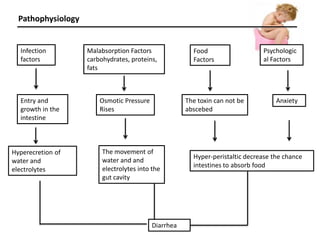
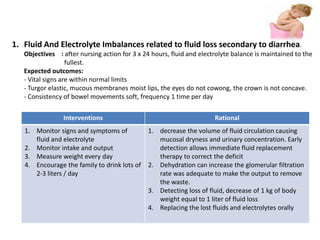
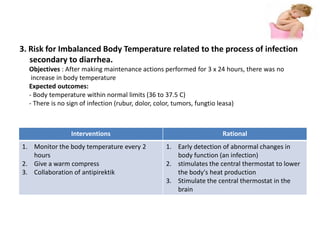
This document discusses diarrhea in children. It defines diarrhea as having more than 3 loose or watery bowel movements per day. Diarrhea can be caused by infections from bacteria, viruses or parasites, malabsorption of nutrients, poor diet, psychological factors, and other infections elsewhere in the body. The pathophysiology involves increased secretion of water and electrolytes into the gut due to infection or malabsorption. Nursing assessments for children with diarrhea include monitoring fluid and electrolyte balance, nutrition status, body temperature, and skin integrity. Nursing care plans aim to prevent dehydration, maintain nutrition, monitor for infection, and prevent skin breakdown.