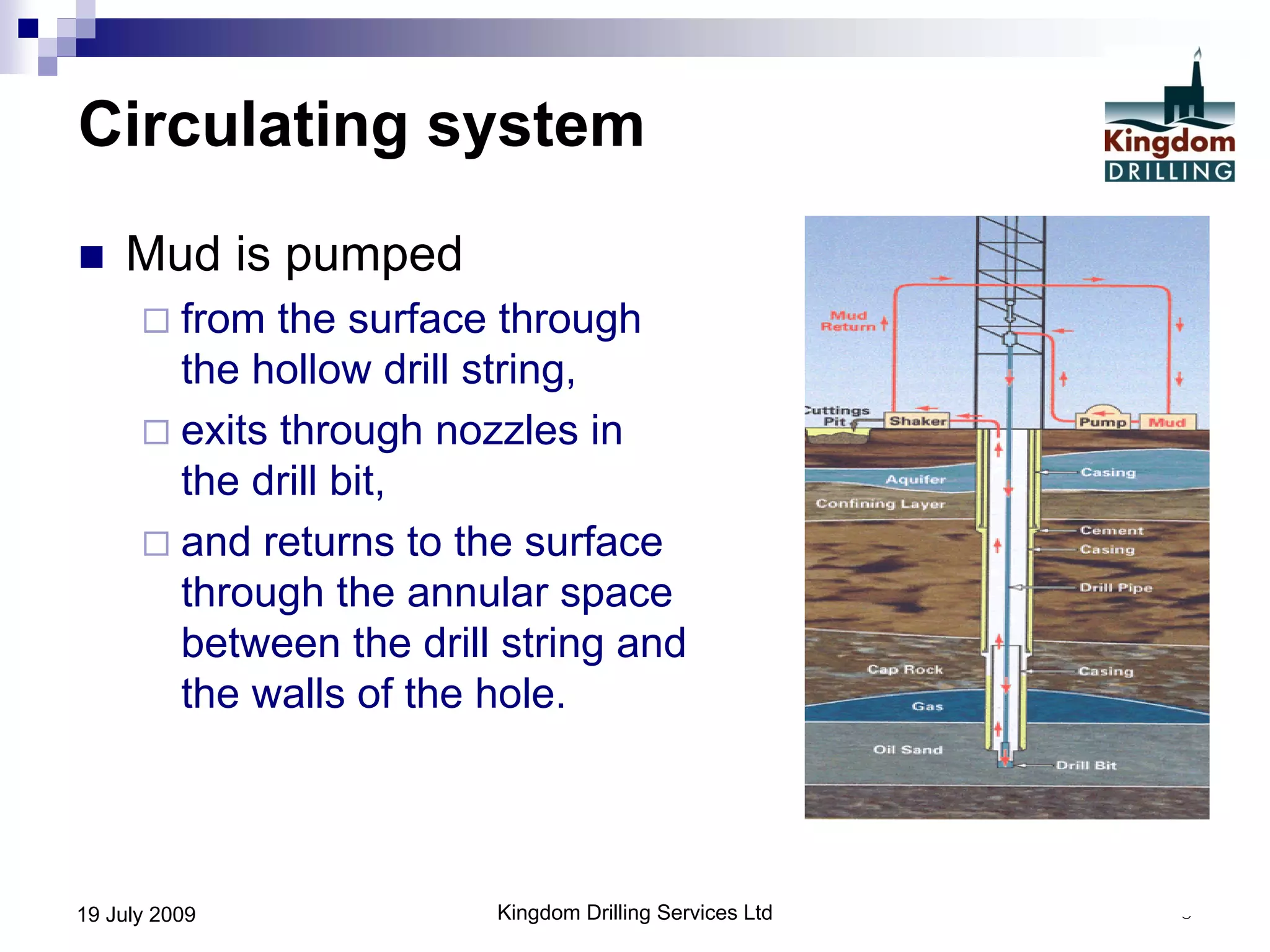
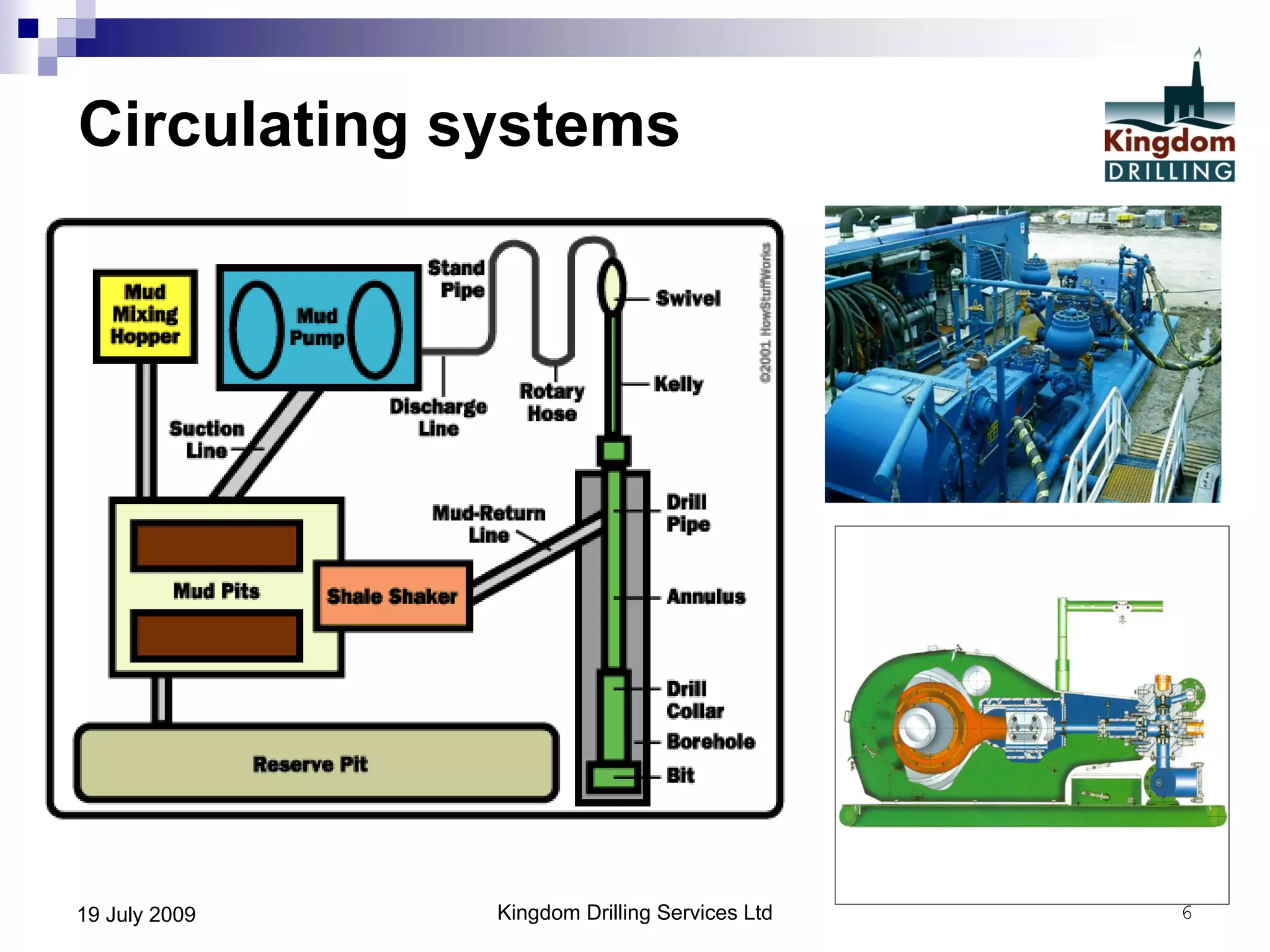
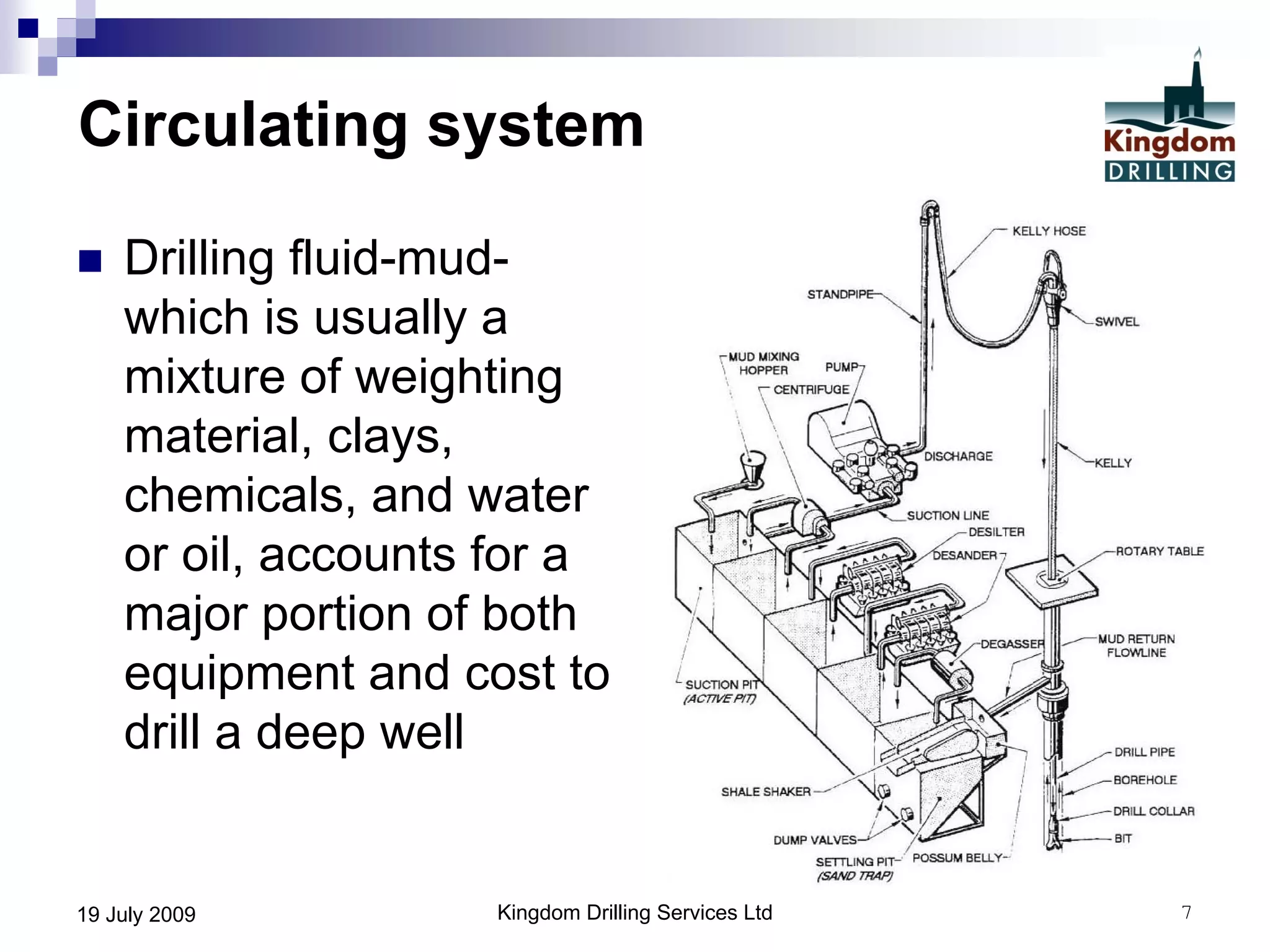
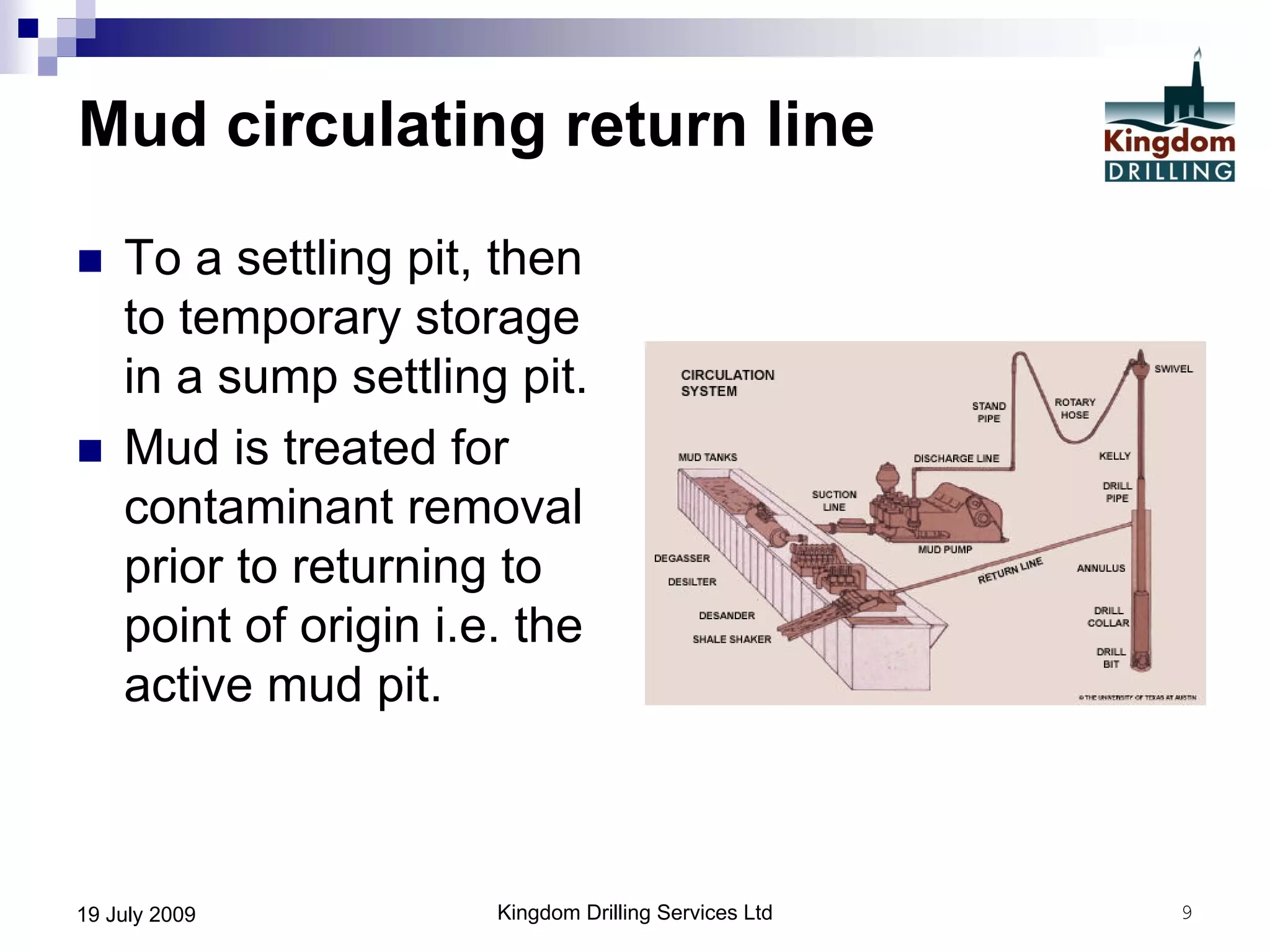
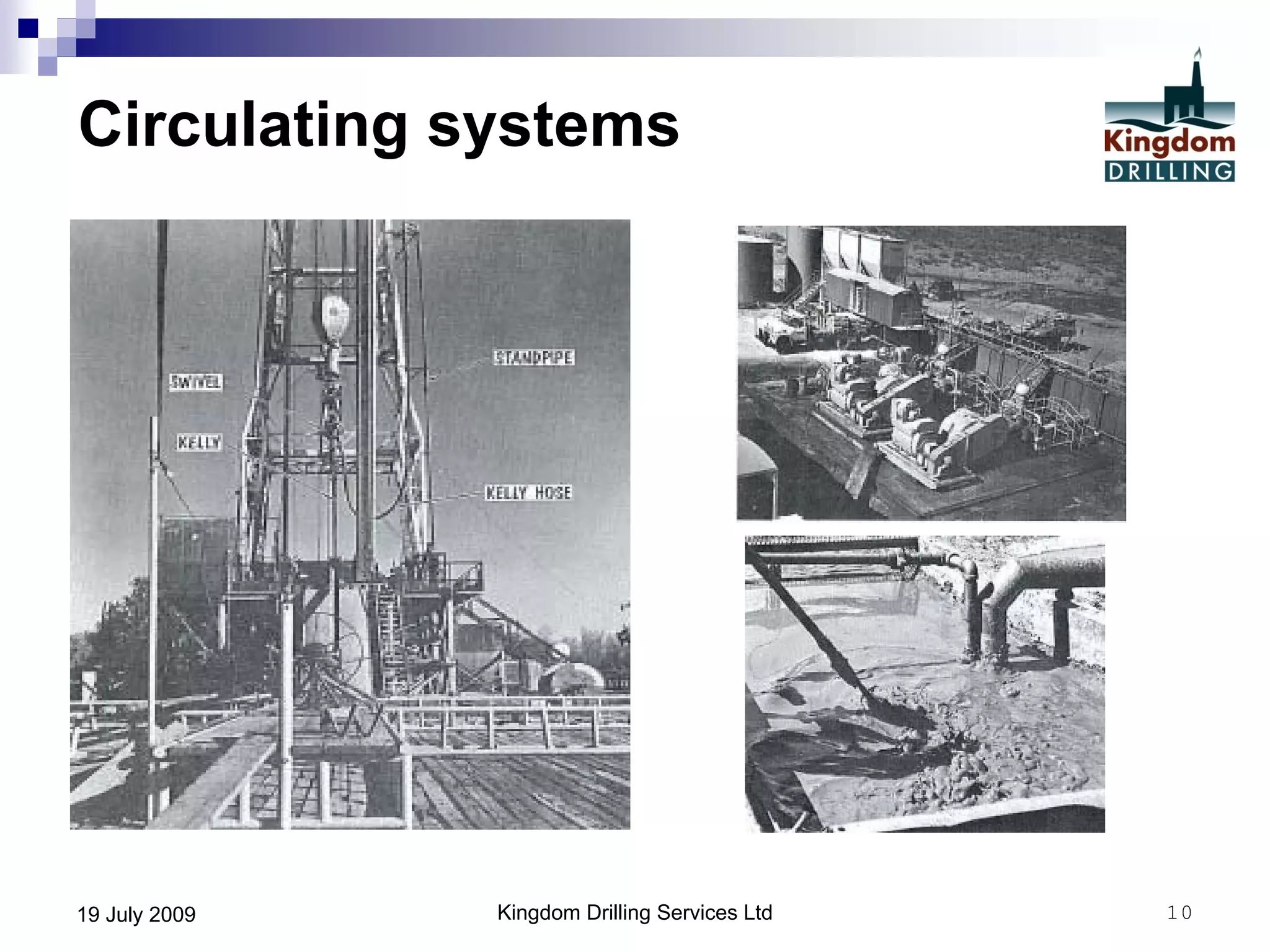
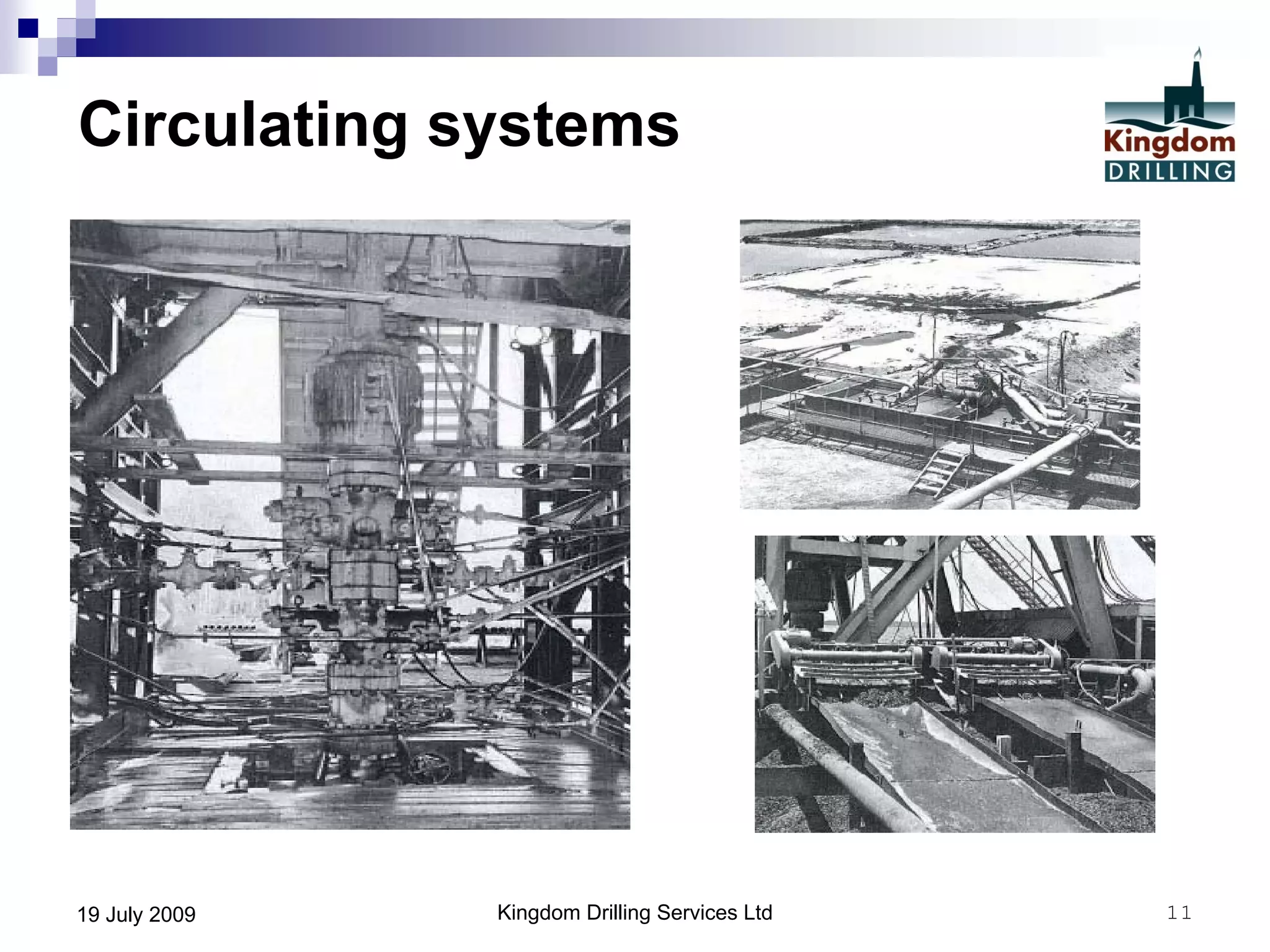
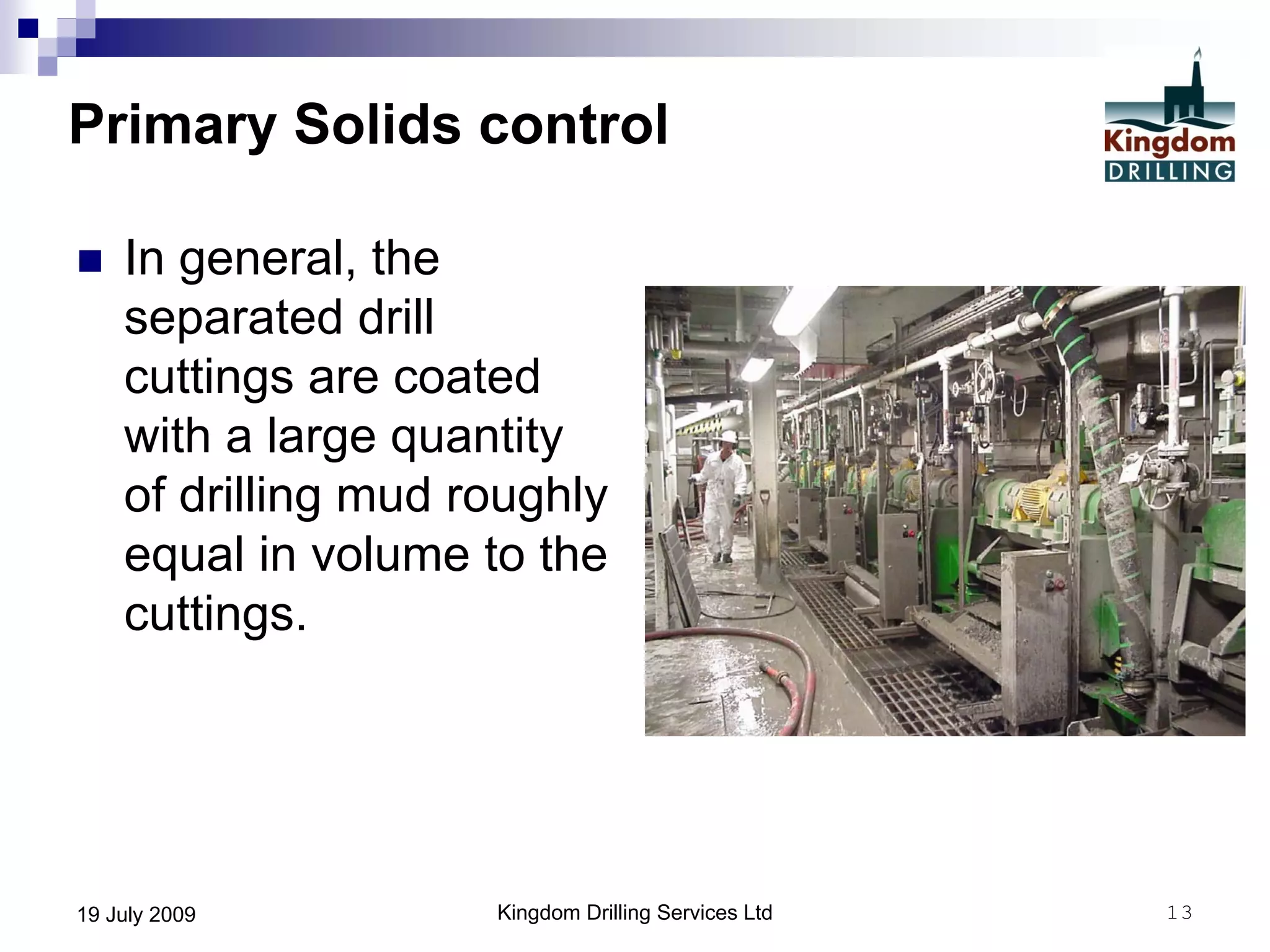
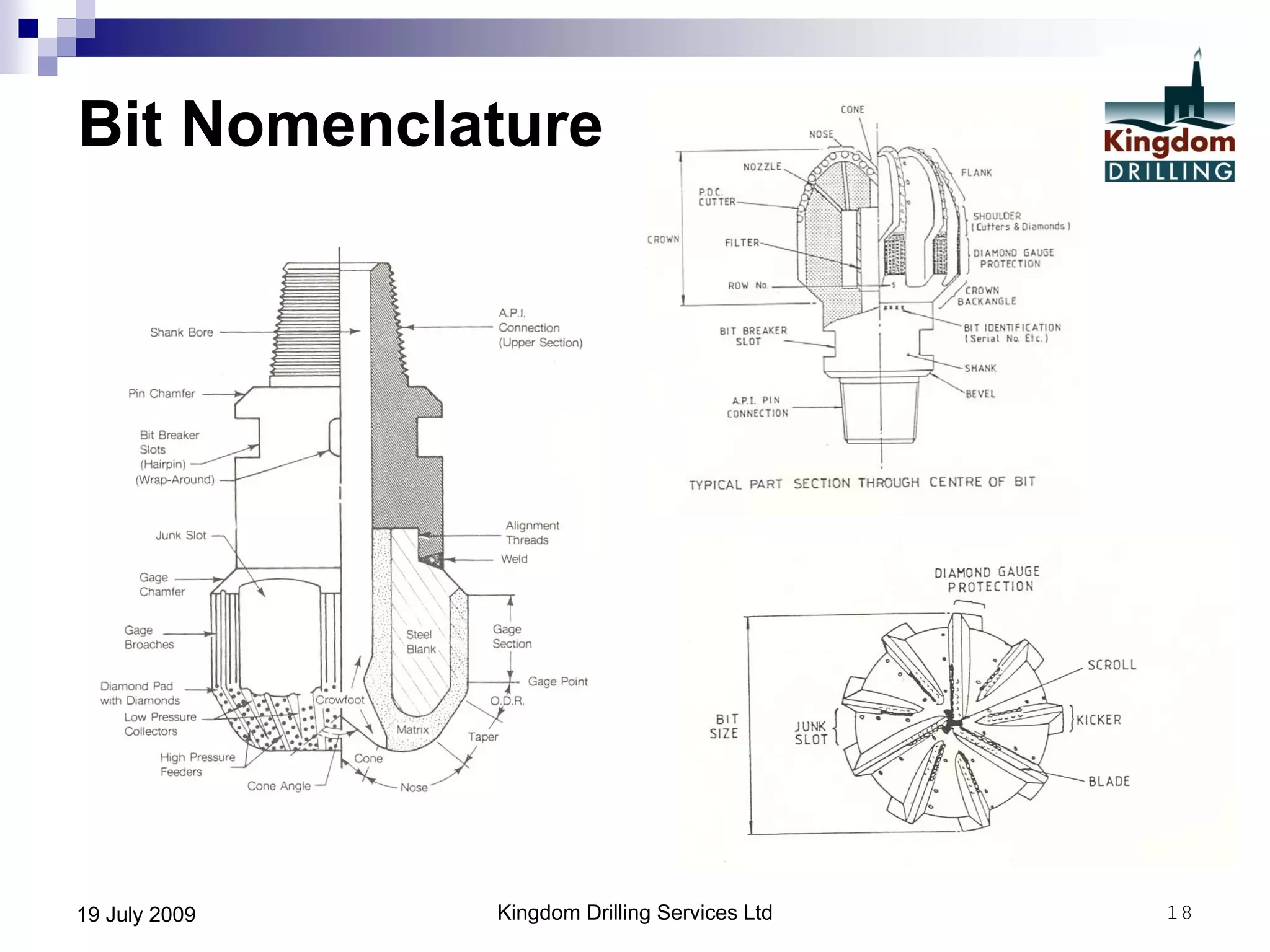
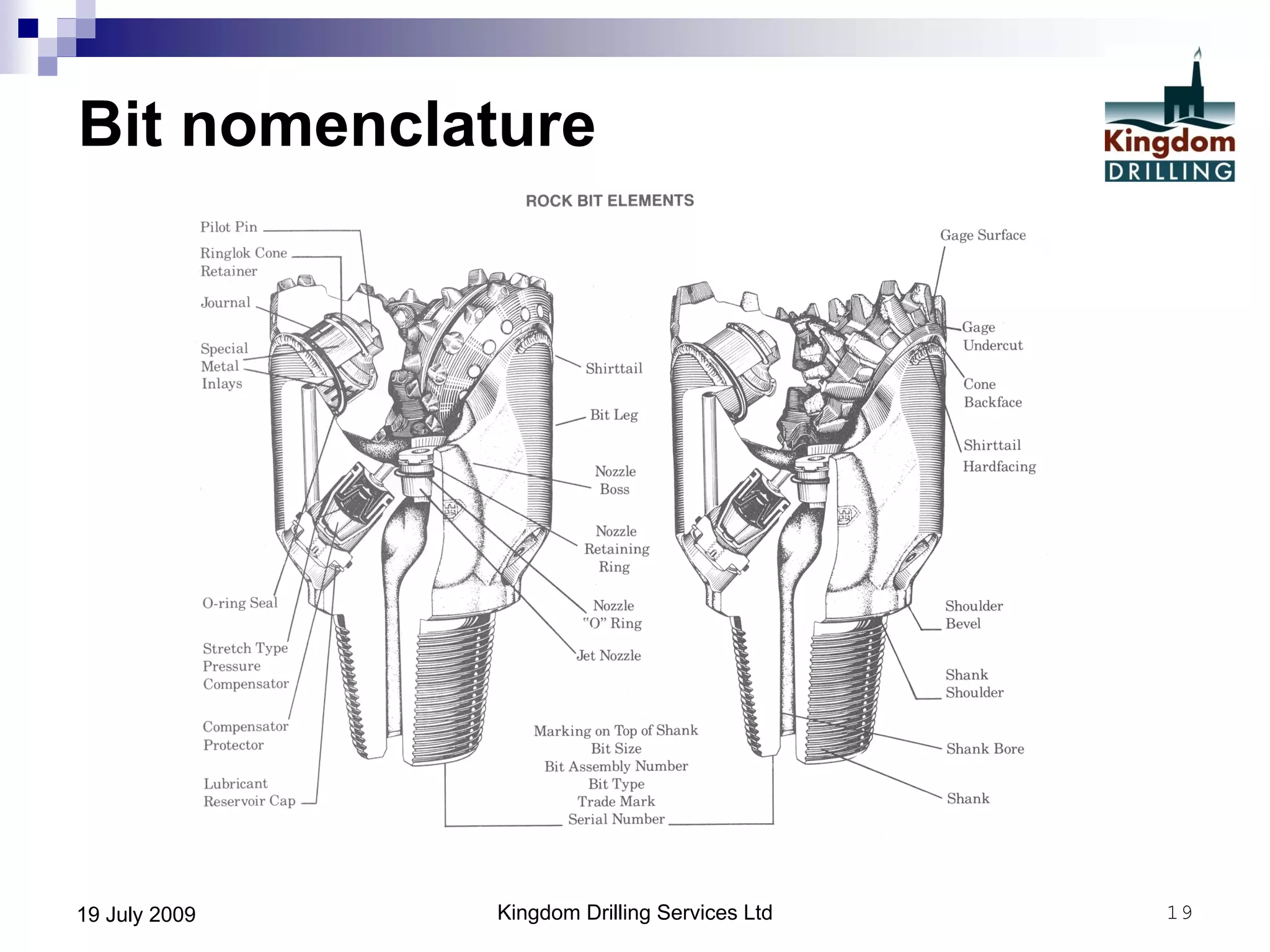
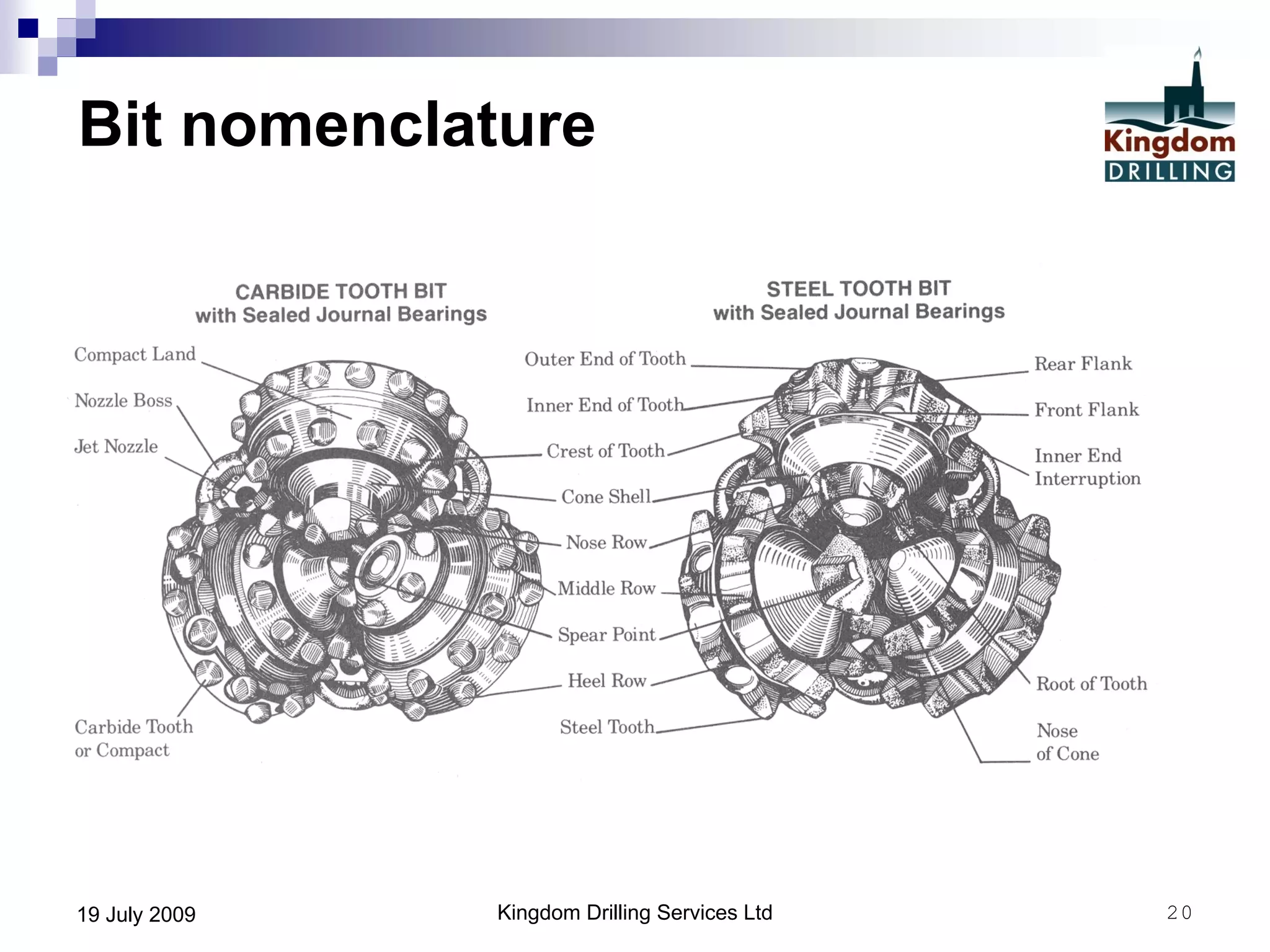
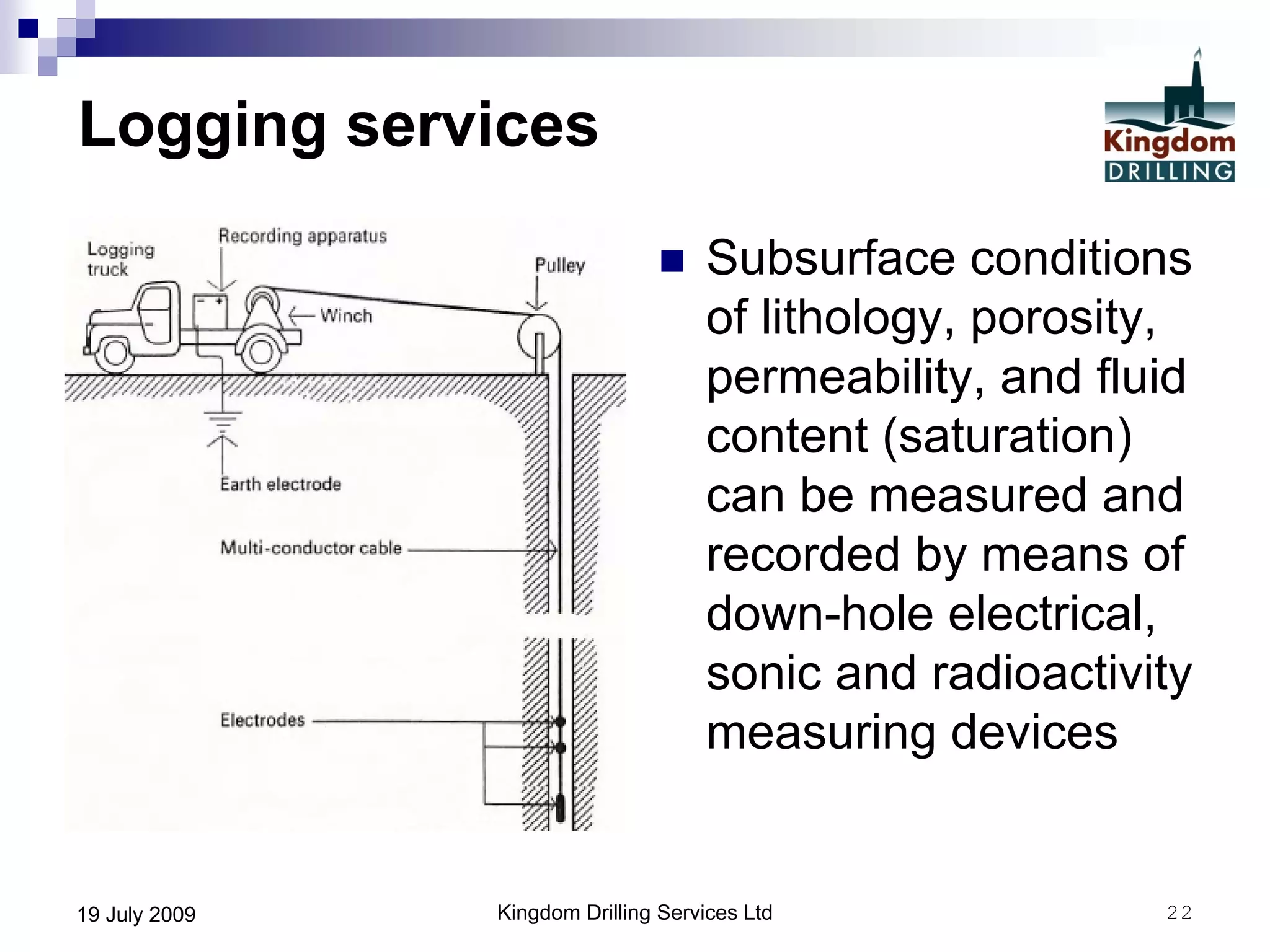
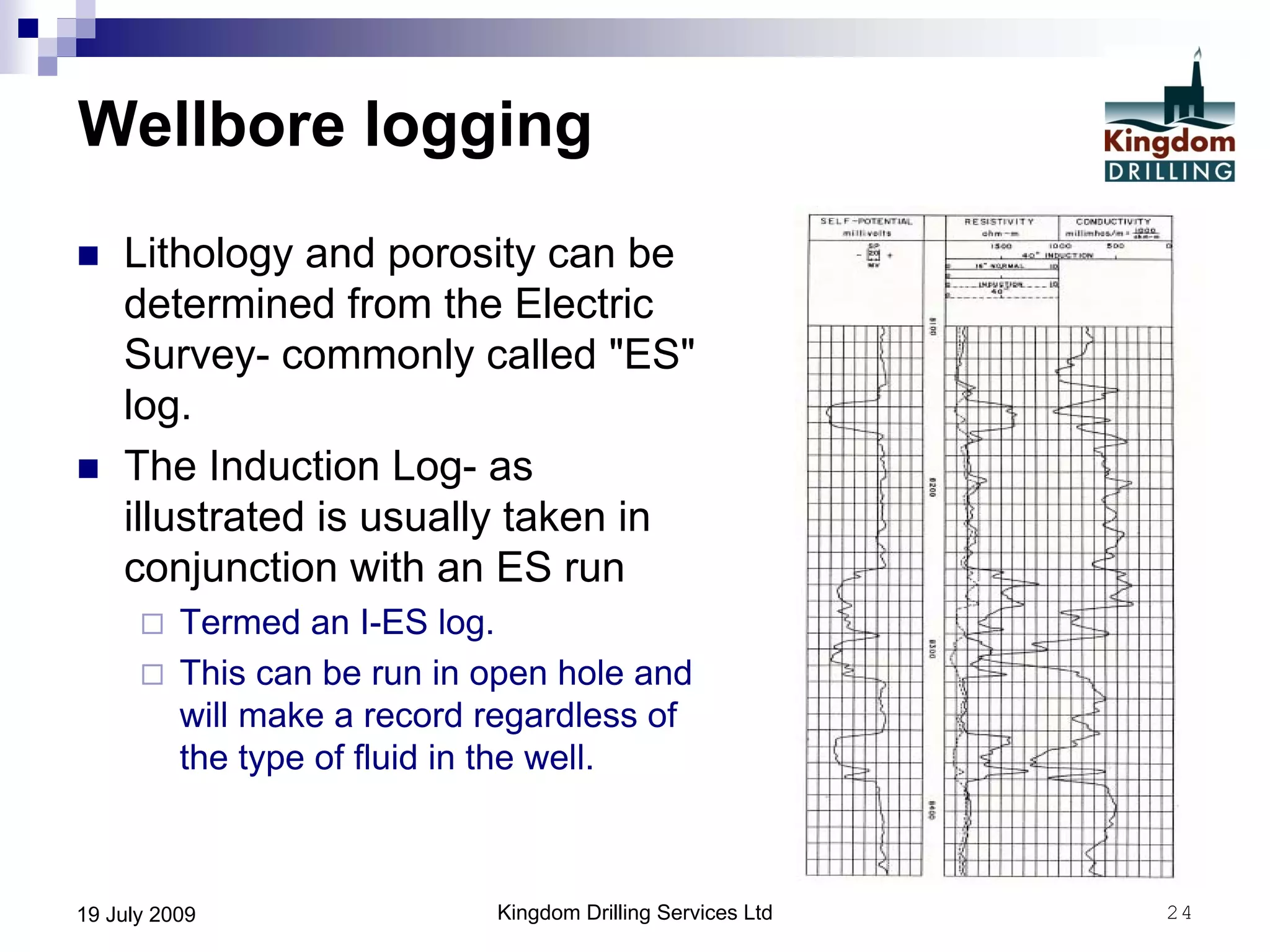
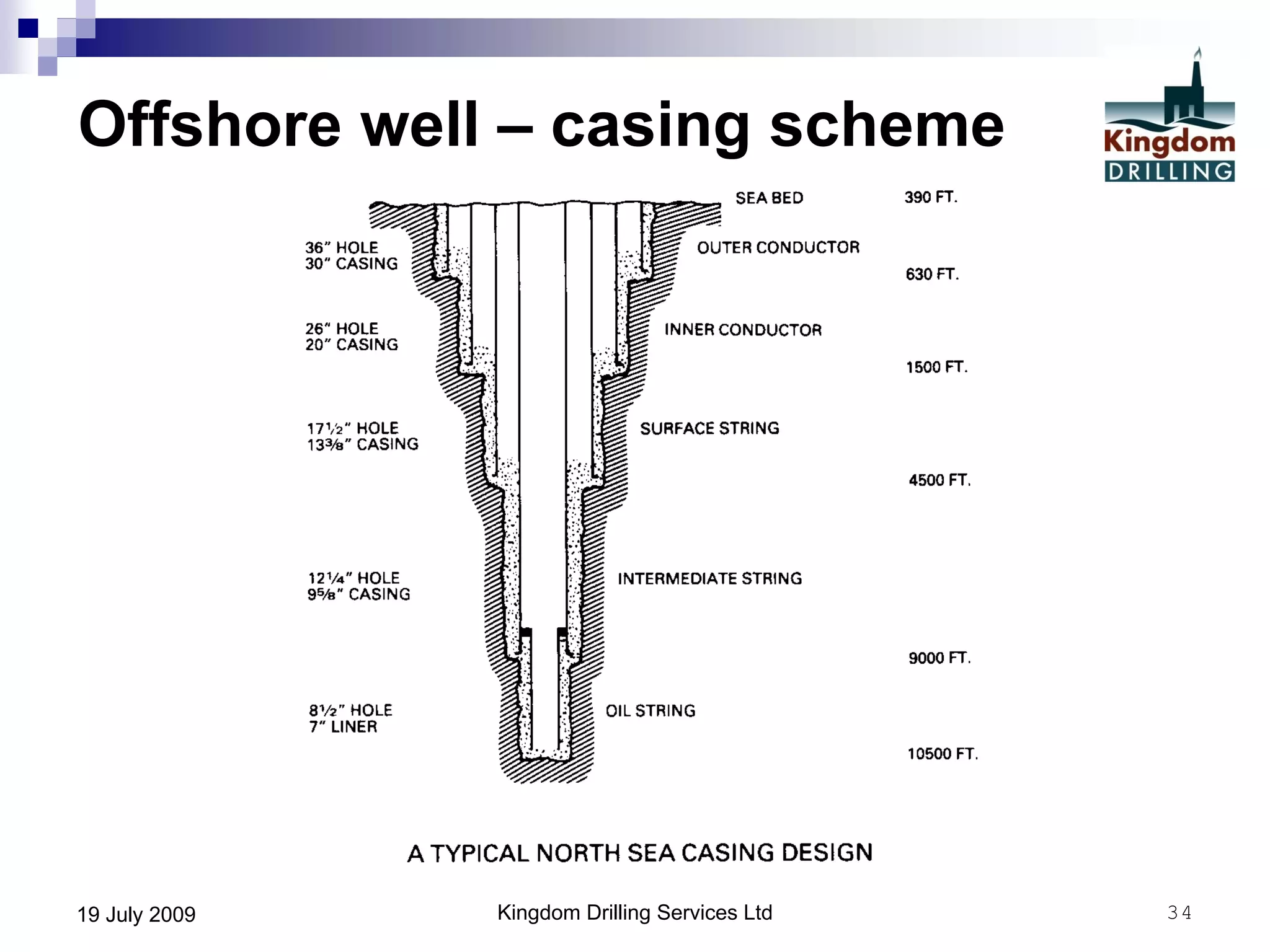
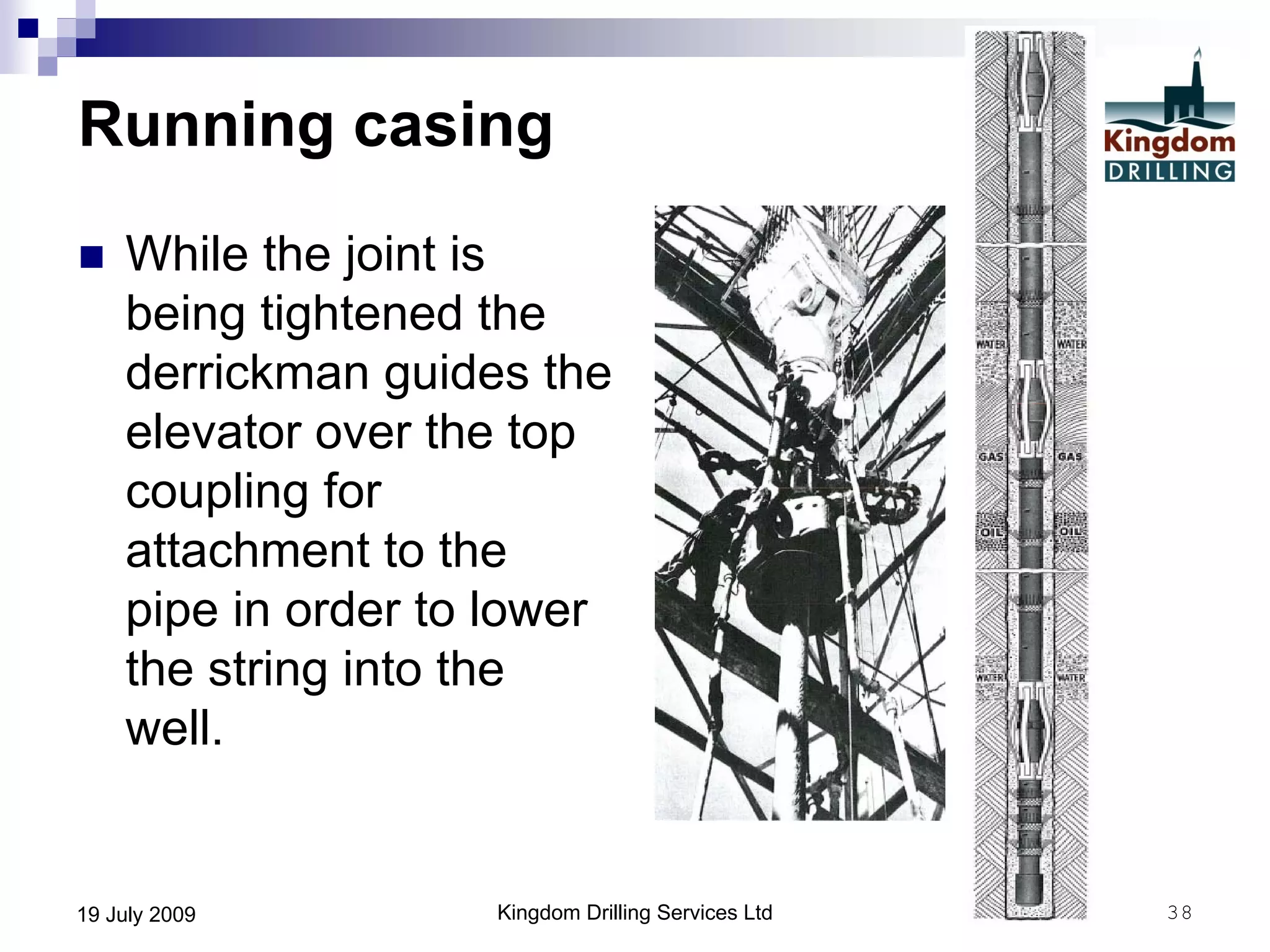
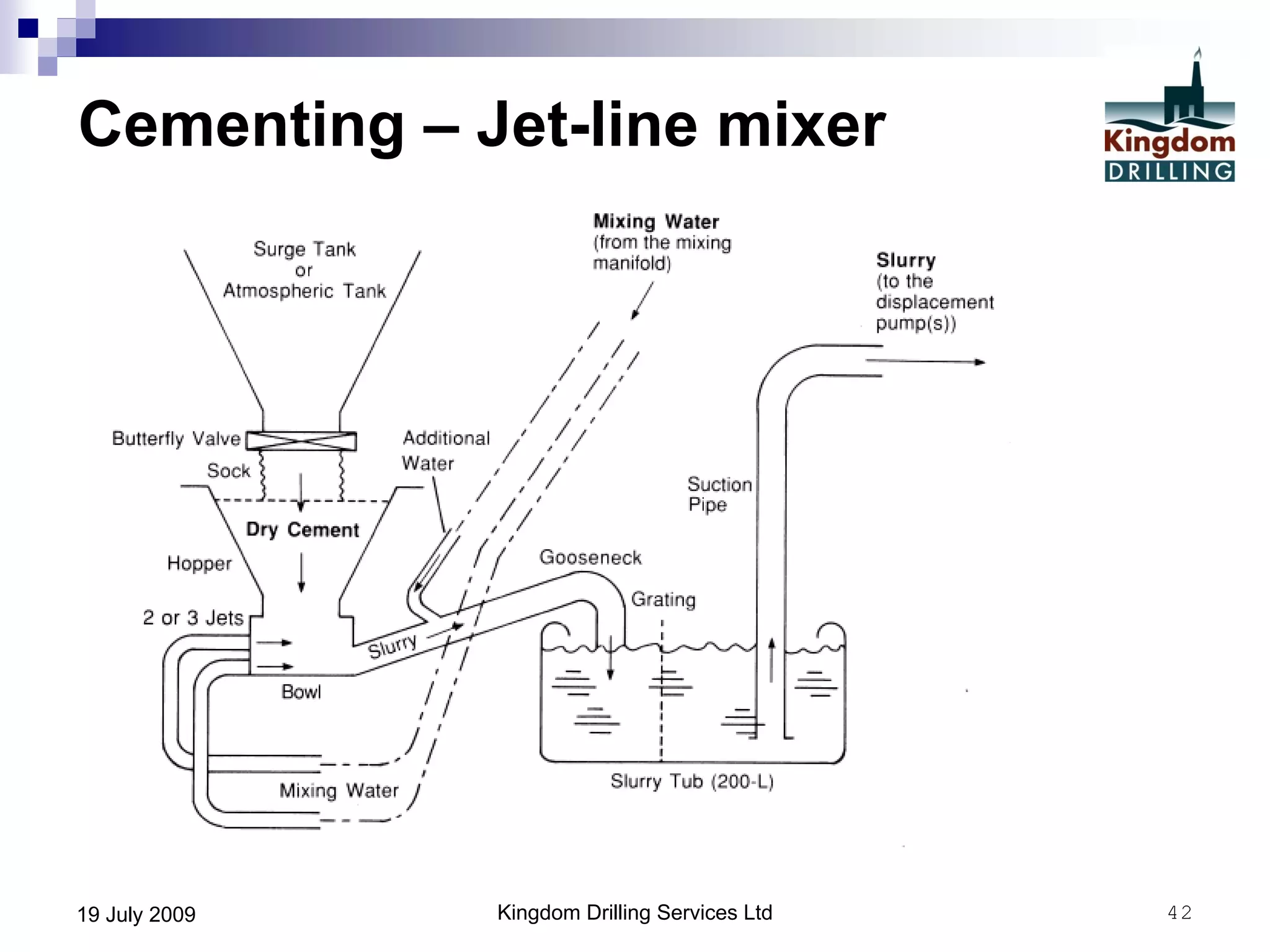
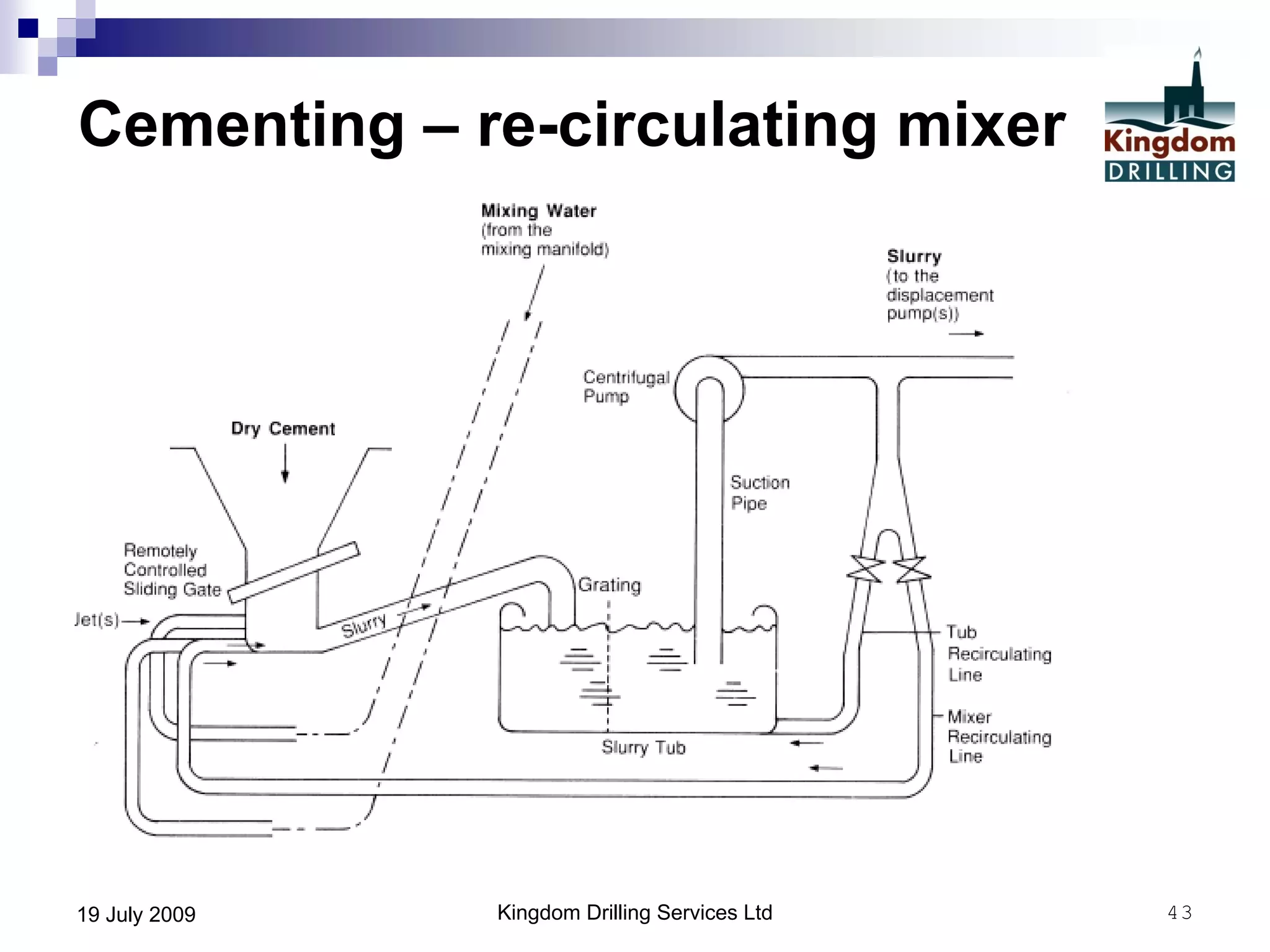
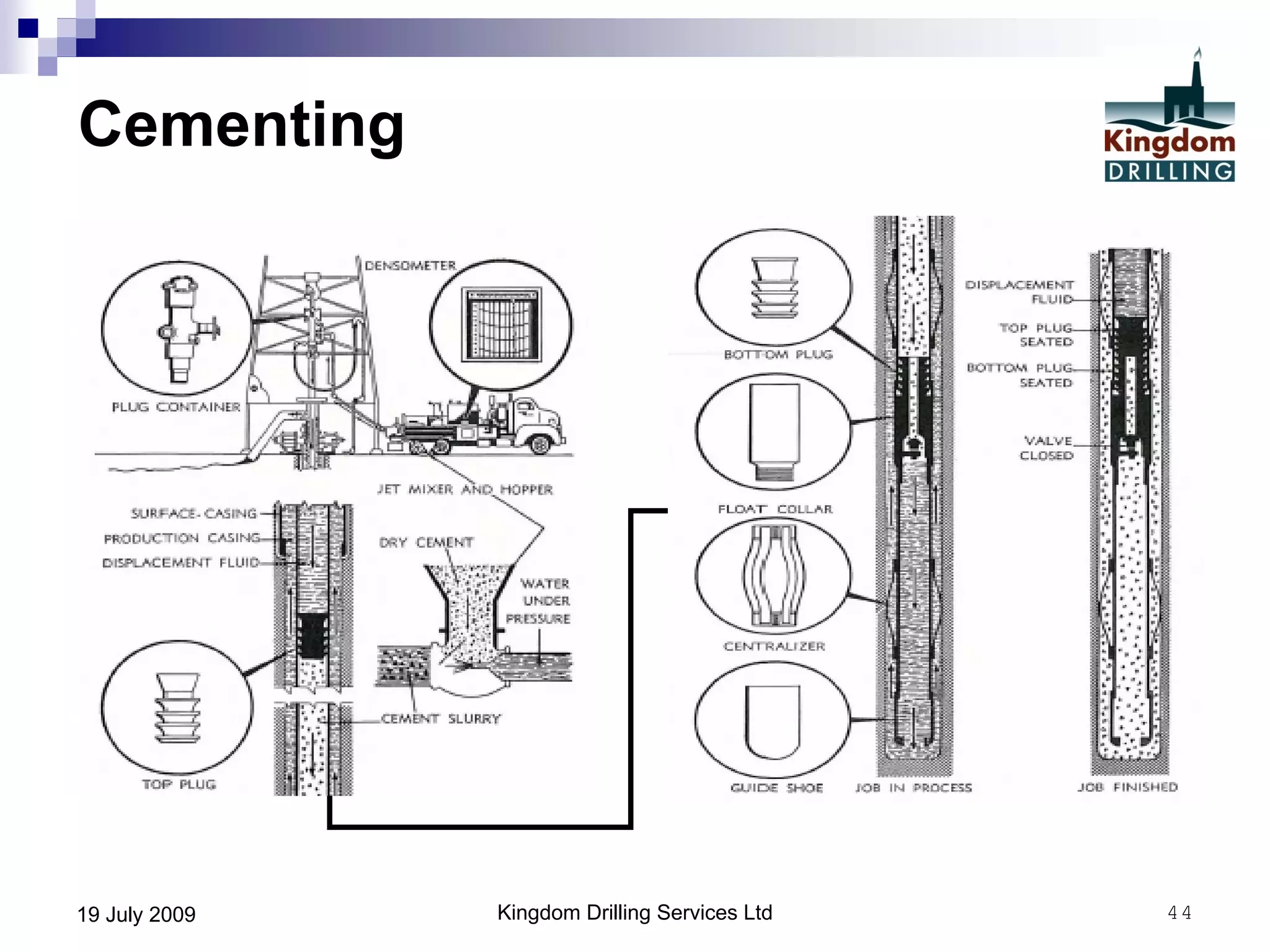
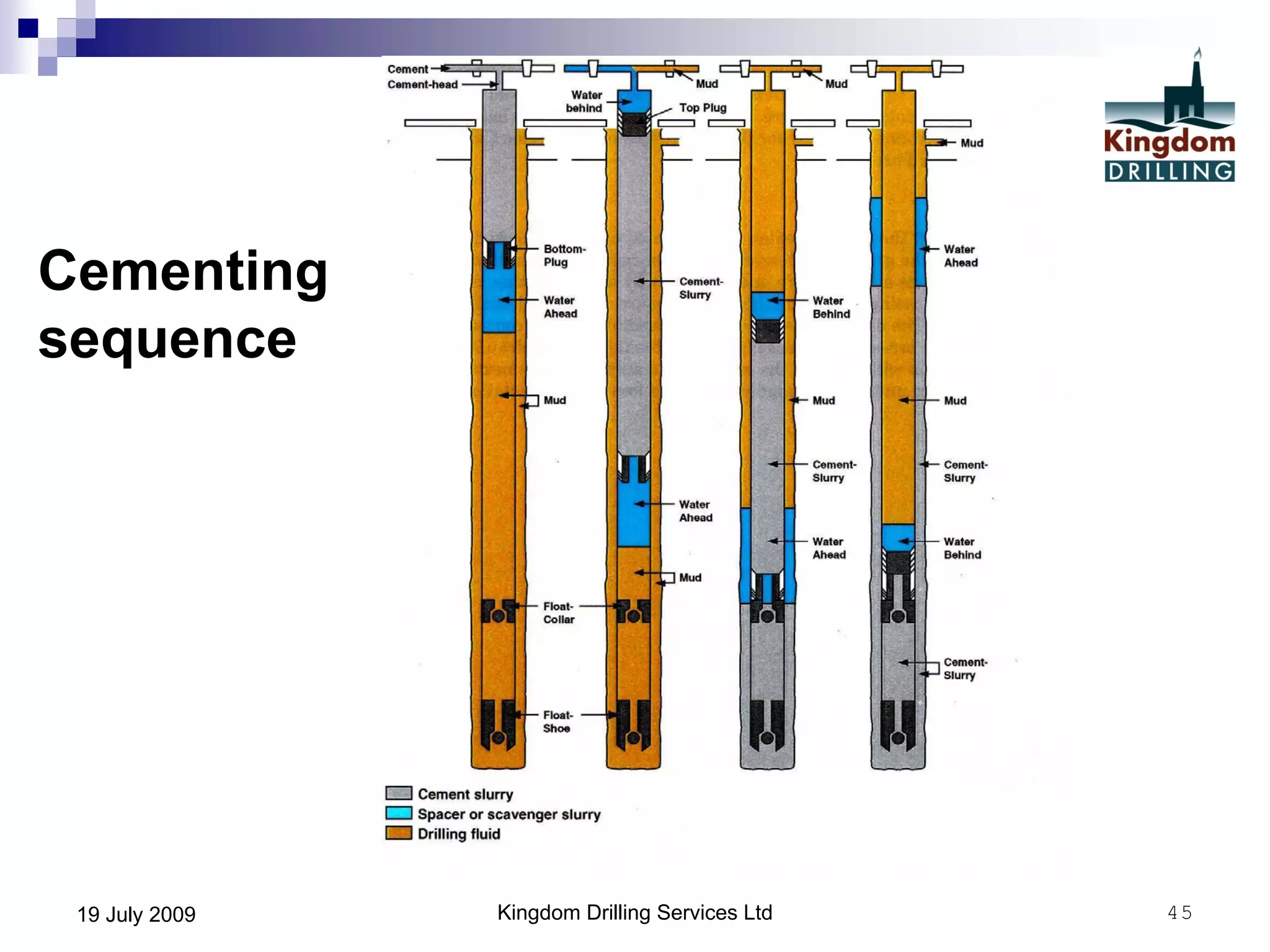
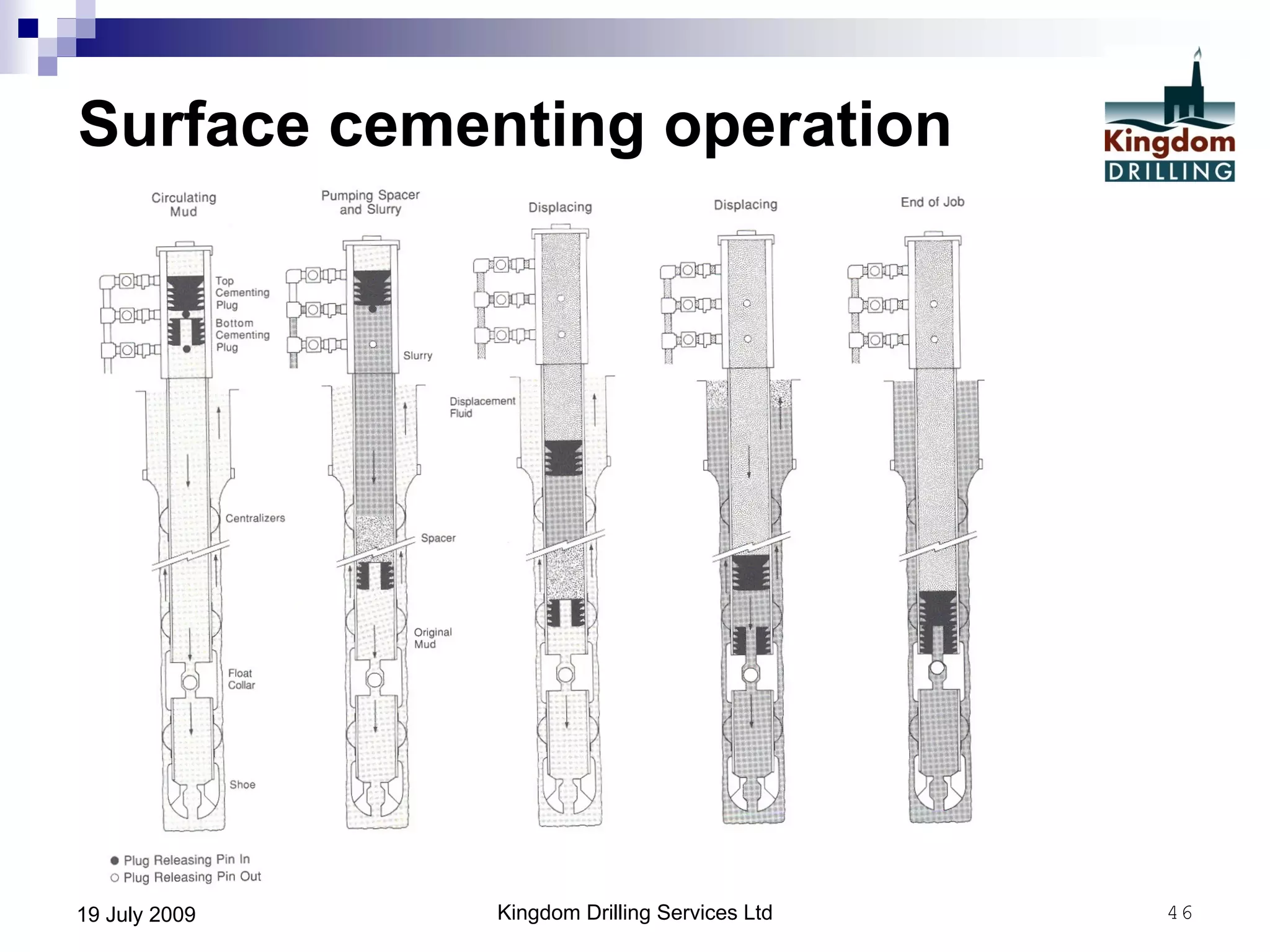
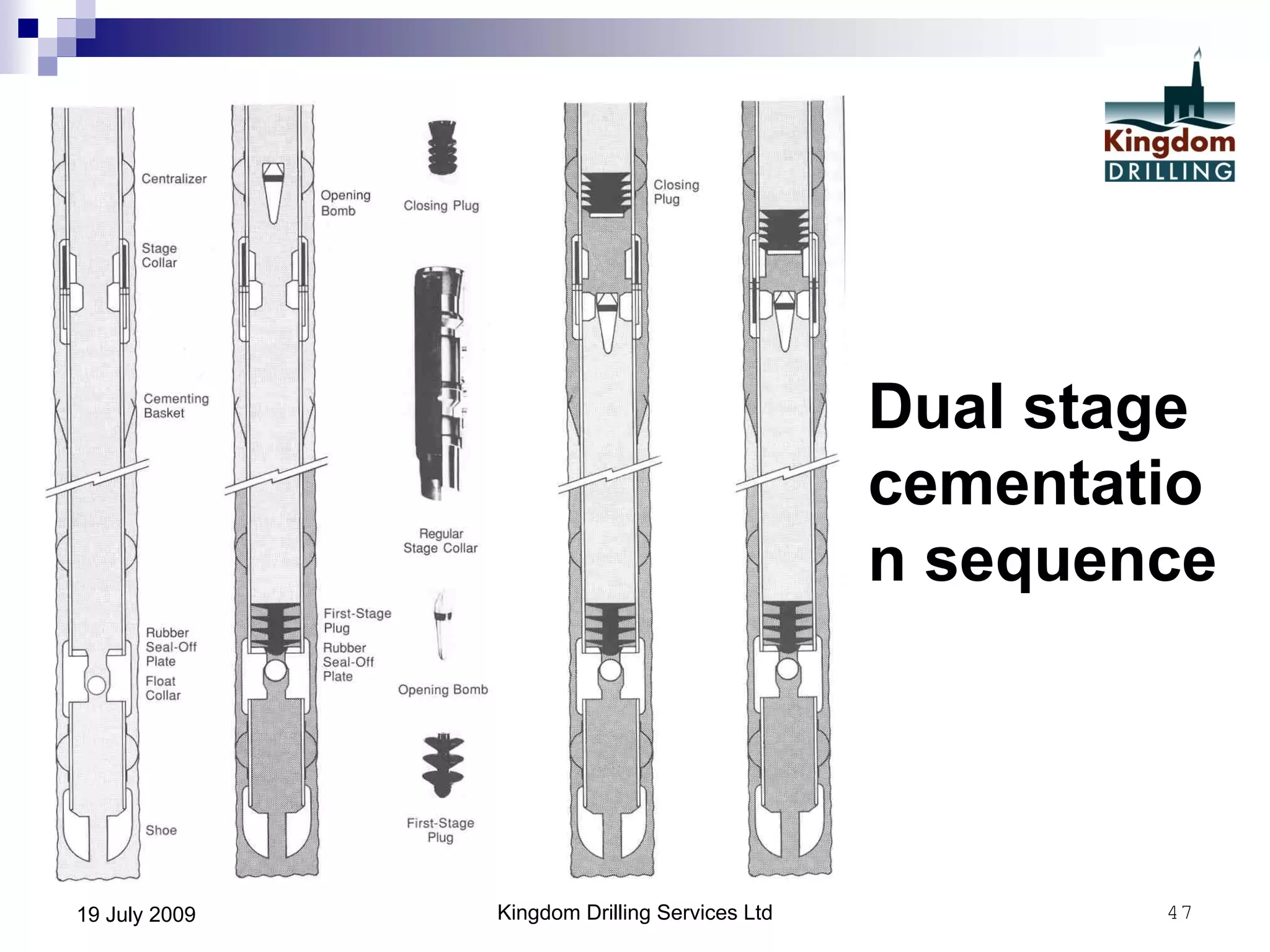
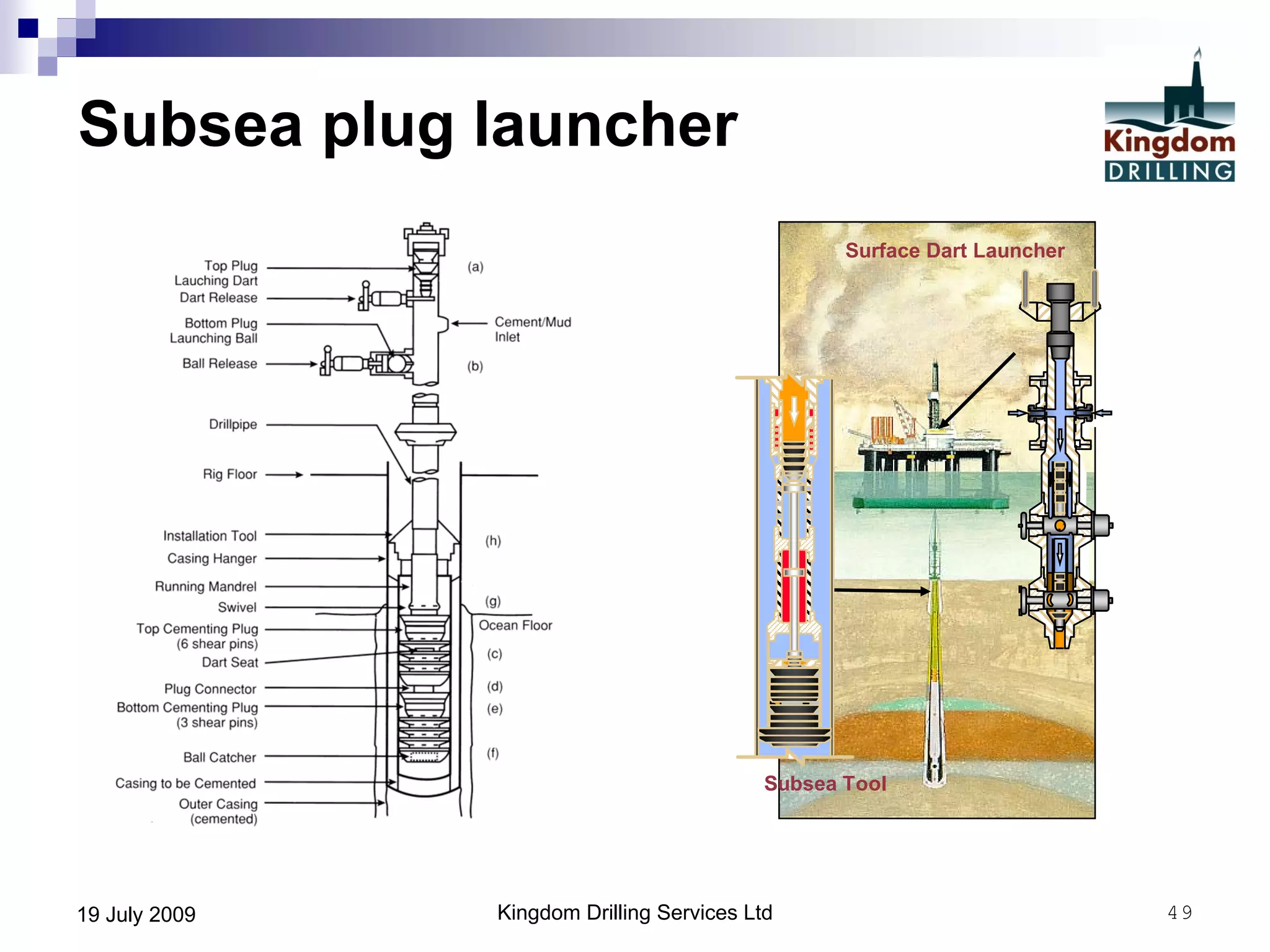
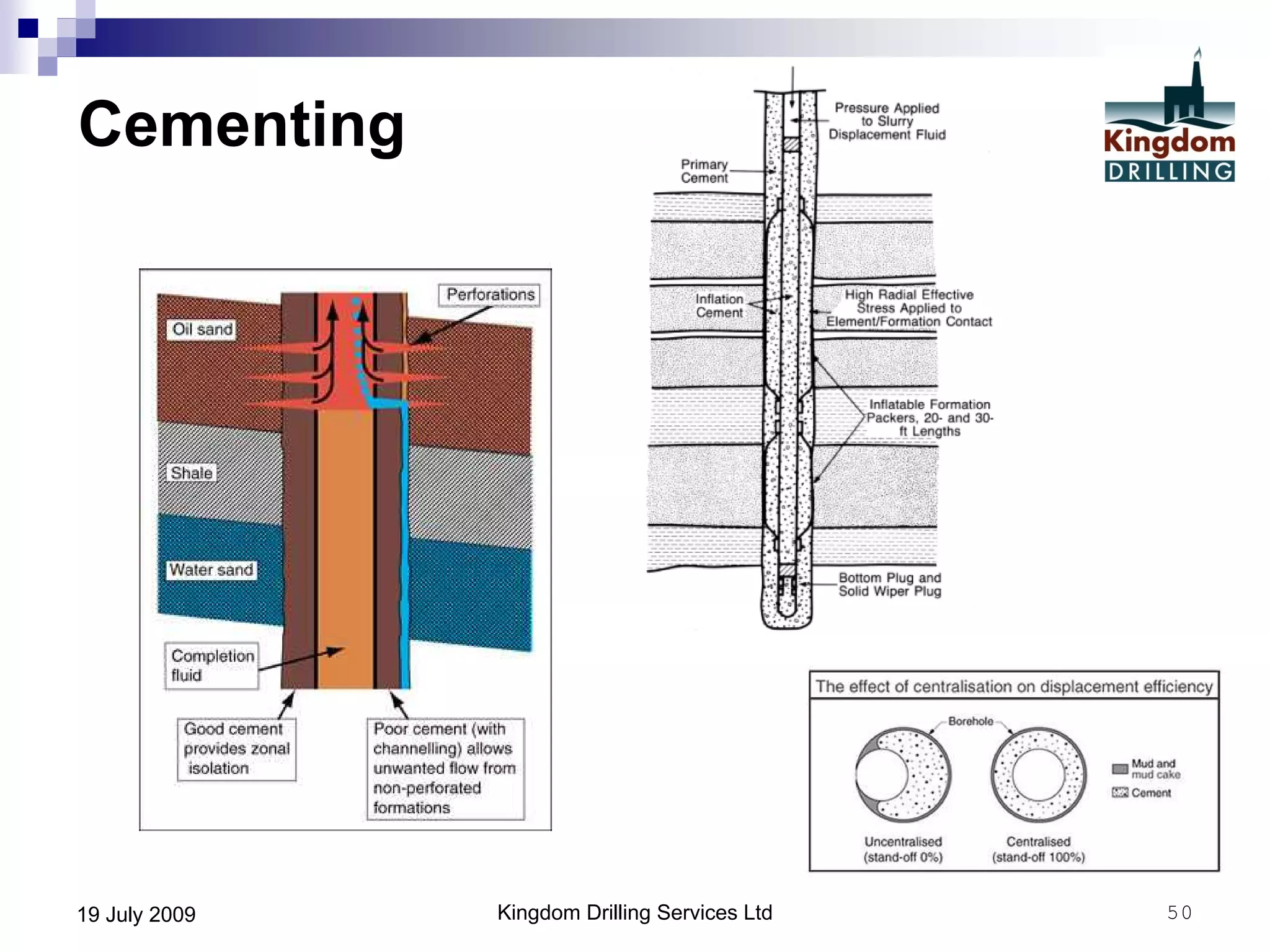
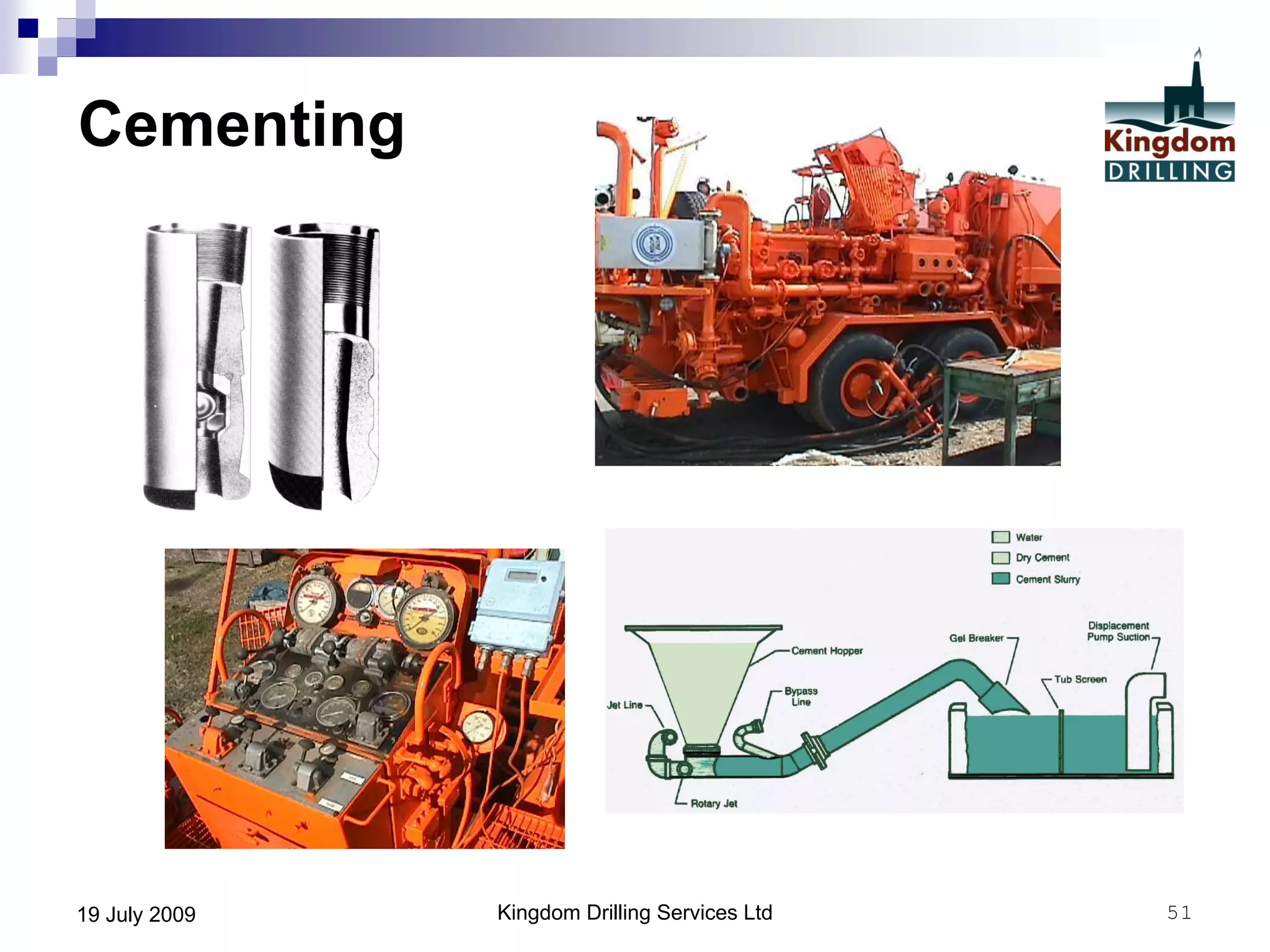
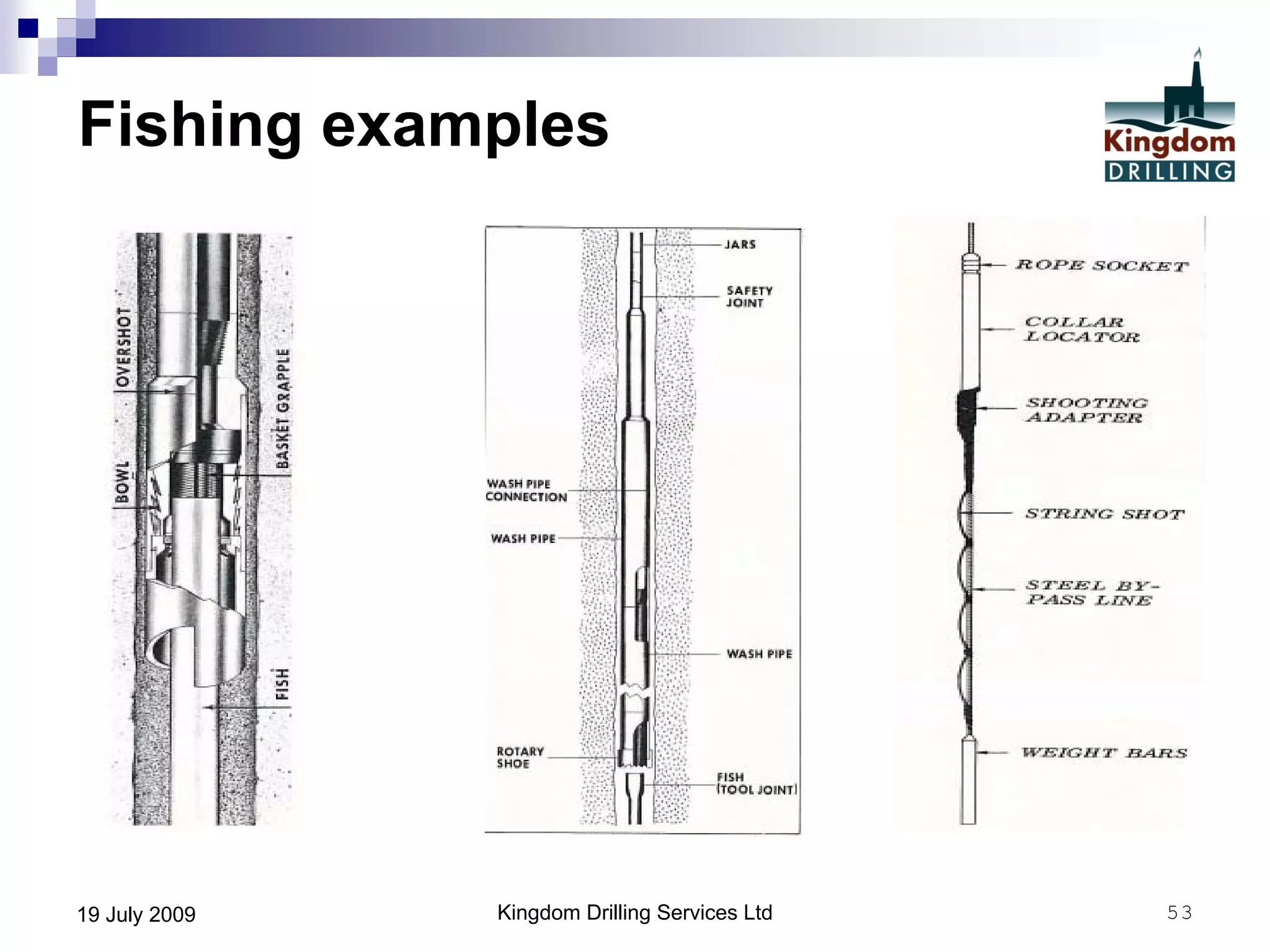
This document provides an overview of well drilling and associated operations in four parts. It discusses the functions of drilling fluid in circulating cuttings up from the bit and carrying them back to the surface. It also summarizes the various stages of drilling including running and setting casing, cementing, mud systems, coring, logging, and fishing operations if tools are lost downhole. The document is intended as an advisory guide on drilling operations and does not represent any standards or regulations.