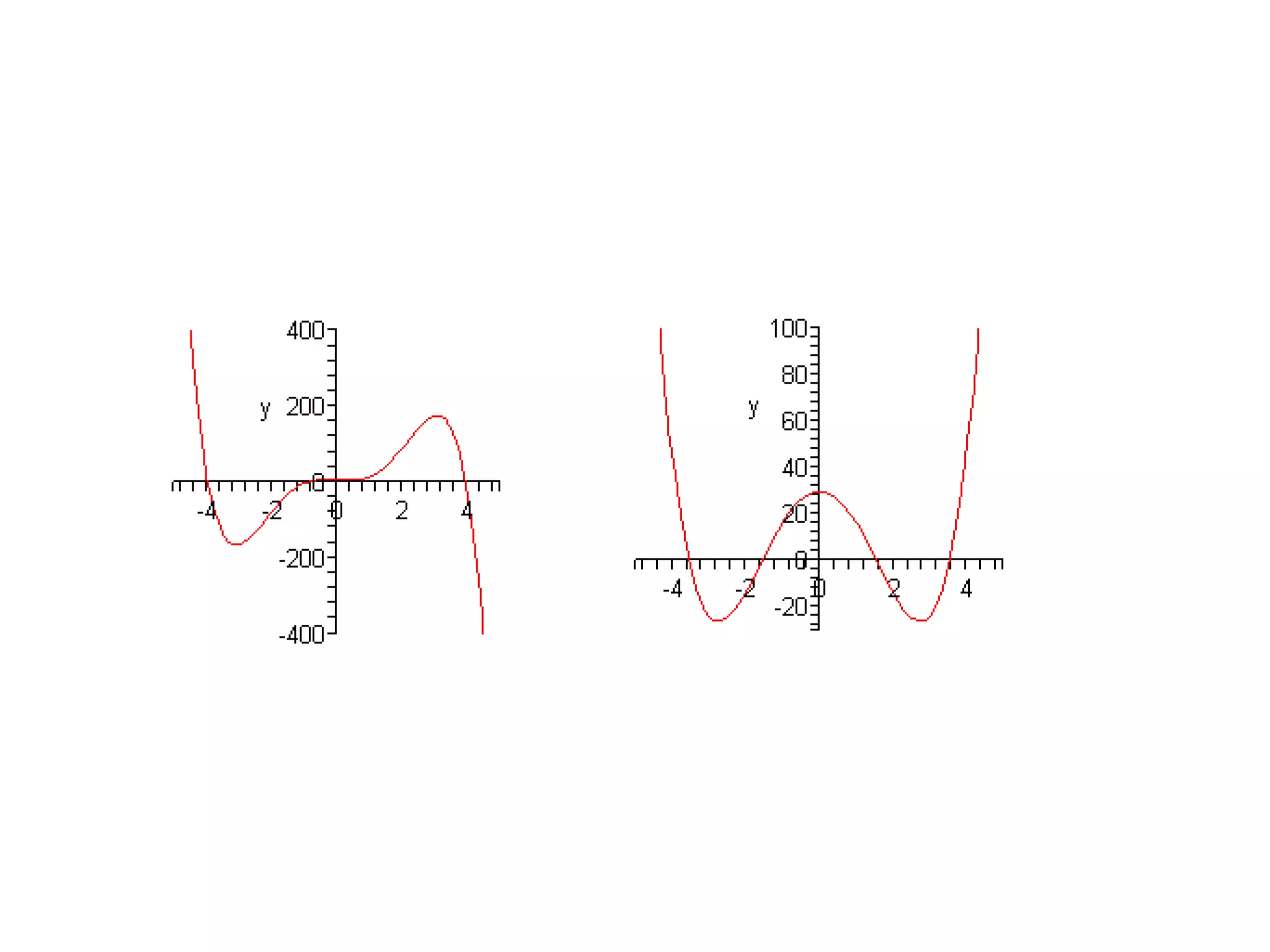
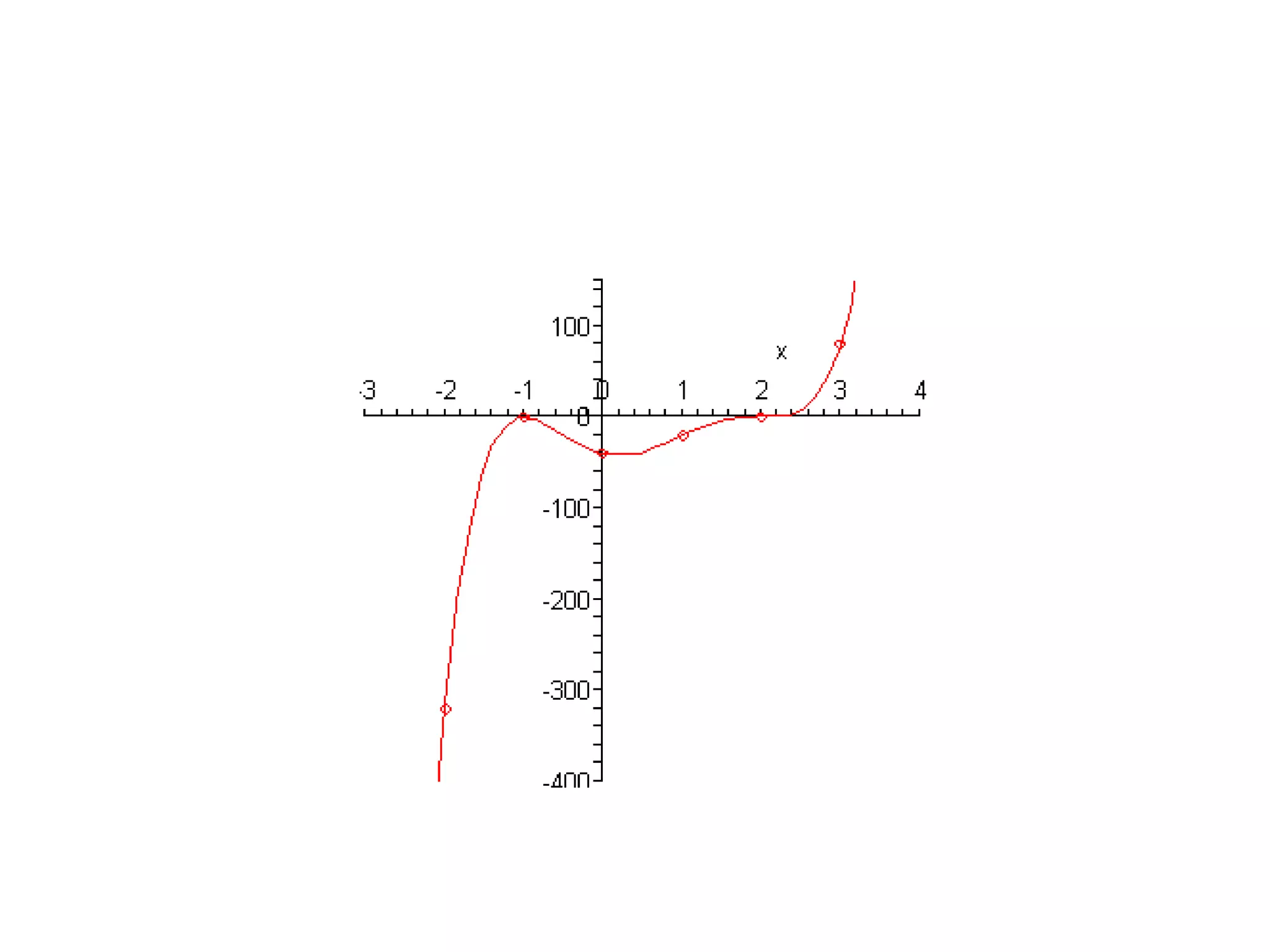
The document discusses how to graph polynomials by determining the x-intercepts from the zeros of the polynomial, the y-intercept, and the behavior at infinity using the leading coefficient test. It provides details on how the multiplicity of zeros relates to whether x-intercepts cross or touch the x-axis, and whether the graph is flat at those points. An example graphing the polynomial f(x)=x^5-5x^4+10x^3-10x^2+5x-40 is worked through step-by-step.