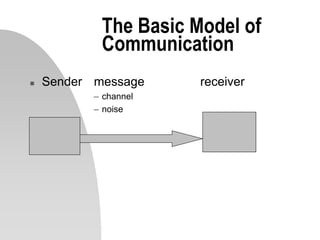
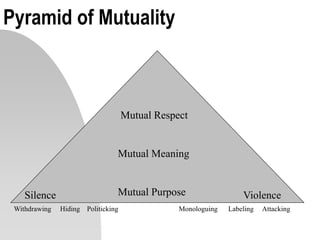
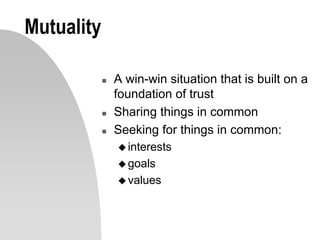
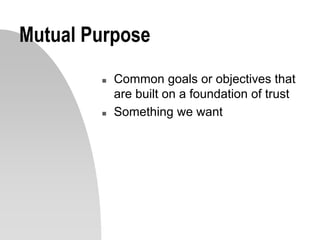
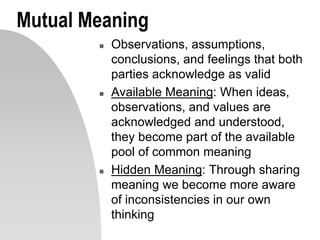
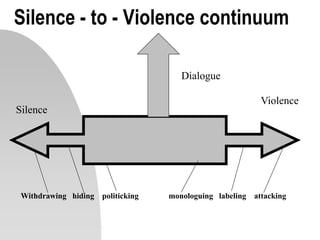
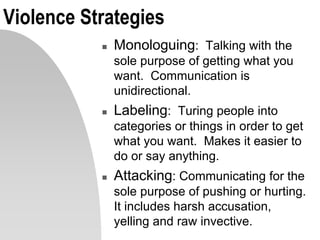
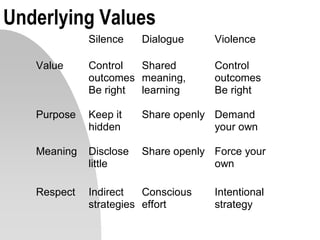
This document discusses interpersonal communication and effective communication models. It introduces the basic sender-receiver communication model and the pyramid of mutuality model which emphasizes mutual purpose, meaning, and respect. Communication styles are discussed along a continuum from silence to violence, outlining strategies like politicking, hiding, withdrawing, monologuing, labeling and attacking. The importance of mutual understanding, shared goals and values, and treating others with dignity are emphasized for effective communication. Practical exercises and scripts are provided to help improve communication skills.