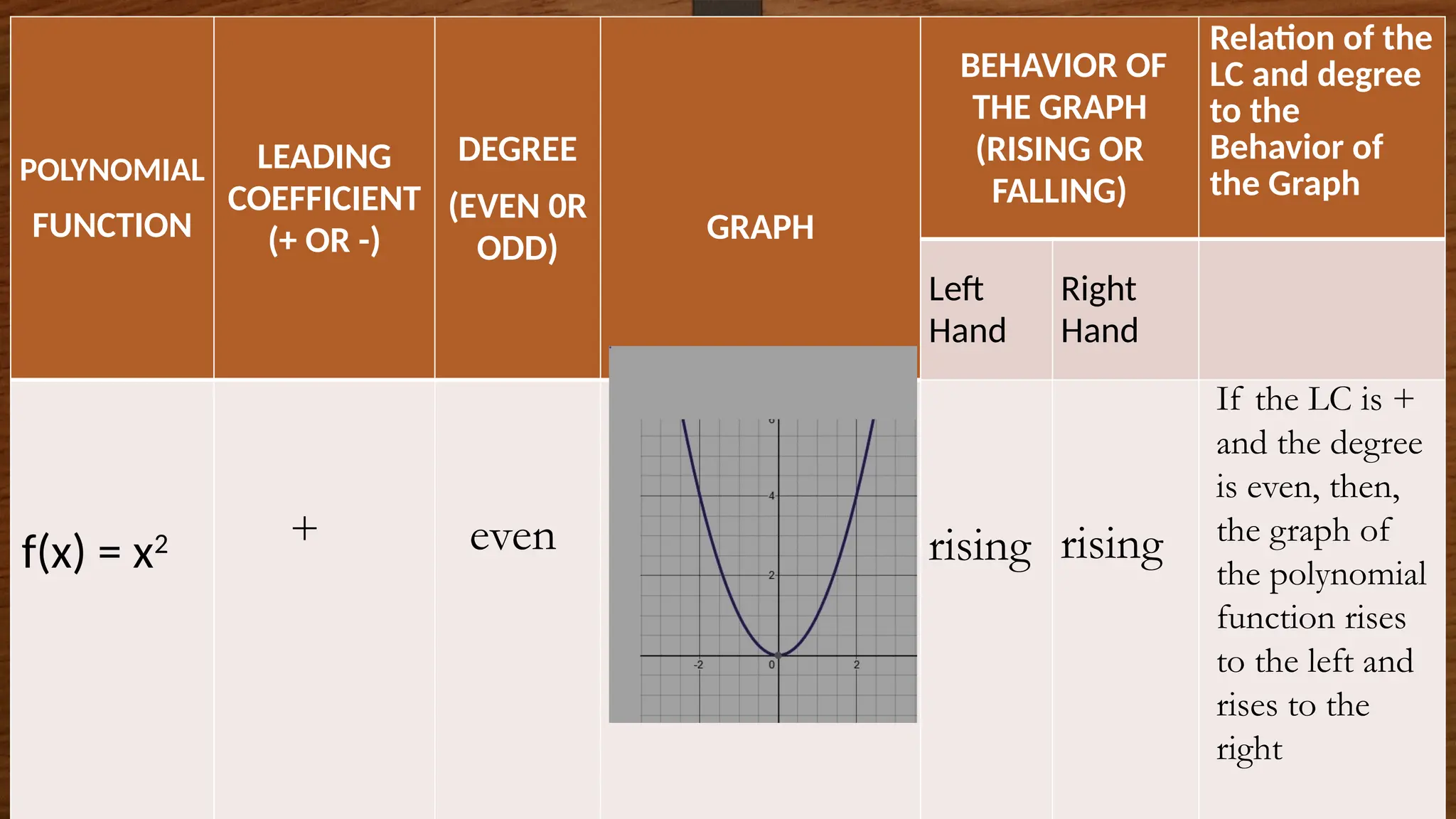
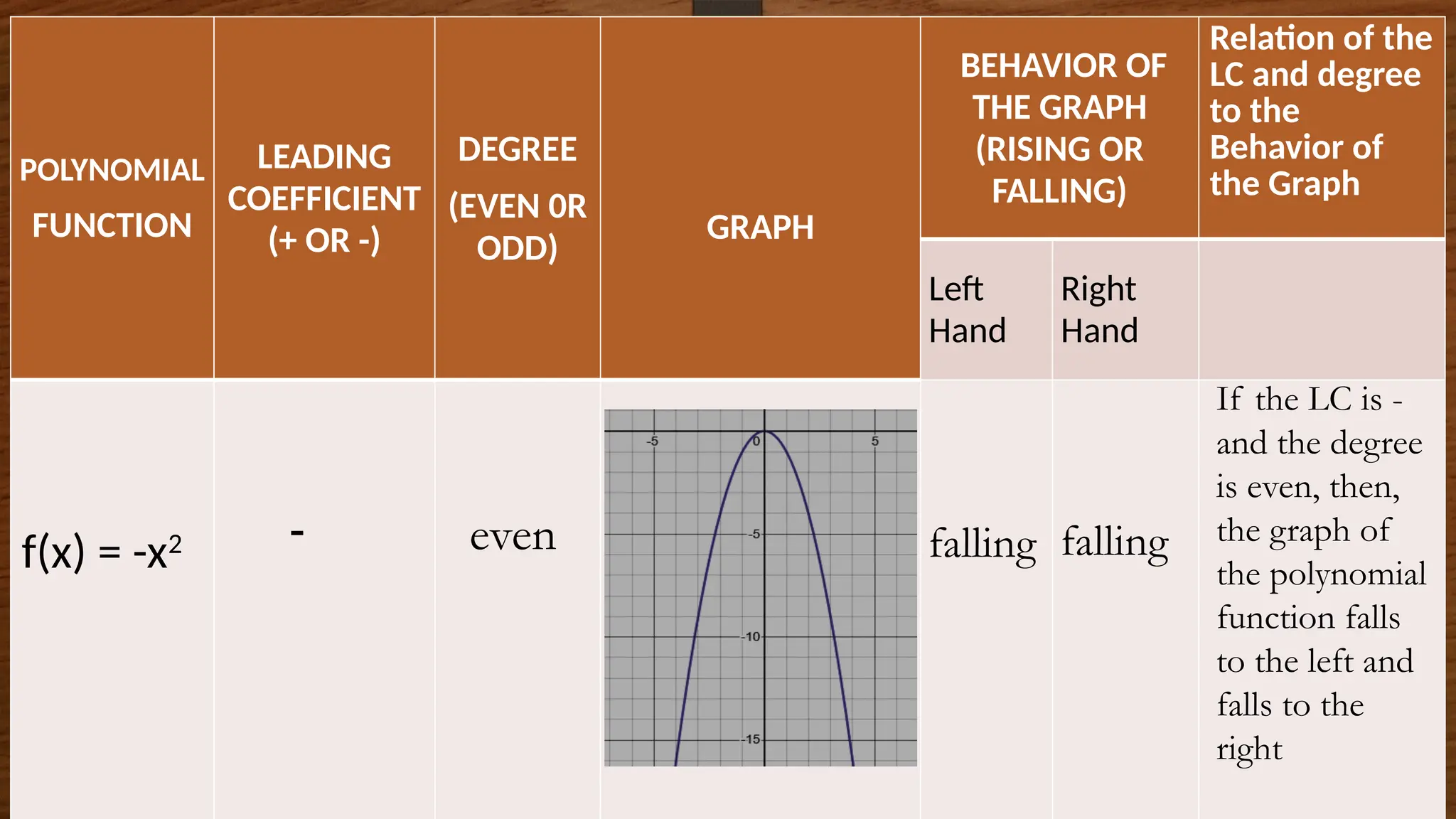
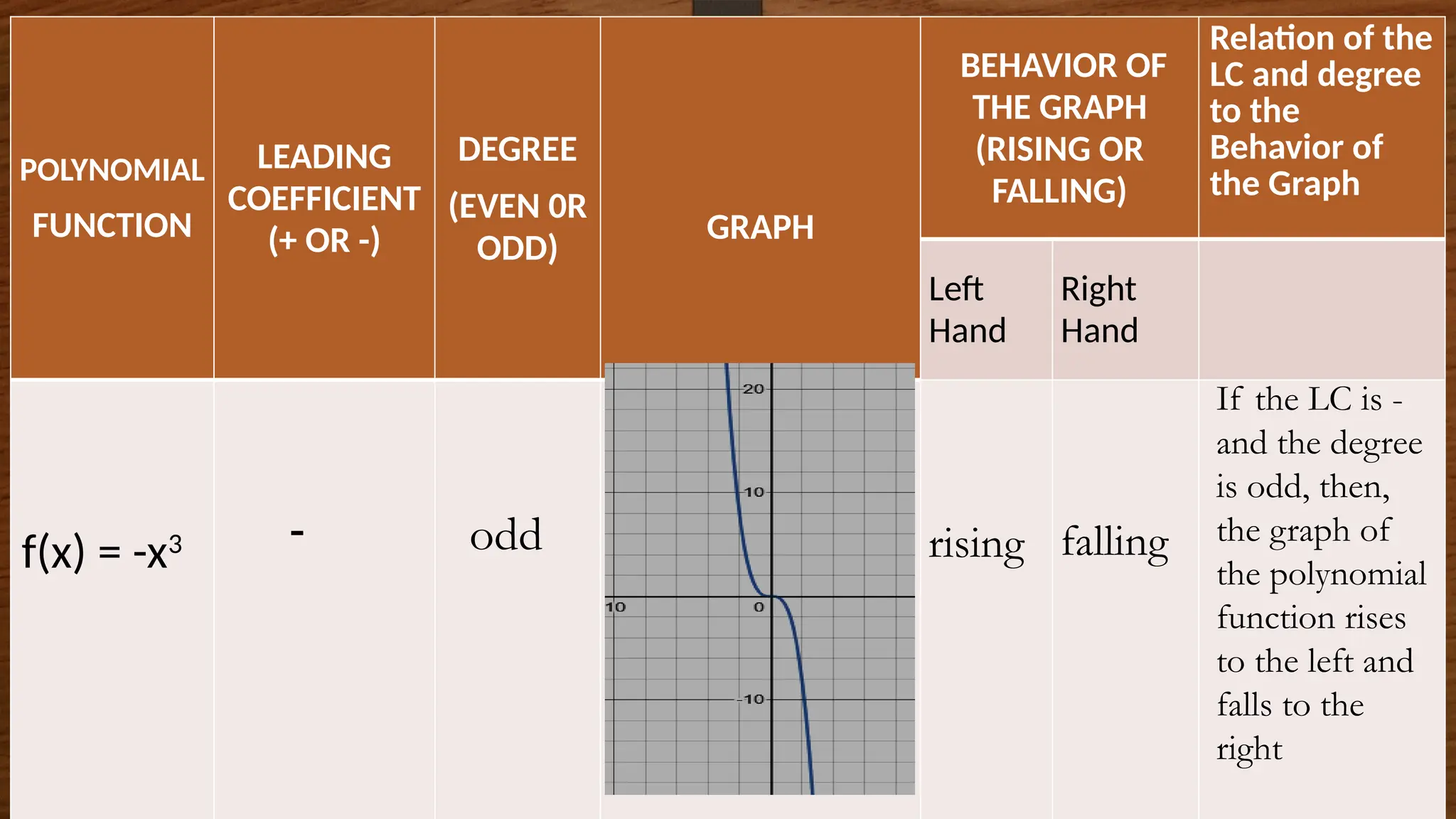
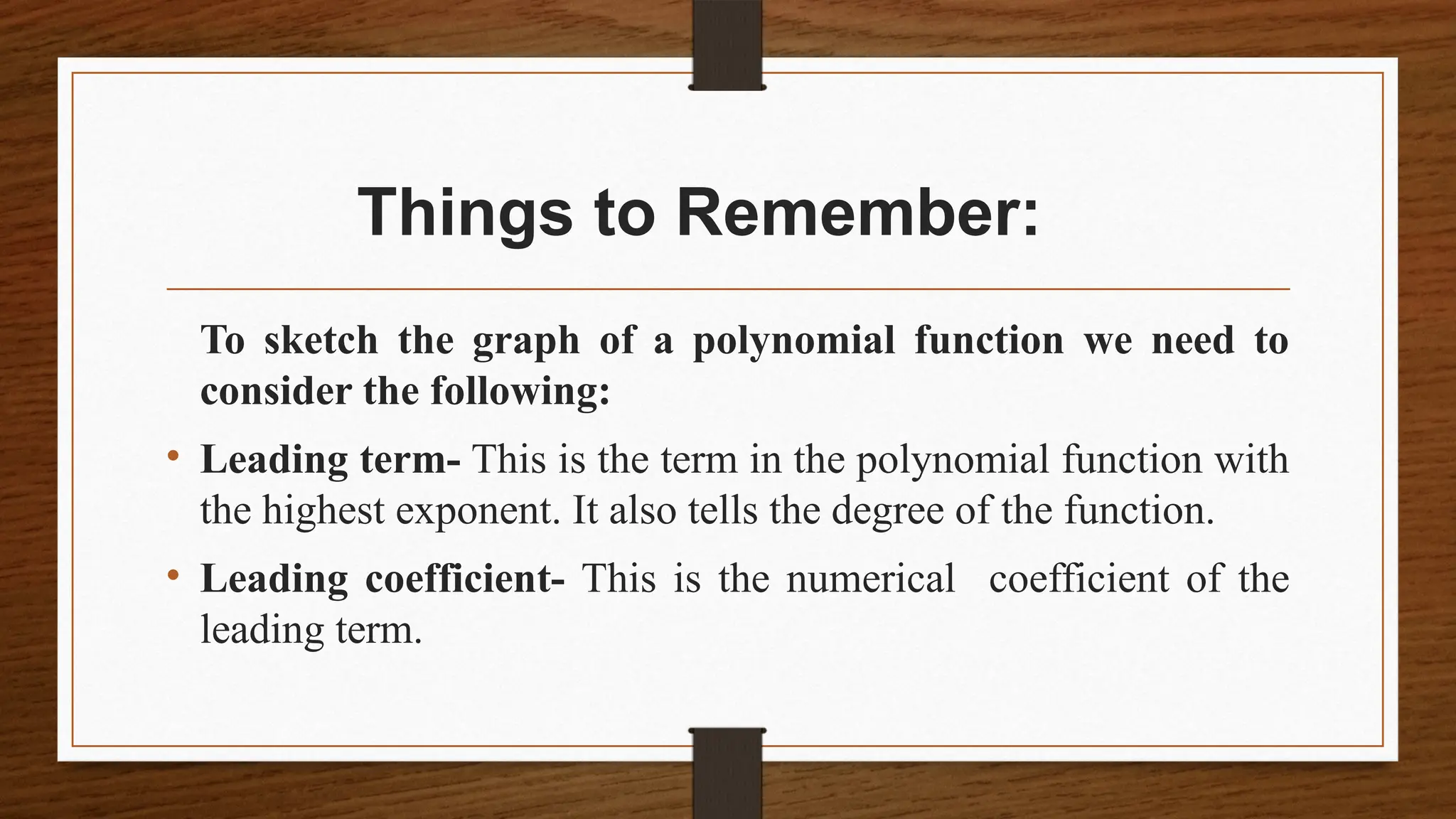
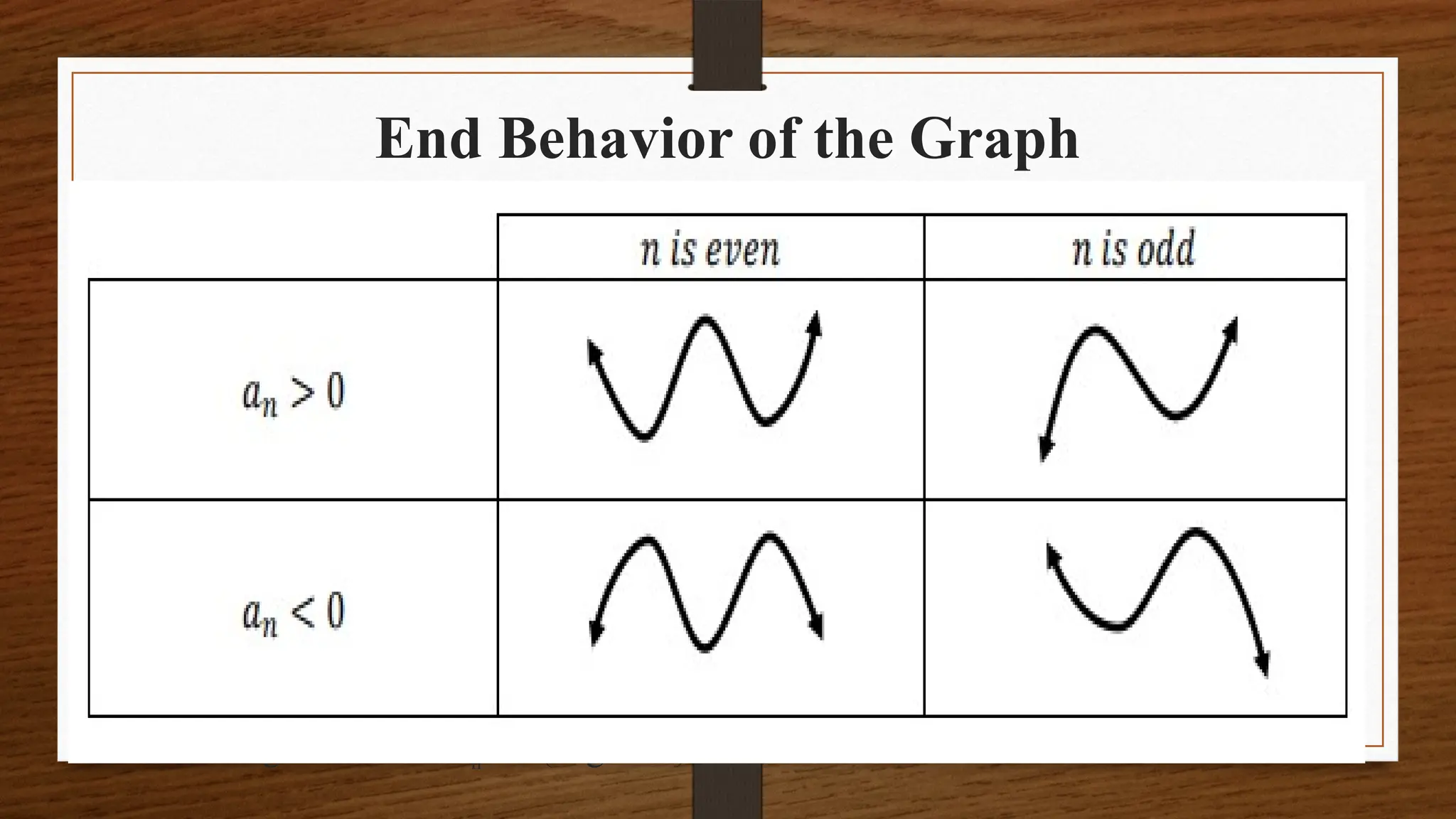
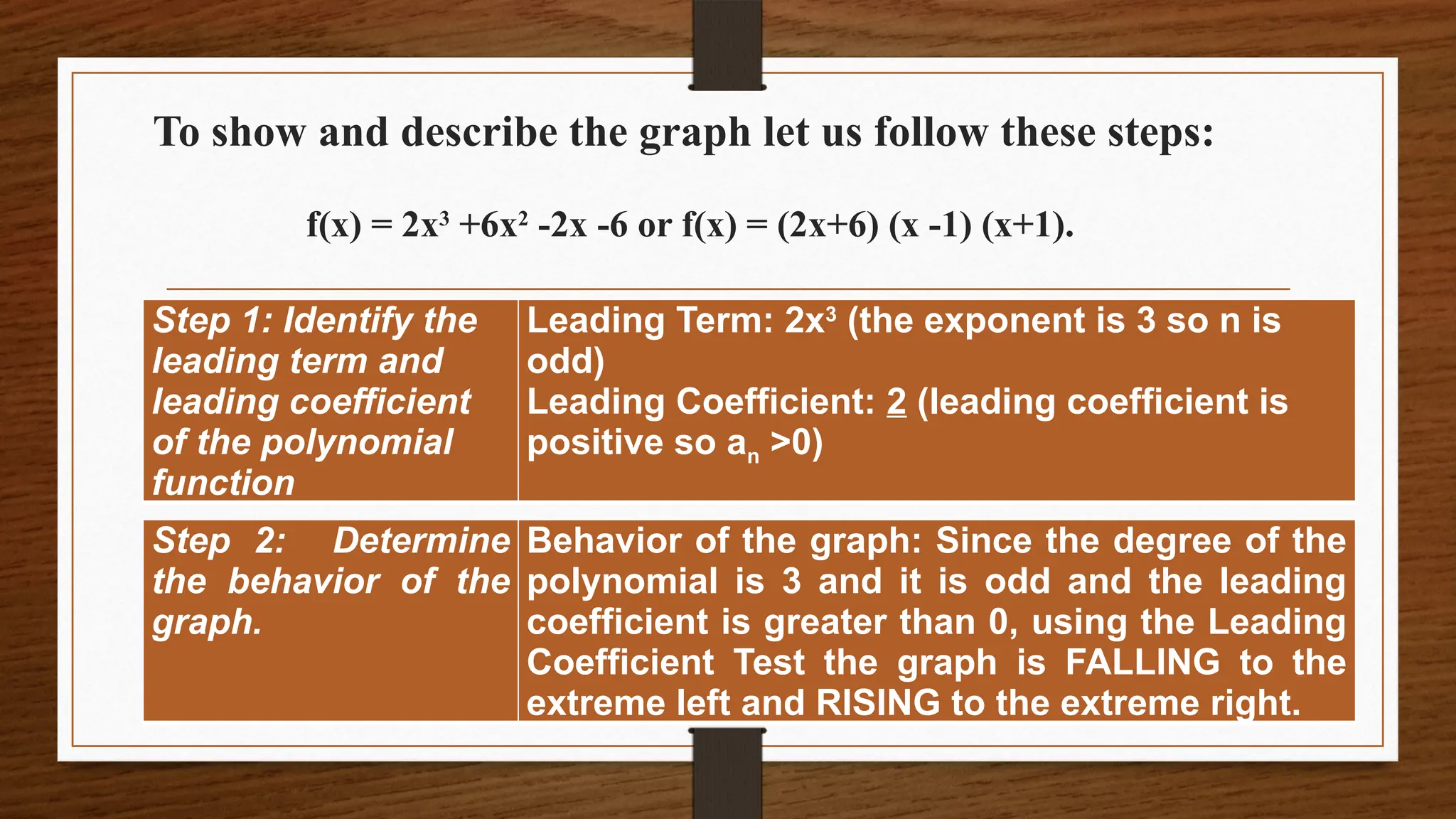
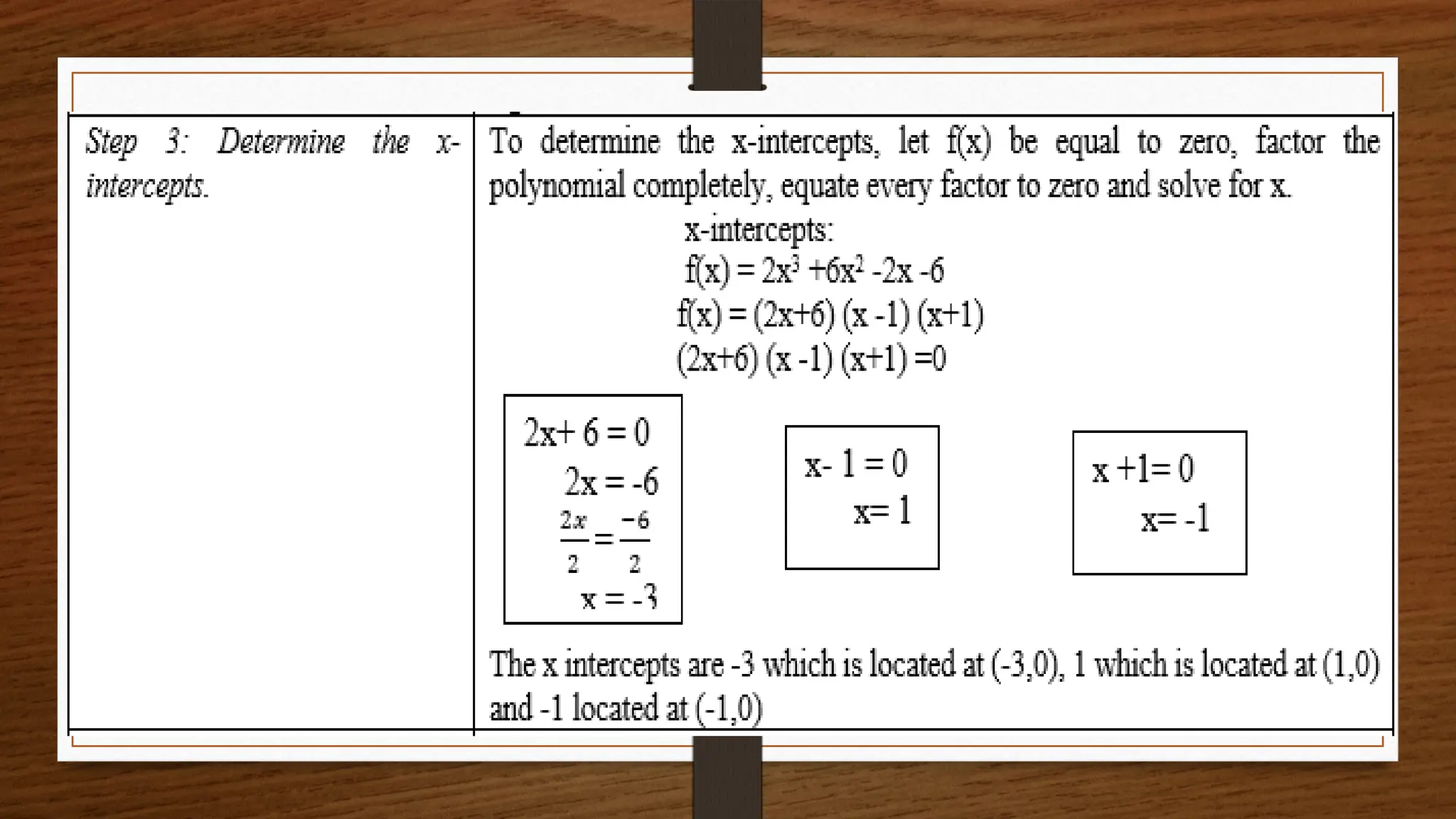
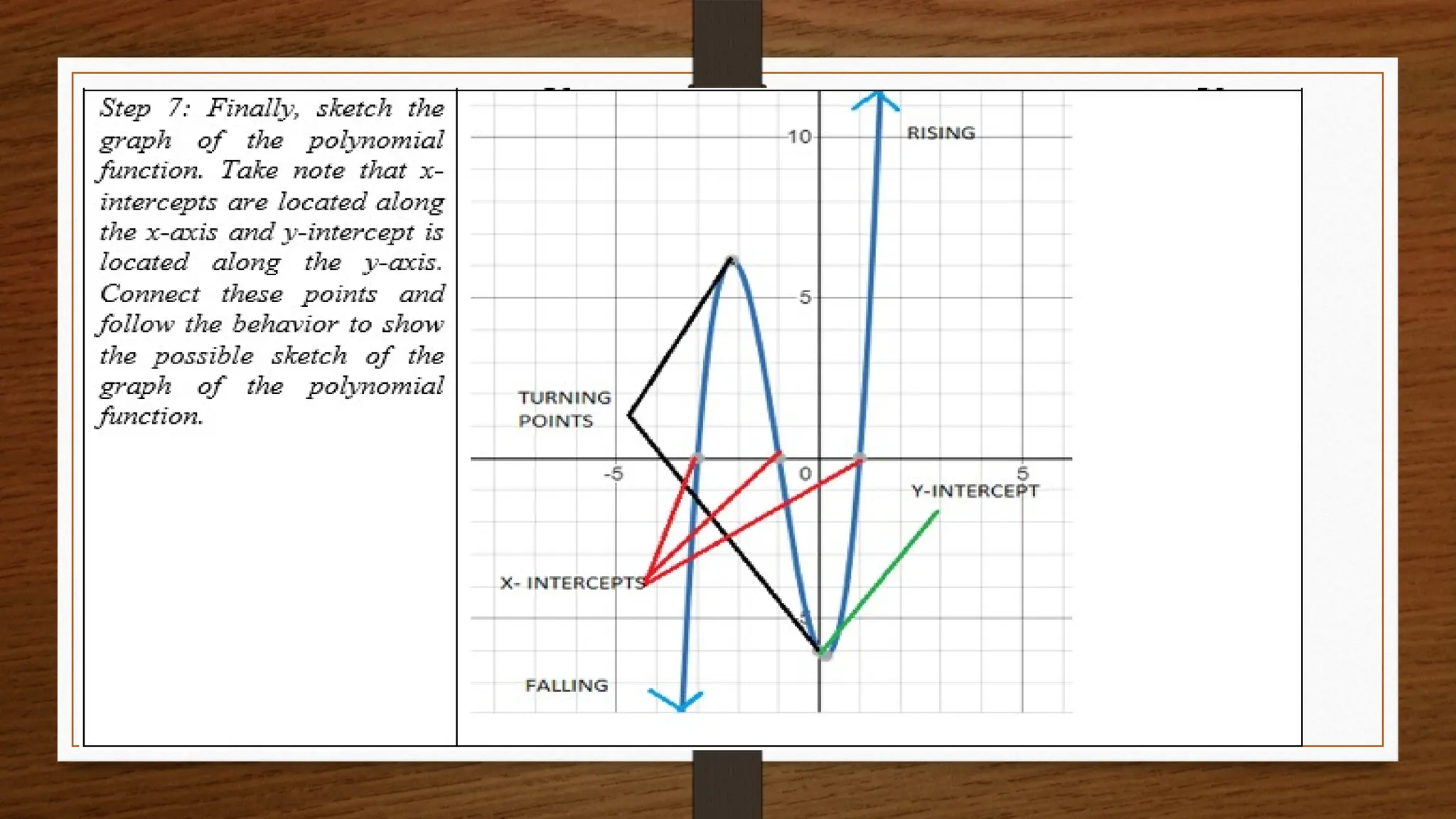
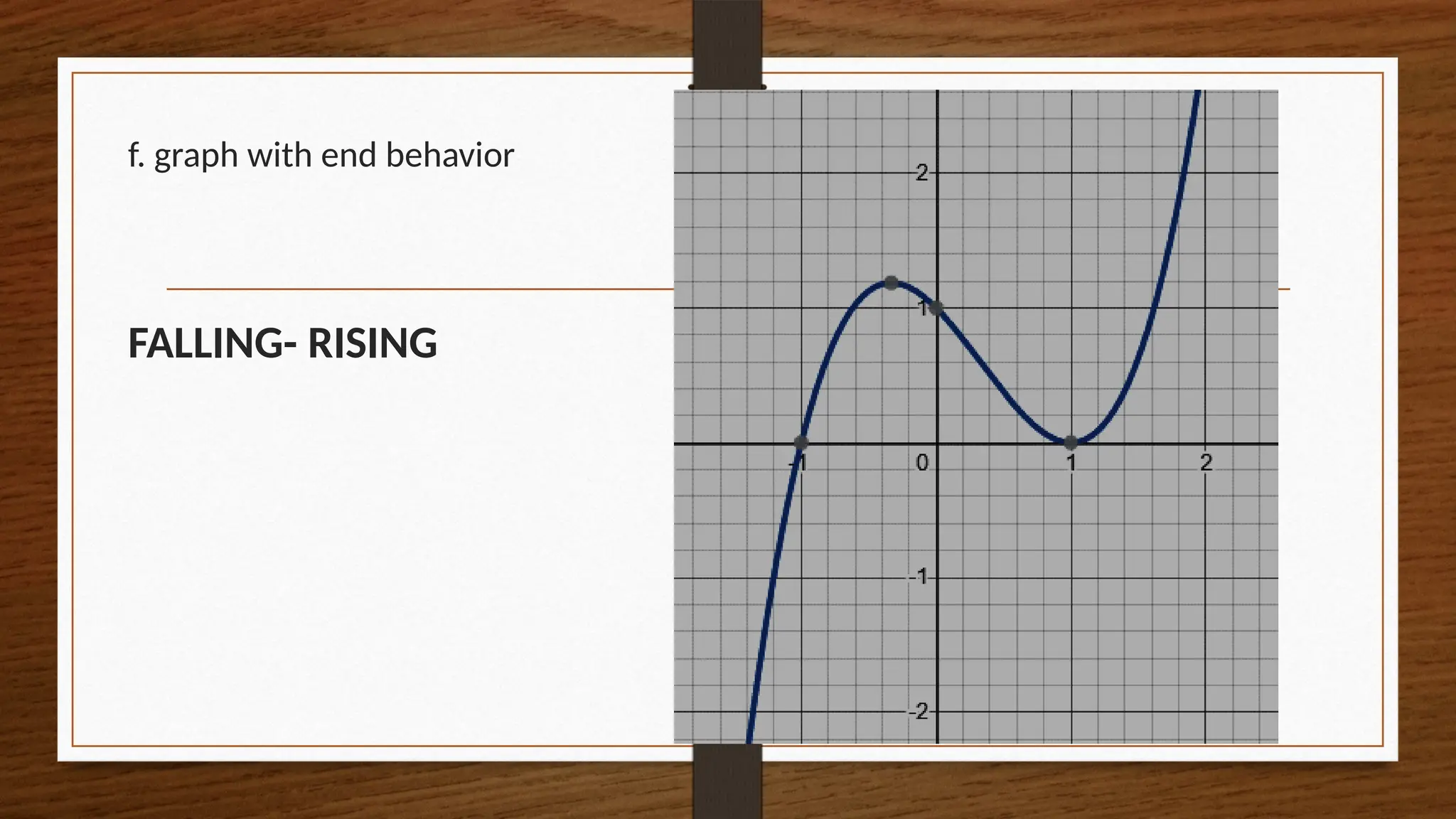
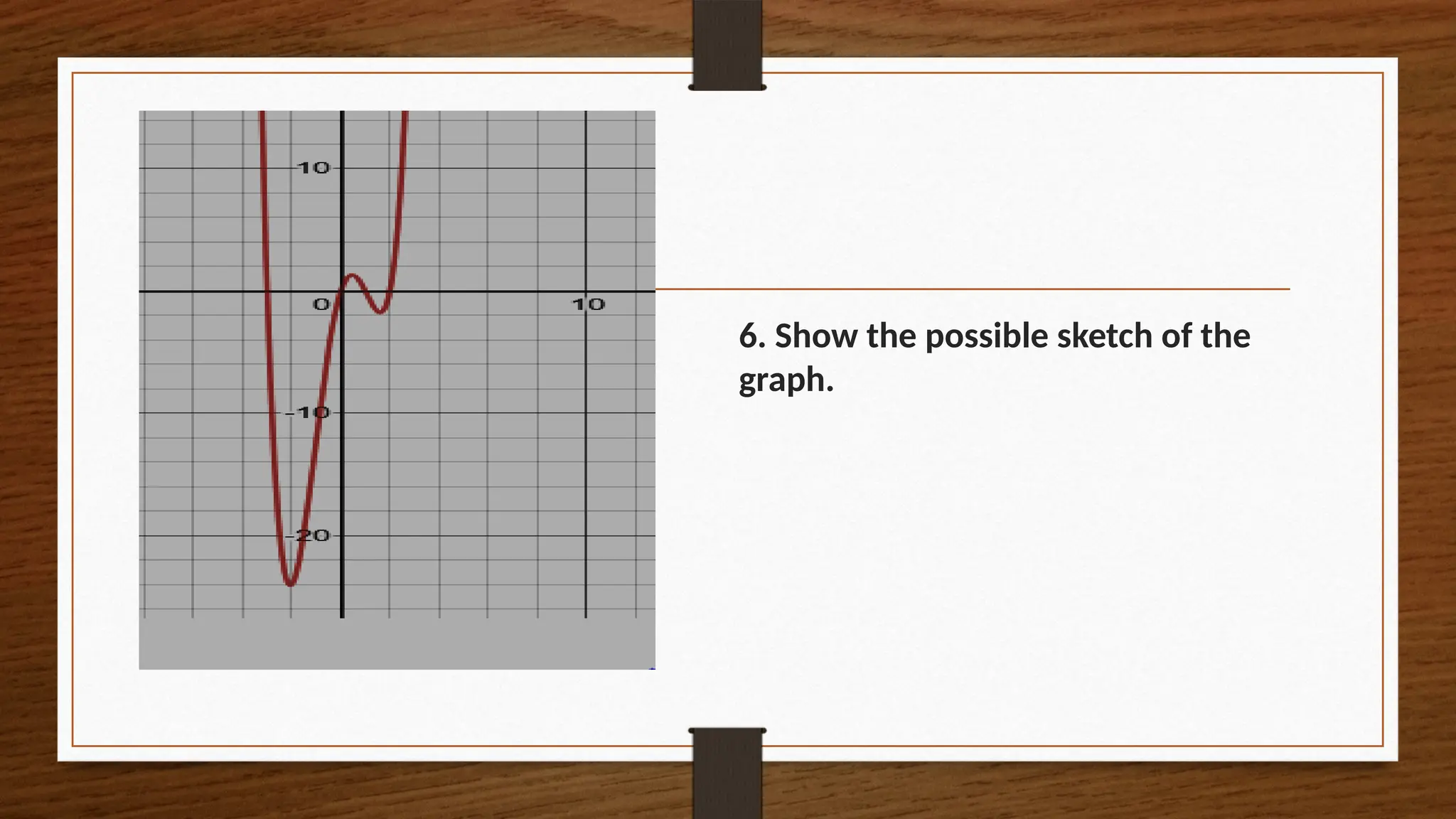
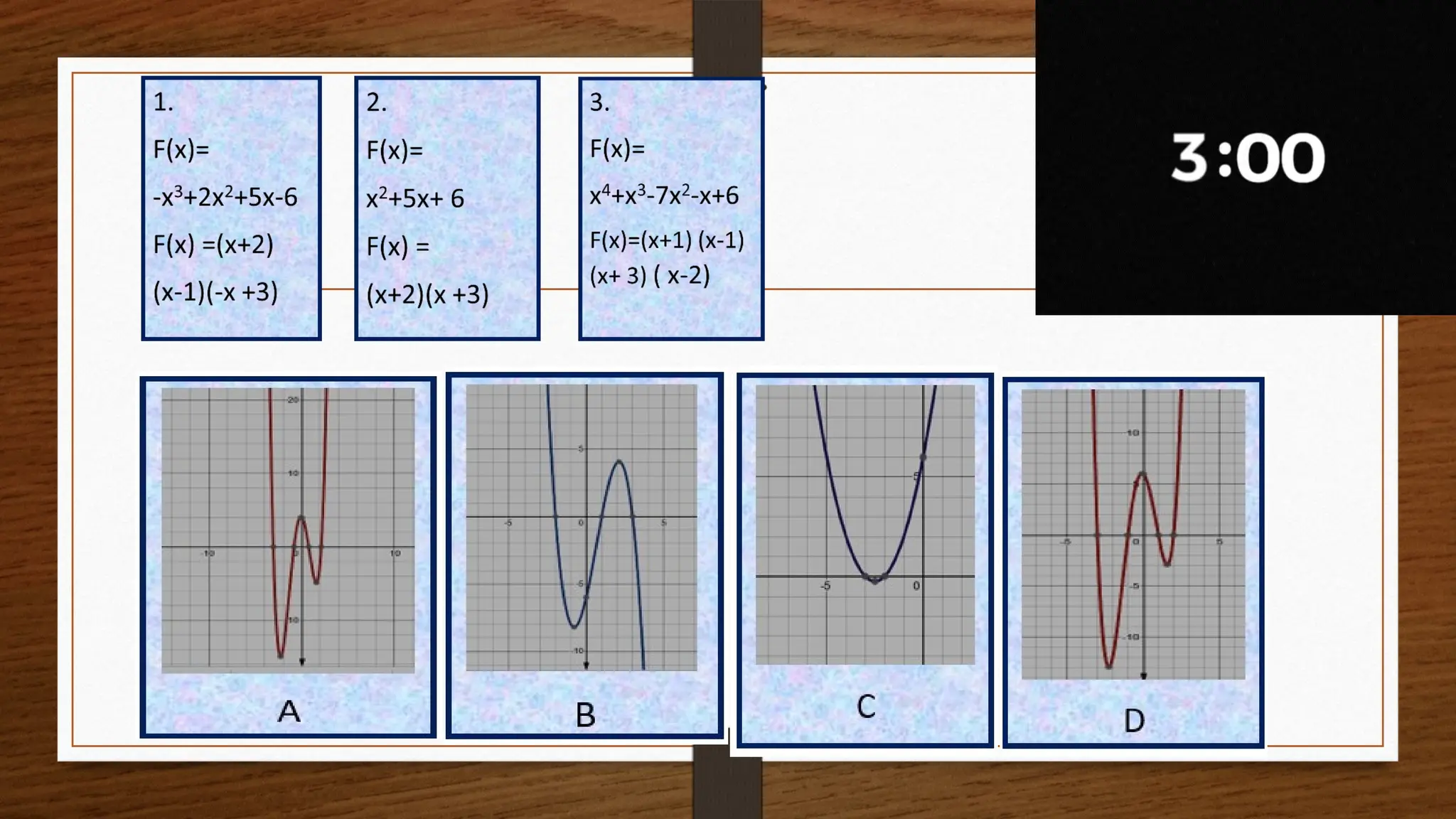
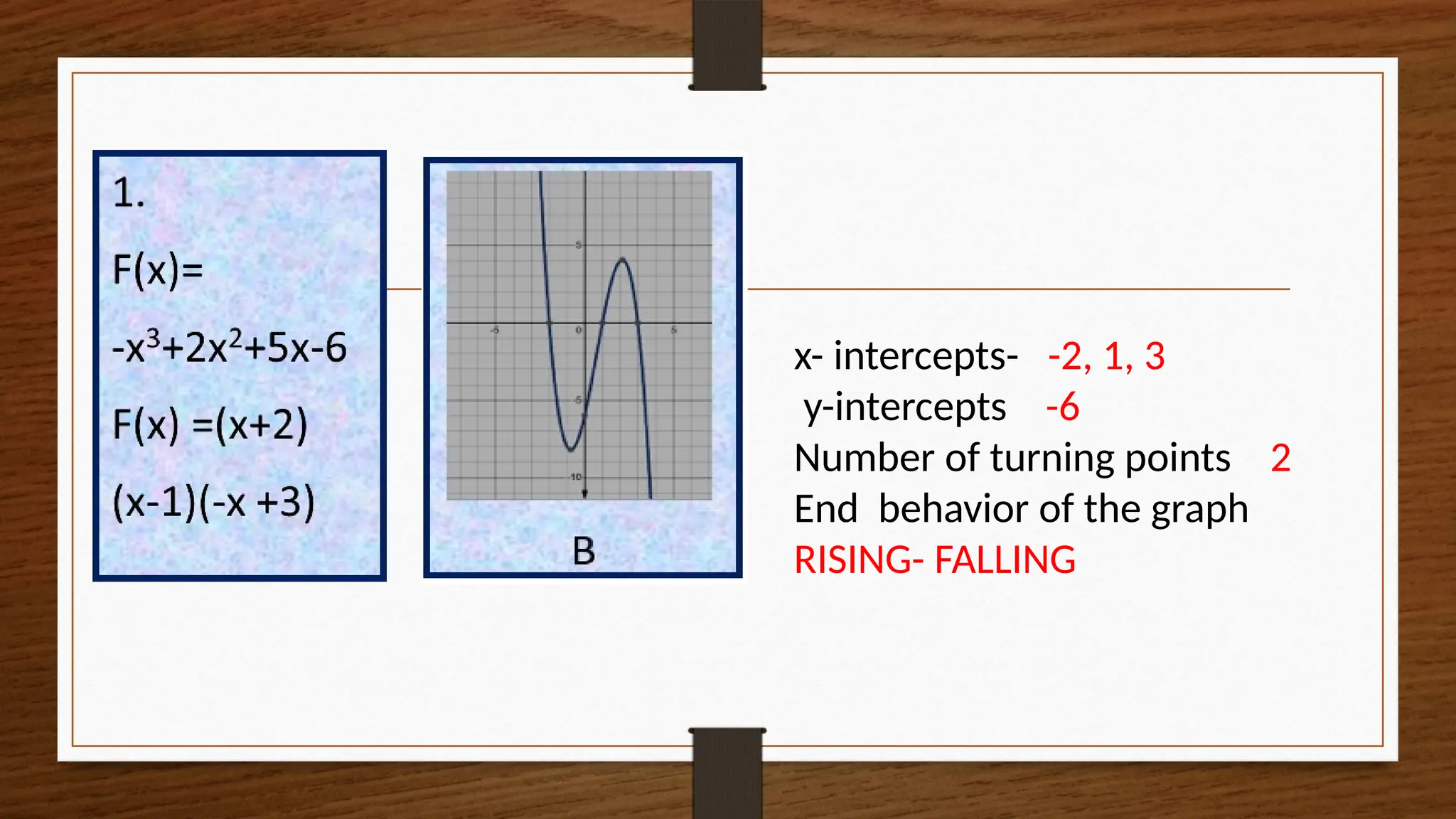
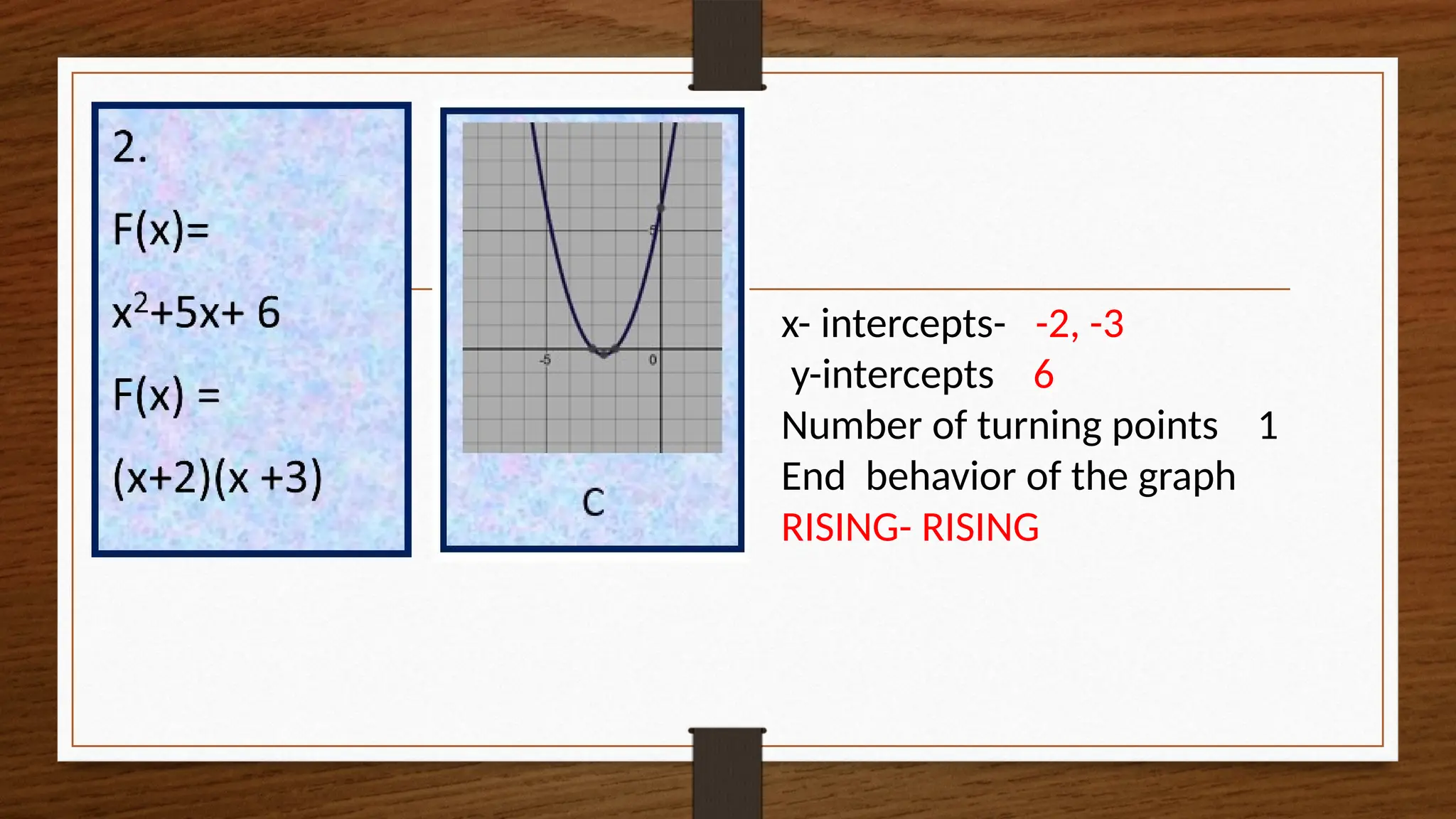
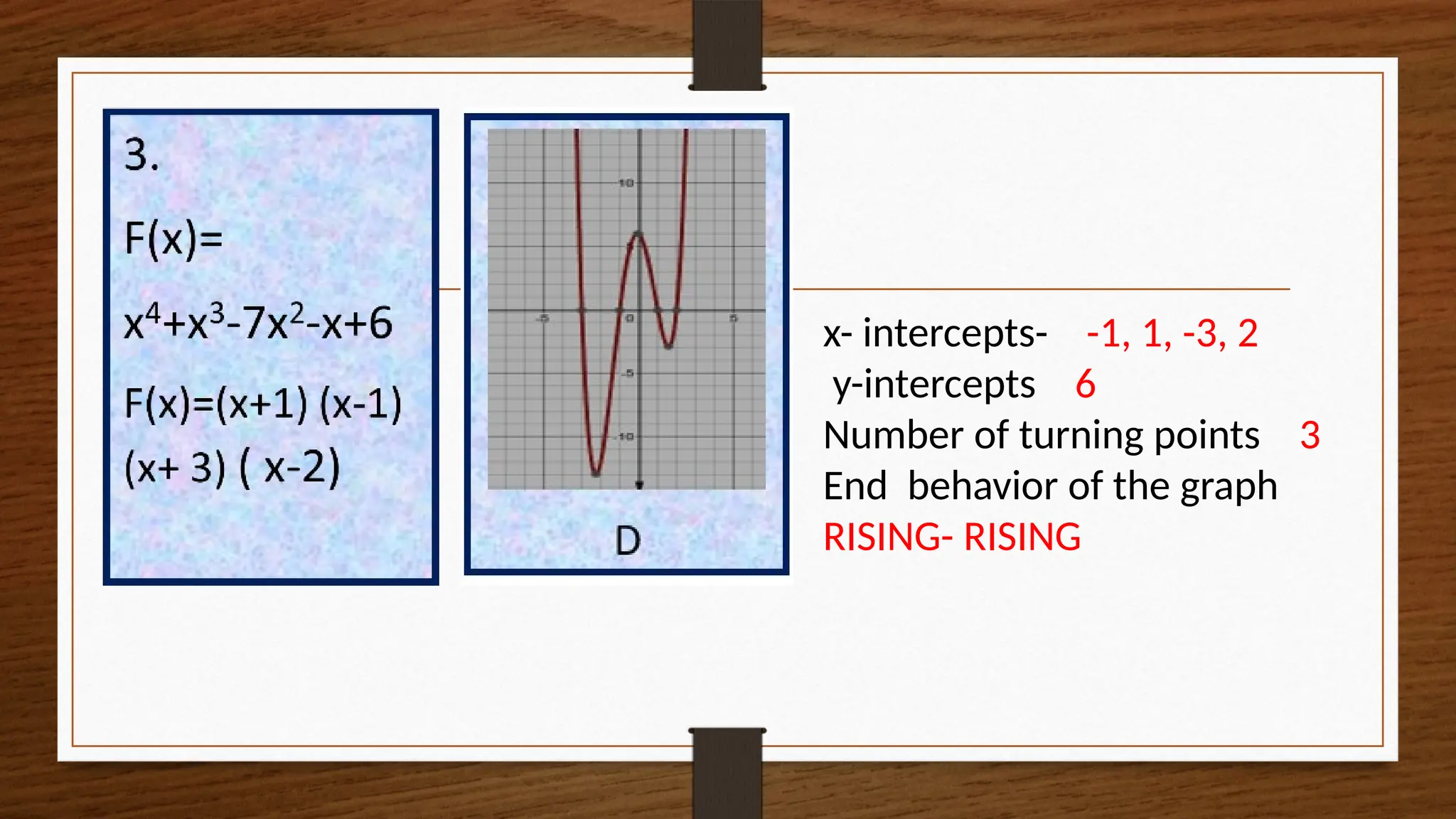
The document focuses on the properties and behaviors of polynomial functions, teaching learners to understand, describe, and interpret their graphs. Key concepts include the leading term, leading coefficient, end behavior, x-intercepts, y-intercepts, and turning points, along with activities to apply these concepts. Additionally, it highlights the relationship between polynomial function graphs and real-life scenarios, such as mathematical garden projects.