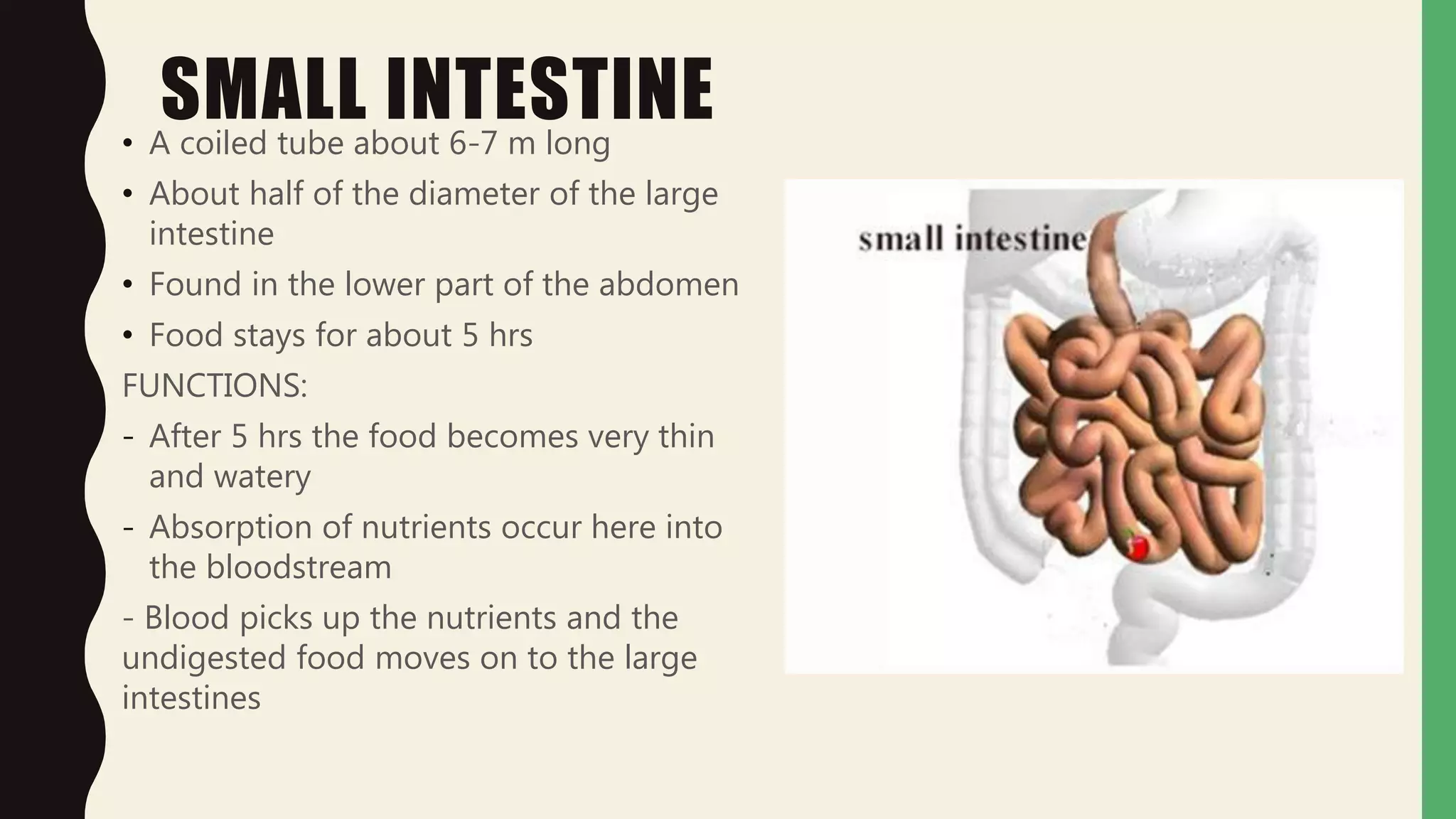
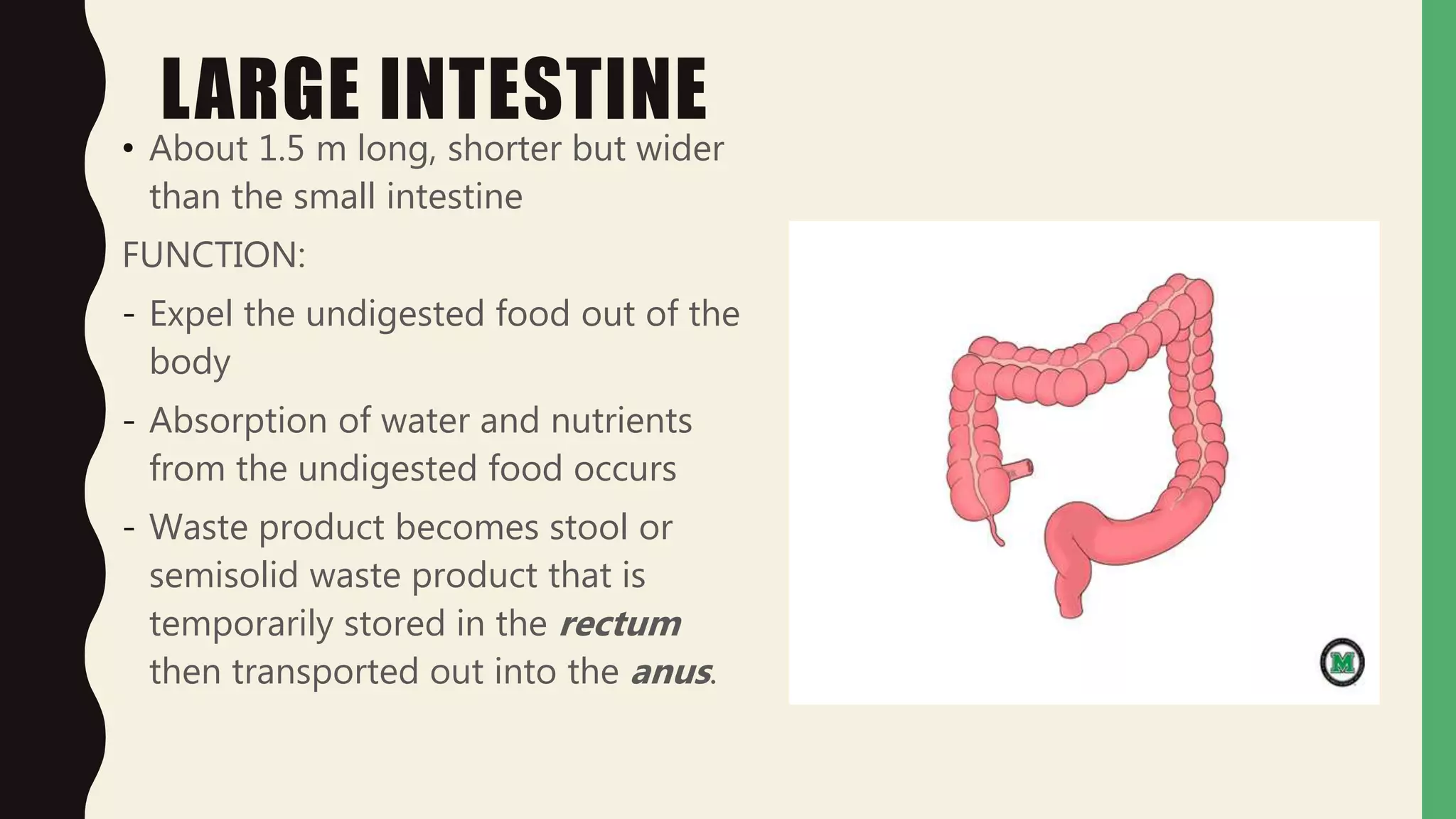
This document discusses the anatomy and functions of the small intestine, large intestine, and liver. It describes how the small intestine absorbs nutrients from food over 5 hours before passing the remaining waste to the large intestine. The large intestine absorbs water and nutrients before expelling waste. The liver produces bile to break down fats, cleans the blood, and stores glycogen. Common diseases like hepatitis, cirrhosis, diarrhea, and irritable bowel syndrome are also summarized, along with their symptoms and treatments. Proper care of the digestive system through diet and exercise is outlined.